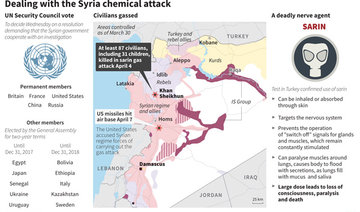
In the early hours of April 7, the US military launched a series of missile strikes against an air base in northern Syria, in retaliation for the Syrian regime’s chemical weapons attack against civilians three days earlier.
The strike shows that President Donald Trump is more willing to use military force in Syria than his predecessor, Barack Obama. But it raises another crucial question: Why would Syrian President Bashar Assad, whose regime has consolidated control over Syria’s largest cities in the past year and put the opposition on the defensive, risk a new international backlash by using chemical weapons? If he’s winning, why would Assad take such a risk?
The answer lies in Assad’s refusal to compromise or offer any significant concessions since the Syrian uprising began in March 2011, and later morphed into a civil war. Assad overplayed his hand this time, after being emboldened by recent statements from White House officials that it was time for Western powers to accept the “political reality” of Assad’s continued dominance. Assad likely decided to test those boundaries, not expecting Trump to respond militarily because the US president has made it clear that he sees fighting Islamic State as his highest priority in Syria and Iraq.
Aside from his brutality – the war has killed more than 500,000 people and displaced nearly half of Syria’s population – Assad’s staying power is rooted in a convoluted foreign policy, pioneered by his father, Hafez Assad. Syria played the role of a regional broker and Arab nationalist standard-bearer since 1970, when the elder Assad seized power through a military coup. He perfected the art of creating defensive alliances, nurturing proxies in neighboring countries and keeping his enemies stalled in costly battles.
Since he rose to power after his father’s death in June 2000, the younger Assad learned to keep all of his options open, and to play Syria’s friends and enemies off one another. Assad has portrayed himself as the only one capable of keeping Syria’s army and other state institutions from disintegrating, and preventing the country from falling entirely into the grip of Islamic extremists. To the West, Assad projected himself as the lesser evil – compared to Islamic State, and other jihadists affiliated with Al-Qaeda – even if his regime has instigated more death and destruction than his enemies.
Assad seems determined to replicate the foreign policy of his past, when he was able to hold on to power by being brutal, focusing outward and waiting for regional dynamics to change in his favor. To endure the pressure and international isolation imposed by the George W. Bush administration after its invasion of Iraq in 2003, Assad relied on his father’s foreign policy. The younger Assad feared that Syria was vulnerable to an American invasion, so his regime facilitated the recruiting, training and safe passage for hundreds of Syrian and foreign volunteers to join Al-Qaeda in Iraq to fight US troops and destabilize the Iraqi government.
When popular protests first swept the Arab world in early 2011, Assad was confident that he had nothing to fear because he continued his father’s foreign policy legacy – he did not depend on American military and political support like the leaders of Tunisia, Egypt, Bahrain and Yemen.
Instead, Assad and his allies formed the “axis of resistance” – Iran, Syria and the Islamist militant groups Hezbollah and Hamas. They boasted that the revolts had proven that they are the true representative of the majority of people in the Arab and Muslim worlds, who for decades had been stifled under regimes that “sold out” to the United States.
In refusing to make substantial concessions, Assad has relied on another tactic he learned from his father: The Syrian regime does not make compromises under pressure, whether external or internal, and this principle had served it well in times of crisis. Assad also saw the initial response to popular protests in Tunisia and Egypt, and he likely concluded that by not cracking down forcefully, those rulers appeared weak and encouraged protesters to broaden their demands. So when his own people revolted, Assad decided to hunker down and crush the uprising.
At the start of the rebellion in 2011, Assad used Islamic militants to destabilize his opponents, as he had done nearly a decade earlier in Iraq. The Syrian regime released hundreds of Al-Qaeda activists and other militants from its prisons, and they went on to become leaders of Islamic State and other jihadist groups. Many of those militants ended up fighting Assad’s regime, but they also became the focus for Western leaders worried about jihadist attacks in their own countries.
Throughout the presidential campaign, Trump said he wanted to avoid direct US involvement in the Syrian conflict, which has expanded into a regional proxy war. Russia and Iran, along with Shi’ite militias like Lebanon’s Hezbollah, helped Assad consolidate control and regain territory he lost to the opposition. In December, with intensive Russian air strikes and Iranian ground support, Assad recaptured the opposition-held sections of Aleppo, Syria’s largest city. It was Assad’s biggest victory since the war began.
After Trump was elected, Assad became more confident because Trump had pledged to end US support for the opposition fighting the Syrian regime and direct most American efforts to fighting Islamic State. Assad and his allies have rarely fought directly against the jihadist group, which established its self-proclaimed capital in the eastern city of Raqqa.
Since November, the United States has helped mobilize nearly 50,000 Kurdish and Sunni Arab fighters to encircle Raqqa, and cut it off from all sides. The offensive is supported by American air strikes and hundreds of US troops. But Trump’s missile strikes could slow the offensive to oust Islamic State from Raqqa and other parts of eastern Syria. The Pentagon coordinates with Russian forces in Syria, especially in launching air strikes, and Russian officials threatened to suspend the communications hotline after the April 7 US attack on the Syrian airfield.
Analysis: Why Assad used chemical weapons
Analysis: Why Assad used chemical weapons

Iraq begins repatriating Syrian soldiers amid border security assurances

DUBAI: Iraq has begun the process of returning Syrian soldiers to their home country, according to state media reports on Wednesday.
Lt. Gen. Qais Al-Muhammadawi, deputy commander of joint operations, emphasized the robust security measures in place along Iraq’s borders with Syria.
“Our borders are fortified and completely secure,” he said, declaring that no unauthorized crossings would be permitted.
Muhammadawi said that all border crossings with Syria are under tight control, stating: “We will not allow a terrorist to enter our territory.”
Turkiye won’t halt Syria military activity until Kurd fighters ‘disarm’

ISTANBUL: Turkiye will push ahead with its military preparations until Kurdish fighters “disarm,” a defense ministry source said Thursday as the nation faces an ongoing threat along its border with northern Syria.
“Until the PKK/YPG terrorist organization disarms and its foreign fighters leave Syria, our preparations and measures will continue within the scope of the fight against terrorism,” the source said.
Hamas says Israeli strikes in Yemen ‘dangerous development’

GAZA: Palestinian militant group Hamas said Thursday that Israel’s strikes in Yemen after the Houthi rebels fired a missile at the country were a “dangerous development.”
“We regard this escalation as a dangerous development and an extension of the aggression against our Palestinian people, Syria and the Arab region,” Hamas said in a statement as Israel struck ports and energy infrastructure in Yemen after intercepting a missile attack by the Houthis.
Separated for decades, Assad’s fall spurs hope for families split by Golan Heights buffer zone

- Golan Heights is a rocky plateau that Israel seized from Syria in 1967 and annexed in 1981
- US is the only country to recognize Israel’s control; the rest of the world considers the Golan Heights occupied Syrian territory
MAJDAL SHAMS, Golan Heights: The four sisters gathered by the side of the road, craning their necks to peer far beyond the razor wire-reinforced fence snaking across the mountain. One took off her jacket and waved it slowly above her head.
In the distance, a tiny white speck waved frantically from the hillside.
“We can see you!” Soha Safadi exclaimed excitedly on her cellphone. She paused briefly to wipe away tears that had begun to flow. “Can you see us too?”
The tiny speck on the hill was Soha’s sister, Sawsan. Separated by war and occupation, they hadn’t seen each other in person for 22 years.
The six Safadi sisters belong to the Druze community, one of the Middle East’s most insular religious minorities. Its population is spread across Syria, Lebanon, Israel and the Golan Heights, a rocky plateau that Israel seized from Syria in 1967 and annexed in 1981. The US is the only country to recognize Israel’s control; the rest of the world considers the Golan Heights occupied Syrian territory.
Israel’s seizure of the Golan Heights split families apart.
Five of the six Safadi sisters and their parents live in Majdal Shams, a Druze town next to the buffer zone created between the Israeli-controlled Golan Heights and Syria. But the sixth, 49-year-old Sawsan, married a man from Jaramana, a town on the outskirts of the Syrian capital, Damascus, 27 years ago and has lived in Syria ever since. They have land in the buffer zone, where they grow olives and apples and also maintain a small house.
With very few visits allowed to relatives over the years, a nearby hill was dubbed “Shouting Hill,” where families would gather on either side of the fence and use loudspeakers to speak to each other.
The practice declined as the Internet made video calls widely accessible, while the Syrian war that began in 2011 made it difficult for those on the Syrian side to reach the buffer zone.
But since the Dec. 8 fall of Syrian President Bashar Assad’s regime, families like the Safadis, are starting to revive the practice. They cling to hope, however faint, that regime change will herald a loosening of restrictions between the Israeli-controlled area and Syria that have kept them from their loved ones for so long.
“It was something a bit different. You see her in person. It feels like you could be there in two minutes by car,” Soha Safadi, 51, said Wednesday after seeing the speck that was her sister on the hill. “This is much better, much better.”
Since Assad’s fall, the sisters have been coming to the fence every day to see Sawsan. They make arrangements by phone for a specific time, and then make a video call while also trying to catch a glimpse of each other across the hill.
“She was very tiny, but I could see her,” Soha Safadi said. “There were a lot of mixed feelings — sadness, joy and hope. And God willing, God willing, soon, soon, we will see her” in person.
After Assad fell, the Israeli military pushed through the buffer zone and into Syria proper. It has captured Mount Hermon, Syria’s tallest mountain, known as Jabal Al-Sheikh in Arabic, on the slopes of which lies Majdal Shams. The buffer zone is now a hive of military and construction activity, and Sawsan can’t come close to the fence.
While it is far too early to say whether years of hostile relations between the two countries will improve, the changes in Syria have sparked hope for divided families that maybe, just maybe, they might be able to meet again.
“This thing gave us a hope … that we can see each other. That all the people in the same situation can meet their families,” said another sister, 53-year-old Amira Safadi.
Yet seeing Sawsan across the hill, just a short walk away, is also incredibly painful for the sisters.
They wept as they waved, and cried even more when their sister put their nephew, 24-year-old Karam, on the phone. They have only met him once, during a family reunion in Jordan. He was 2 years old.
“It hurts, it hurts, it hurts in the heart,” Amira Safadi said. “It’s so close and far at the same time. It is like she is here and we cannot reach her, we cannot hug her.”
Israel’s deprivation of water in Gaza is act of genocide – Human Rights Watch

- ‘What we have found is that the Israeli government is intentionally killing Palestinians in Gaza by denying them the water that they need to survive’
- Israel’s campaign has killed more than 45,000 Palestinians, displaced most of the 2.3 million population and reduced much of the coastal enclave to ruins
THE HAGUE: Human Rights Watch said on Thursday that Israel has killed thousands of Palestinians in Gaza by denying them clean water which it says legally amounts to acts of genocide and extermination.
“This policy, inflicted as part of a mass killing of Palestinian civilians in Gaza, means Israeli authorities have committed the crime against humanity of extermination, which is ongoing. This policy also amounts to an ‘act of genocide’ under the Genocide Convention of 1948,” Human Rights Watch said in its report.
Israel has repeatedly rejected any accusation of genocide, saying it has respected international law and has a right to defend itself after the cross-border Hamas-led attack from Gaza on Oct. 7, 2023 that precipitated the war.
Although the report described the deprivation of water as an act of genocide, it noted that proving the crime of genocide against Israeli officials would also require establishing their intent. It cited statements by some senior Israeli officials which it said suggested they “wish to destroy Palestinians” which means the deprivation of water “may amount to the crime of genocide.”
“What we have found is that the Israeli government is intentionally killing Palestinians in Gaza by denying them the water that they need to survive,” Lama Fakih, Human Rights Watch Middle East director told a press conference.
Human Rights Watch is the second major rights group in a month to use the word genocide to describe the actions of Israel in Gaza, after Amnesty International issued a report that concluded Israel was committing genocide.
Both reports came just weeks after the International Criminal Court issued arrest warrants for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and his former defense chief for alleged war crimes and crimes against humanity. They deny the allegations.
The 1948 Genocide Convention, enacted in the wake of the mass murder of Jews in the Nazi Holocaust, defines the crime of genocide as “acts committed with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group.”
The 184-page Human Rights Watch report said the Israeli government stopped water being piped into Gaza and cut off electricity and restricted fuel which meant Gaza’s own water and sanitation facilities could not be used.
As a result, Palestinians in Gaza had access to only a few liters of water a day in many areas, far below the 15-liter-threshold for survival, the group said. Israel launched its air and ground war in Gaza after Hamas-led fighters attacked Israeli communities across the border 14 months ago, killing 1,200 people and taking over 250 hostages back to Gaza, according to Israeli tallies.
Israel’s campaign has killed more than 45,000 Palestinians, displaced most of the 2.3 million population and reduced much of the coastal enclave to ruins.