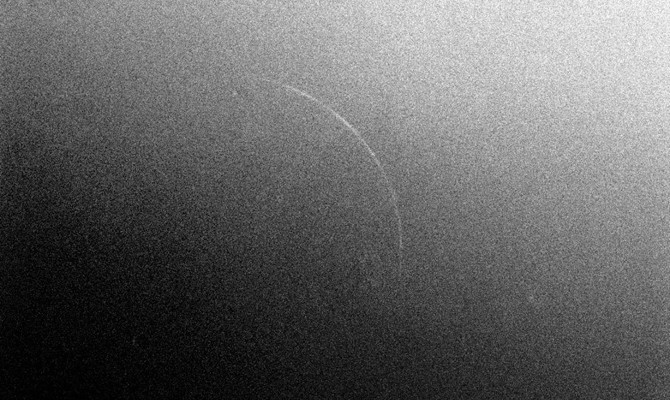
The Supreme Court has announced that due to the inability to witness the crescent moon on May 15, the month of Shaban will continue for a 30th day, and the first day of Ramadan will therefore be on Thursday.
As the holy month of Ramadan approaches, Muslims are preparing to abstain from food and drink during daylight hours, and to discipline their minds and spirits.
The start of Ramadan is determined by the lunar calendar which, unlike the Gregorian calendar, follows a 29- or 30-day cycle determined by the cycle of the moon. Muslims anticipate the end of Shaaban, the month preceding Ramadan, by watching for the absence or presence of the crescent moon, which respectively indicate the continuation of Shaban or beginning of Ramadan.
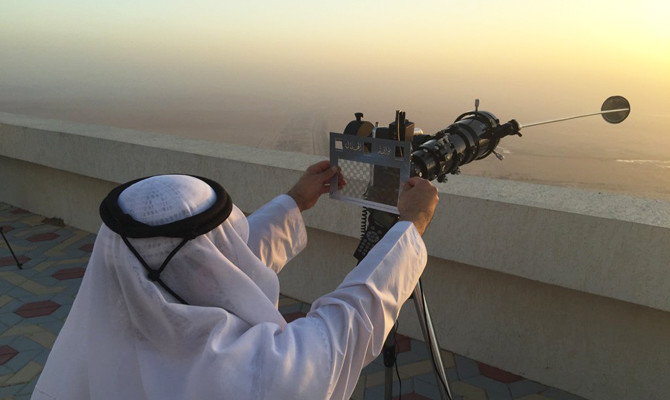
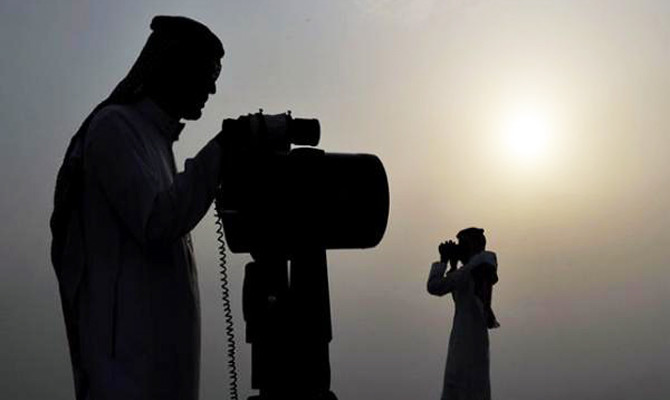
Sighting of the Ramadan crescent can be achieved by three methods: Through telescopes and binoculars; using astronomy; or viewing with the naked eye.
 “Proving the beginning of Ramadan is not limited to crescent sighting,” said Sheikh Abdullah bin Sulaiman Al-Manea, a member of the Council of Senior Scholars in Saudi Arabia. “There are other ways and means to determine the first day of the month, including astronomy. Astronomy is, in fact, more accurate and more convincing than moon sighting, which is only hypothetical while astronomy is conclusive and definitive.”
“Proving the beginning of Ramadan is not limited to crescent sighting,” said Sheikh Abdullah bin Sulaiman Al-Manea, a member of the Council of Senior Scholars in Saudi Arabia. “There are other ways and means to determine the first day of the month, including astronomy. Astronomy is, in fact, more accurate and more convincing than moon sighting, which is only hypothetical while astronomy is conclusive and definitive.”
He said the findings of Muslims who specialize in astronomy must be taken into account because it is a proven means for confirming the crescent. The testimony of a moon sighter should not be accepted if it contradicts the astronomers’ opinion.
The crescent-screening method takes place during the emergence of the crescent moon, when it is precisely aligned with the sun and the Earth. Once it has completed a full cycle around the Earth and started a new one, the moon’s crescent is evident before the month’s first sunset. When the sun disappears below the horizon, the crescent moon remains perched in the sky where the sun went down. It has to remain visible in the sky for at least 30 minutes after sunset.
The crescent moon cannot be seen with the naked eye until 15 hours have passed since the beginning of the cycle, and can only be seen through a telescope 12 hours after a new cycle begins.
A record was created by Stephen O’Meara in 1990, who witnessed the closest thing to a new moon — or youngest moon — with his naked eye. The young crescent appeared in the sky 15 hours and 32 minutes after the new moon.
Mohsen Mirsaeed surpassed that record in 2002, when he saw the crescent after 11 hours and 40 minutes of the new moon.
To see the crescent moon clearly, it should be viewed from a high vantage point, far from heavily populated and built-up areas, and from natural and man-made obstructions that could obscure the sighting, such as mountains, hills and skyscrapers. The area should also be clear of atmospheric factors such as humidity and dust.
Scholars and experienced astronomers are the only ones who can determine whether the crescent moon has arrived to dictate the beginning of the holy month. If they fail to witness the crescent moon on the 29th of the month, Ramadan will not start until after the 30th day of Shaaban.
“Astronomical calculations indicate that the month of Shaaban is a 30-day full month, which means that Thursday, May 17, will be the first day of Ramadan,” said Khalid Saleh Al-Zaaq, a member of the Arab Union for Astronomy and Space Sciences.
He said that Ramadan this year will be a 29-day month, with June 15 marking the first day of Eid.
Oman was the first country to declare that its Ramadan will begin on May 17, after no crescent was sighted on Tuesday, while Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Bahrain said they will begin fasting only once the crescent moon has been sighted and if it is not seen, they will wait until after the 30th day of Shaban.