KATMANDU: A South African who attempted to climb Mount Everest without permission has been arrested in Nepal where he faces a $22,000 fine — double the cost of the permit he was trying to avoid.
Ryan Sean Davy handed himself in to authorities in Katmandu on Tuesday after being caught last week hiding in a cave near Everest’s base camp without a permit.
The 43-year-old began swearing and threatening officials from the tourism department during questioning and was arrested under Nepal’s strict public order laws, Tourist Police Inspector Tulasha Khatiwada told AFP.
He is now in custody and will appear in court next week to face charges related to his Everest attempt and possible additional offenses over his conduct during the investigation.
“He will be fined and deported as per the Tourism Act of Nepal. He may face further penalty for misbehaving with the police,” director of the tourism department Dinesh Bhattarai told AFP.
Foreigners have to pay the Nepal government $11,000 for permission to climb the 8,848-meter (29,029-foot) peak — a major earner for the impoverished country.
Under Nepali law, climbers caught without the mandatory permit are fined $22,000.
Davy could also be blacklisted from the Himalayan nation for five years, or face a 10-year climbing ban when he appears in court next week.
The South African — who describes himself on social media as a film director and producer — was caught a short distance from Everest base camp and ordered off the mountain.
He had pitched a tent away from the other climbers to try and dodge government officials who monitor all Everest ascents.
He told officials he had climbed alone as far as camp two — at 6,400 meters — to acclimatize in preparation for a solo summit bid.
The officials confiscated his passport and instructed him to return to Katmandu to collect it.
Davy said he couldn’t afford to fly and would instead walk.
S. African Everest permit dodger arrested
S. African Everest permit dodger arrested

Europe posts record year for clean energy use as Trump pulls US toward fossil fuels

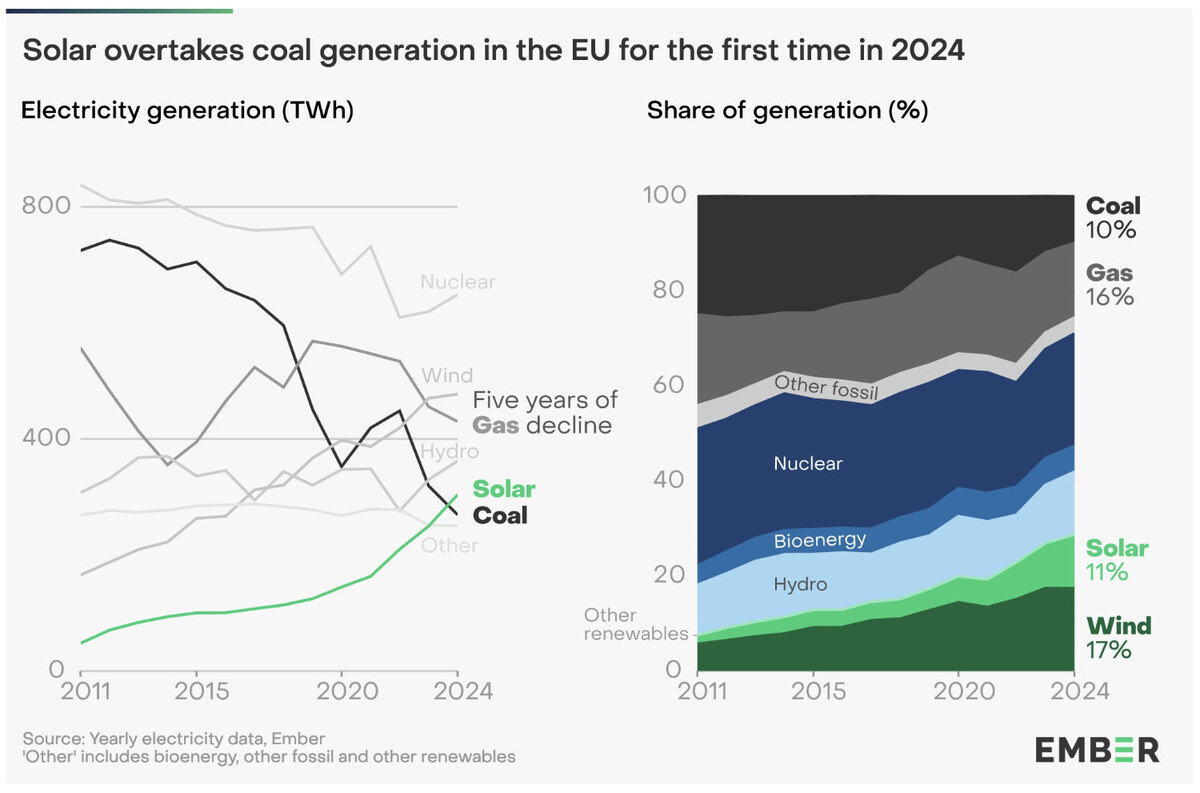
- With another 24% of electricity in the bloc coming from nuclear power, nearly 3/4 of EU's electricity is considered clean energy
- In contrast, economic giants China and the US still get nearly 2/3 of their energy from carbon-polluting fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas
A record 47 percent of the European Union’s electricity now comes from solar and other renewables, a report Thursday said, in yet another sign of the growing gap between the bloc’s push for clean energy and the new US administration’s pursuit of more fossil fuels.
Nearly three-quarters of the EU’s electricity doesn’t emit planet-warming gases into the air — with another 24 percent of electricity in the bloc coming from nuclear power, a report released by the climate energy think tank Ember found. This is far higher than in countries like the United States and China, where nearly two-thirds of their energy is still produced from carbon-polluting fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. Around 21 percent of the US’s electricity comes from renewable sources.
Experts say they’re encouraged by Europe’s fossil fuel reductions, particularly as the US looks set to increase its emissions as its new president pledges cheaper gas prices, has halted leases for wind projects and pledged to revoke Biden-era incentives for electric vehicles.
“Fossil fuels are losing their grip on EU energy,” said Chris Rosslowe, an energy expert at Ember. In 2024, solar power generated 11 percent of EU electricity, overtaking coal which fell below 10 percent for the first time. Clean wind power generated more electricity than gas for the second year in a row.
Green policies and war drive clean energy growth
One reason for Europe’s clean power transition moving at pace is the European Green Deal, an ambitious policy passed in 2019 that paved the way for climate laws to be updated. As a result of the deal, the EU made their targets more ambitious, aiming to cut 55 percent of the region’s emissions by the end of the decade. The policy also aims to make Europe climate neutral — reducing the amount of additional emissions in the air to practically zero — by 2050.
Hundreds of regulations and directives in European countries to incentivize investment in clean energy and reduce carbon pollution have been passed or are in the process of being ratified across Europe.
“At the start of the Deal, renewables were a third and fossil fuels accounted for 39 percent of Europe’s electricity,” Rosslowe said. “Now fossils generate only 29 percent and wind and solar have been driving the clean energy transition.” The amount of electricity generated by nuclear energy has remained relatively stable in the bloc.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has also spurred the move to clean energy in Europe. Gas prices skyrocketed — with much of Europe’s gas coming from Russia becoming unviable — forcing countries to look for cheaper, cleaner alternatives. Portugal, Netherlands and Estonia witnessed the highest increase in clean power in the last five years.
Europe cements its place as a clean energy leader
The transition to clean power helped Europe avoid more than $61 billion worth of fossil fuel imports for generating electricity since 2019.
“This is sending a clear message that their energy needs are going to be met through clean power, not gas imports,” said Pieter de Pous, a Brussels-based energy analyst at European think tank E3G. De Pous said the EU’s origins were “as a community of coal and steel because those industries were so important,” but it is now rapidly becoming a “community of solar and wind power, batteries and smart technologies.”
Nuclear growth in the bloc, meanwhile, has slowed. Across the European Union, retirements of nuclear plants have outpaced new construction since around the mid-2000s, according to Global Energy Monitor.
As President Trump has pulled the United States out of the Paris Agreement aimed at curbing warming and is pursuing a “drill, baby, drill” energy policy, Rosslowe said the EU’s leadership in clean power becomes all the more important. “It’s about increasing European energy independence, and it’s about showing this climate leadership,” he said.
On Tuesday, EU chief Ursula von der Leyen said: “Europe will stay the course, and keep working with all nations that want to protect nature and stop global warming.”
Pentagon is sending up to 1,500 active duty troops to help secure US-Mexico border

Acting Defense Secretary Robert Salesses said the Pentagon will provide military aircraft to support Department of Homeland Security deportation flights for more than 5,000 detained migrants and the troops will assist in the construction of barriers.
The number of troops and their mission may soon change, Salesses said in a statement. “This is just the beginning,” he said.
It remains to be seen if they will end up doing law enforcement, which would put American troops in a dramatically different role for the first time in decades.
The active duty forces will join the roughly 2,500 US National Guard and Reserve forces already there. There are currently no active duty troops working along the roughly 2,000-mile border.
Personnel started moving to the border earlier Wednesday, according to a military official briefing reporters on the condition of anonymity to provide additional details on the deployment. The troops will include 500 Marines from Camp Pendleton in California, and the remainder will be Army.
Troops have done similar duties in support of Border Patrol agents in the past, when both Trump and former President Joe Biden sent active duty troops to the border.
Troops are prohibited by law from doing law enforcement duties under the Posse Comitatus Act, but that may change. Trump has directed through executive order that the incoming secretary of defense and incoming homeland security chief report back within 90 days if they think an 1807 law called the Insurrection Act should be invoked. That would allow those troops to be used in civilian law enforcement on US soil.
The last time the act was invoked was in 1992 during rioting in Los Angeles in protest of the acquittal of four police officers charged with beating Rodney King.
The widely expected deployment, coming in Trump’s first week in office, was an early step in his long-touted plan to expand the use of the military along the border. In one of his first orders on Monday, Trump directed the defense secretary to come up with a plan to “seal the borders” and repel “unlawful mass migration.”
“This is something President Trump campaigned on,” said Karoline Leavitt, White House press secretary. “The American people have been waiting for such a time as this — for our Department of Defense to actually implement homeland security seriously. This is a No. 1 priority for the American people.”
On Tuesday, just as Trump fired the Coast Guard commandant, Adm. Linda Fagan, the service announced it was surging more cutter ships, aircraft and personnel to the “Gulf of America” — a nod to the president’s directive to rename the Gulf of Mexico.
Trump said during his inaugural address on Monday that “I will declare a national emergency at our southern border. All illegal entry will immediately be halted, and we will begin the process of returning millions and millions of criminal aliens back to the places in which they came.”
Military personnel have been sent to the border almost continuously since the 1990s to help address migration. drug trafficking and transnational crime.
In executive orders signed Monday, Trump suggested the military would help the Department of Homeland Security with “detention space, transportation (including aircraft), and other logistics services.”
There are about 20,000 Border Patrol agents, and while the southern border is where most are located, they’re also responsible for protecting the northern border with Canada. Usually agents are tasked with looking for drug smugglers or people trying to enter the country undetected.
More recently, however, they have had to deal with migrants actively seeking out Border Patrol in order to get refuge in America — taxing the agency’s staff.
In his first term, Trump ordered active duty troops to the border in response to a caravan of migrants slowly making its way through Mexico toward the United States in 2018. More than 7,000 active duty troops were sent to Texas, Arizona and California, including military police, an assault helicopter battalion, various communications, medical and headquarters units, combat engineers, planners and public affairs units.
At the time, the Pentagon was adamant that active duty troops would not do law enforcement. So they spent much of their time transporting Border Patrol agents to and along the border, helping them erect additional vehicle barriers and fencing along the border, assisting them with communications and providing some security for border agent camps.
The military also provided Border Patrol agents with medical care, pre-packaged meals and temporary housing.
It’s also not yet clear if the Trump administration will order the military to use bases to house detained migrants.
Bases previously have been used for that purpose, and after the 2021 fall of Kabul to the Taliban, they were used to host thousands of Afghan evacuees. The facilities struggled to support the influx.
In 2018, then-Defense Secretary Jim Mattis ordered Goodfellow Air Force Base in San Angelo, Texas, to prepare to house as many as 20,000 unaccompanied migrant children, but the additional space ultimately wasn’t needed and Goodfellow was determined not to have the infrastructure necessary to support the surge.
In March 2021, the Biden administration greenlighted using property at Fort Bliss, Texas, for a detention facility to provide beds for up to 10,000 unaccompanied migrant children as border crossings increased from Mexico.
The facility, operated by DHS, was quickly overrun, with far too few case managers for the thousands of children that arrived, exposure to extreme weather and dust and unsanitary conditions, a 2022 inspector general report found.
South Sudan orders temporary ban on social media over violence in neighboring Sudan

- Many South Sudanese have been angered by footage from Sudan that purports to show killings by militia groups of South Sudanese in Gezira state
JUBA, South Sudan: South Sudanese authorities on Wednesday ordered telecoms to block access to social media for at least 30 days, citing concerns over the dissemination of graphic content relating to the ongoing violence against South Sudanese in neighboring Sudan.
The temporary ban, which could be extended to up to 90 days, will come into force at midnight Thursday, according to a directive from the National Communication Authority, NCA, to telecom companies stressing that the measure was necessary to protect the public.
“This directive may be lifted as soon as the situation is contained,” the NCA said. “The contents depicted violate our local laws and pose a significant threat to public safety and mental health.”
Many South Sudanese have been angered by footage from Sudan that purports to show killings by militia groups of South Sudanese in Gezira state. South Sudanese authorities imposed a dusk-to-dawn curfew on Jan. 17 after a night of retaliatory violence during which shops owned by Sudanese traders were looted.
Moussa Faki Mahamat, chairperson of the African Union Commission, condemned “the brutal killings of South Sudanese nationals” in Sudan and urged restraint.
Civil war in Sudan has created a widening famine and the world’s largest displacement crisis. Fighting between forces loyal to rival military leaders exploded in the capital, Khartoum, in April 2023 and has since spread to other areas.
The conflict has been marked by atrocities, including ethnically motivated killing and rape, according to the UN and rights groups.
Trump administration freezes many health agency reports and online posts

- Shutting down public health communication stops a basic function of public health
The Trump administration has put a freeze on many federal health agency communications with the public through at least the end of the month.
In a memo obtained by The Associated Press, acting Secretary of the US Department of Health and Human Services Dorothy Fink told agency staff leaders Tuesday that an “immediate pause” had been ordered on — among other things — regulations, guidance, announcements, press releases, social media posts and website posts until such communications had been approved by a political appointee.
The pause also applies to anything intended to be published in the Federal Register, where the executive branch communicates rules and regulations, and the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention scientific publication.
The pause is in effect through Feb. 1, the memo said. Agencies subject to the HHS directive include the CDC, the National Institutes of Health and the Food and Drug Administration — entities that fight epidemics, protect the nation’s food supply and search for cures to diseases.
HHS officials did not respond to requests for comment on the pause, which was first reported by The Washington Post. Four federal health officials speaking on condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to discuss the issue confirmed the communication pause to the AP.
A former HHS official said Wednesday that it’s not unusual for incoming administrations to pause agency communications for review. But typically, officials working on the president’s transition team have the process for issuing documents running smoothly by inauguration day.
“The executive branch is a hierarchy,” said Steven Grossman, who now consults for food and drug companies, in an email. “Whether stated publicly or not, every new administration wants important commitments and positions to wait until new teams are in place and some semblance of hierarchy restored.”
A pause is reasonable as a changing executive branch takes steps to become coordinated, said Dr. Ali Khan, a former CDC outbreak investigator who is now dean of the University of Nebraska’s public health college.
“The only concern would be is if this is a prelude to going back to a prior approach of silencing the agencies around a political narrative,” he added.
During his first term, President Donald Trump’s political appointees tried to gain control over the CDC’s MMWR journal, which had published information about the COVID-19 pandemic that conflicted with messaging from the White House.
Fink wrote in her memo that some exceptions would be made for communications affecting “critical health, safety, environmental, financial or nation security functions,” but that those would be subject to review. The FDA on Tuesday and Wednesday posted notices about warning letters sent to companies and a drug safety notice.
A consumer advocacy group said the communications pause could still threaten public safety.
Americans depend on timely information from the CDC, the FDA and other agencies to avoid foodborne illnesses and stay aware of other health issues, said Dr. Peter Lurie, president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest.
“When it comes to stopping outbreaks, every second counts,” Lurie said in a statement. “Confusion around the vaguely worded gag order is likely to lead to unnecessary delay in publishing urgent public alerts during active outbreaks.”
He was echoed by Dr. Jeffrey Klausner, a University of Southern California public health expert.
“Local health officials and doctors depend on the CDC to get disease updates, timely prevention, testing and treatment guidelines and information about outbreaks,” Klausner wrote in an email. “Shutting down public health communication stops a basic function of public health. Imagine if the government turned off fire sirens or other warning systems.”
Swiss prosecutors examine complaints against Israel president

- The Swiss Keystone-ATS news agency reported that one of the complaints came from an NGO called Legal Action Against Genocide
GENEVA: Swiss prosecutors said Wednesday they were examining several complaints against visiting Israeli President Isaac Herzog, as reports suggested NGOs were accusing him of “incitement to genocide” in Gaza.
The Office of the Attorney General of Switzerland (OAG) confirmed it had received “several criminal complaints” against Herzog, who was at the World Economic Forum in the Swiss resort of Davos this week.
“The criminal complaints are now being examined in accordance with the usual procedure,” the OAG said in an email sent to AFP, adding that the office was in contact with Switzerland’s foreign ministry “to examine the question of the immunity of the person concerned.”
It provided no details on the specific complaints filed.
The Swiss Keystone-ATS news agency reported that one of the complaints came from an NGO called Legal Action Against Genocide.
The NGO was calling for Herzog to be prosecuted “for incitement to genocide and crimes against humanity,” the news agency said.
The complaint, it said, deemed he had played “an active role in the ideological justification of genocide and war crimes in Gaza, by erasing all distinction between the civilian population and combatants.”
Israeli officials have repeatedly denied allegations of war crimes and genocide, accusing Hamas of using civilians as human shields.
Herzog spoke at Davos on Tuesday and held meetings on Wednesday morning but it was unclear if he was still in Switzerland.
Complaints were also filed against him when he attended the Davos meeting a year ago but the OAG refrained from opening an investigation that time, Keystone-ATS reported.
The war in Gaza was sparked by Hamas’s October 7, 2023 attack, the deadliest in Israeli history, resulted in the deaths of 1,210 people, mostly civilians, according to an AFP tally of official Israeli figures.
It sparked a war that has levelled much of Gaza and, according to the health ministry in the Hamas-run territory, killed more than 47,100, a majority of them civilians, figures the United Nations has said are reliable.

















