DUBAI: Faced with surging energy demand for economic growth, Saudi Arabia is turning to nuclear power to meet a twin challenge — how to diversify its electricity-generating mix while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. And with electricity demand in the country growing by 8 to 10 percent annually, compared with less than 1 percent in Europe, experts say the move is timely. Last week, an International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) team of experts concluded a 12-day mission to the Kingdom to review its development of infrastructure for a nuclear power program. The review, which ended on July 24, was carried out at the invitation of the Saudi government. “Nuclear is an important way to meet the fast-growing demand for energy in the region, taking into consideration a wish to diversify the energy sources and not rely solely on oil and gas,” said John Bernhard, former Danish ambassador to the IAEA.
“Besides, the use of nuclear power is a significant element in an energy strategy which considers the need to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and implement commitments concerning climate change. Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, are beneficial from a climate change point of view, but will often not be sufficient to cover large energy demands.”
The Kingdom plans to build two large nuclear power reactors as part of a program delivering as many as 16 nuclear power plants over the next 20 to 25 years at a cost of more than $80 billion. It has projected 17 gigawatts (GW) of nuclear capacity by 2032 to provide 15 percent of the power then, along with more than 40 GW of solar capacity.
So far, Saudi Arabia has identified two possible sites for power stations, on the Gulf coast at Umm Huwayd and Khor Duweihin.
Plans for small reactors for desalination are also well advanced. “IAEA missions are of crucial importance when preparing for the introduction of nuclear power programs, especially in so-called newcomer states — those with little or no experience regarding nuclear power,” Bernhard said.
“IAEA experts can provide useful advice technically and with regard to nuclear safety and security.
This is of great value both for the nuclear newcomer and the international community.”cSaudi Arabia is selecting finalists from five countries — the US, China, Russia, France and South Korea —that it invited earlier this year to bid on a project to build the two plants. The selection of a winning bid and the signing of contracts are expected by the end of 2018.
“Saudis have recognized that it is important for them to develop a nuclear power program,” said Lady Barbara Judge, former head of the UK Atomic Energy Authority. “The days of oil and gas are waning, and it is not appropriate for any country to rely on one source of energy — more and more of the world’s population is worrying about climate change.”
Nuclear is a carbon-free techno-logy that provides continuous generation. “Even if a country is investing heavily in renewables, they have the problem of only being available when the sun shines and the wind blows,” said Judge, who is a member of the International Advisory Board for the development of nuclear energy in the UAE.
“Accordingly, back-up generation is needed to assure a continuous supply of energy. To me, it seems the Saudis, like Abu Dhabi, are perfectly situated to build a new nuclear power plant — they have the backing of the government and the funds to build a first-class plant, and they understand that it is inappropriate today to rely solely on oil.
 “They also have the resources to bring in international experts and to conduct an effective public outreach program to educate the population about the benefits of nuclear energy.”
“They also have the resources to bring in international experts and to conduct an effective public outreach program to educate the population about the benefits of nuclear energy.”
Judge said that IAEA missions provide an assurance that the construction, operation and safety culture will be of the highest standard. “The IAEA is an independent appraiser and adviser, and it helps countries to appropriately plan and design their new project.”
The move falls in line with the Kingdom’s Vision 2030, which is based on diversifying its economy away from oil and gas. And with desalination and residential cooling set as the two largest uses of power, and desalinated water demand expected to double in the next decade, experts say that it is more profitable for the country to sell oil and gas while using alternative resources, such as nuclear, for water desalination.
Environmentally, nuclear is also expected to significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
“Saudi Arabia has to find ways to diversify and increase its power production capacity for economic growth and development,” said Dr. Peter Bode, former associate professor in nuclear science and technology at the Delft University in the Netherlands.
“Nuclear power is one of the options in the power mix that could also contain wind energy and solar, but these systems cannot take over the major role in the power mix. Moreover, these are also somehow much more vulnerable to damage, like sabotage, and even the effects of climate change.”
He said nuclear power is a proven technology with high reliability and safety — a nuclear power plant typically operates for about 60 to 70 years, and provides jobs for about 1,000 people over that period. “Wind and solar energy are options for local and domestic energy production, but not to provide the needs of industry.”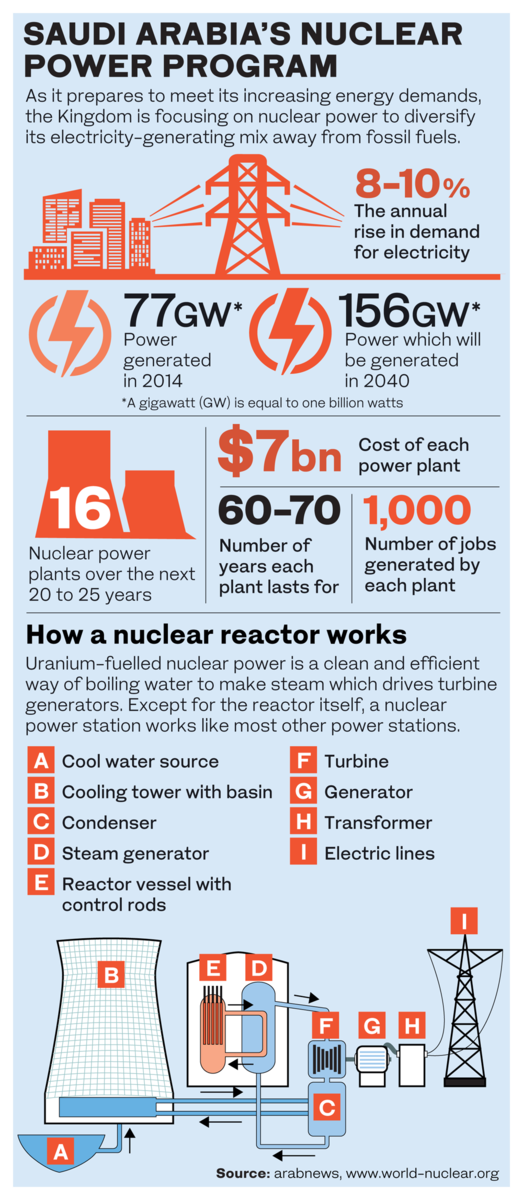
In 2010, a Saudi royal decree said that the development of atomic energy is essential to meet the Kingdom’s growing requirements for energy. The country formed the King Abdullah City for Atomic and Renewable Energy (KA-CARE).
In July last year, the Cabinet approved the establishment of the National Project for Atomic Energy, and new financial and administrative regulations for KA-CARE, which was set up in Riyadh.
Several years ago, a study by the IAEA explored the economics of nuclear power in the Middle East.
“As long as the future international oil market price was above $60 to $65 per barrel, nuclear power made sense,” said Holger Rogner, an Atomic Reporters director, energy economist and former head of the IAEA’s energy planning section.
“The domestic price of oil used for electricity generation and desalination is highly subsidized, so if they replace electricity generation with nuclear power, and sell this oil at market prices abroad, the difference in revenue would basically pay for the nuclear power plant. There are clear thresholds when things make sense,” he said.































