JEDDAH: Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas told a group of Israeli lawmakers and activists on Sunday that US President Donald Trump’s negotiating team had asked whether he would agree to a confederation with neighboring Jordan.
According to Shaqued Morag, Peace Now’s executive director, who attended the meeting, Abbas said that he would agree to a trilateral confederation that includes Israel. Decades ago, Israeli officials mooted the notion of a confederation between the Palestinians and Jordan.
Such an announcement was received with anger from Jordanians and Palestinians, who insisted that there should be no talk on confederation before an independent Palestinian state was established with East Jerusalem as its capital.
Jumana Ghunaimat, spokesperson for the Jordanian government, said the idea of a confederation between Jordan and Palestine isn’t a subject for discussion. Jordan’s position is based on the proposed two-state solution and the establishment of a Palestinian state with East Jerusalem as its capital, she told the told the Ammon News agency.
Origin of the confederation plan
In 1950, elections were held in the two banks of Jordan won by 20 deputies from the East Bank and the same from the West Bank, and the Senate was formed in a fair representation. The National Assembly representing the two countries held an equal session on April 24, 1950, and unanimously approved the unity decision between the two shores on the basis of parliamentary rule.
It is noted here that the resolution was conditional. The second item states: “To affirm the preservation of all Arab rights in Palestine and to defend those rights by all legitimate means and to fill the right and not to prejudice the final settlement of its just cause within the scope of national aspirations, Arab defense and international justice.”
At the time, no Arab country recognized the unity between the two shores. The Arab League Council held a meeting and issued a decision on June 12, 1950, with a reservation on the unity decision.
The 1950s saw a political movement to form a Palestinian organization working to highlight the Palestinian national identity and establish an independent Palestinian national entity. This movement included all Palestinian factions and attracted ideologues in all directions.
In 1964, the Arab League selected Ahmad Al-Shukairy as the representative of Palestine. As a result, the first founding session of the Palestinian Conference was held in Jerusalem under the auspices of the late King Hussein of Jordan, in which the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) was decided. The second Arab summit, held in Alexandria on Sept. 15, 1964, approved the establishment of the organization headed by Al-Shukairy with its headquarters in Jerusalem, and the Palestinian flag.
In 1967, the Six-Day War erupted between Israel and the Arab countries, ending with Israel occupying the West Bank and Sinai and the Golan Heights. The Arab states agreed to a cease-fire in accordance with UN Security Council Resolution 242.
The war resulted in a wave of hundreds of thousands of Palestinian refugees who, fearing the Israeli gangs’ retaliation, left everything behind and escaped to Jordan.
The Arab leaders held a summit in Khartoum, the Sudanese capital, in late August 1967 and decided no peace, recognition or negotiations, but the Arab states limited their commitment to ending the Israeli occupation and liberating the territories occupied in the Six-Day War.
Al-Shukairy rejected these decisions and resigned. This led to a period of time until the late Yasser Arafat, the head of Fatah, took command of the Palestine Liberation Organization.
By that time, the PLO had become the sole representative of the Palestinian people, despite Jordan’s insisting on the need for unity between Jordan and Palestine.
On March 15, 1972, King Hussein revealed his plan for a “United Arab Kingdom,” which would be a federation consisting of two federal districts — the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan and a Palestinian federal district, which would be located in the West Bank region that was under Jordanian control between 1948 and 1967 and that would have East Jerusalem as its capital.
According to the proposal, the two districts of the federation would be autonomous, except for the military affairs, foreign affairs and security affairs that would be run by a central government located in Amman.
Nevertheless, King Hussein conditioned the establishment of the UAK in achieving a peace agreement between Israel and Jordan. His proposal was ruled out after it was rejected both by Israel and by the PLO and other Arab states.
Disengagement between the two banks
Jordan, meanwhile, continued to carry out its responsibilities in the West Bank without any change. However, this was not to the appeasement of the PLO, which saw this act as a challenge to its existence and to its recognized status by the Arab League as the sole caretaker of all Palestinian affairs.
At the Arab summit conference held in Rabat, the Moroccan capital, in 1974, King Hussein agreed with all the other Arab leaders to a declaration recognizing the PLO as the “sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people.” Consequently, all responsibility for negotiating the return of the occupied Palestinian lands was transferred from Jordan to the PLO. Jordan, however, continued its administrative and financial support to Palestinians in the West Bank.
The pressure continued to mount on Jordan, eventually leading King Hussein to make a decision. In an address to the nation on July 31, 1988, he made his historic announcement, which was one of the most important policy decisions in the era of modern Jordan: Full legal and administrative disengagement from the West Bank.
“Our decision, as you know, comes after 38 years of the unity of the two banks, and 14 years after the Rabat summit resolution designating the PLO as the sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people. It also comes six years after the Fez summit resolution that agreed unanimously on the establishment of an independent Palestinian state in the occupied West Bank and the Gaza Strip as one of the bases and results of the peaceful settlement,” King Hussein said.
Decoder
The Arab League
The Arab League comprises 22 states, including Palestine. It was formed on March 22, 1945 with six members: Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria (now suspended because of the civil war).The Cairo-based forum discusses common policy issues, administers social programs and resolves disputes.
The PLO as well as all other Palestinian factions supported the disengagement. “The disengagement was a courageous step in the interest of the Palestinian people and its struggle, and it achieved a demand by the Palestinian people to push things in the Middle East to a new direction,” said the PLO’s second-in-command at the time, the late Salah Khalaf (Abu Iyad).
Despite the disengagement, Jordan at the same time remains the main source of support for the Palestinians at all forums and by all means continued to join the fight to liberate the occupied Palestinian territories and secure the Palestinians’ right to self-determination and to establish their independent state with Jerusalem as its capital.
Beginning of the peace process
The Eighties and Nineties witnessed extensive regional and international changes: The beginning of the Camp David Accords between Egypt and Israel. This was followed by the collapse of the Soviet Union and its socialist system, and the US domination of the UN and the world. These changes have led to the acceptance of peace in the Arab countries, and some have considered peace a strategic option.
This led to the convening of the Madrid Conference in 1991, in which all Arab countries participated. Jordan allowed the PLO to participate under the political umbrella of the Jordanian delegation, but in a way that maintained the independence of the Palestinian delegation.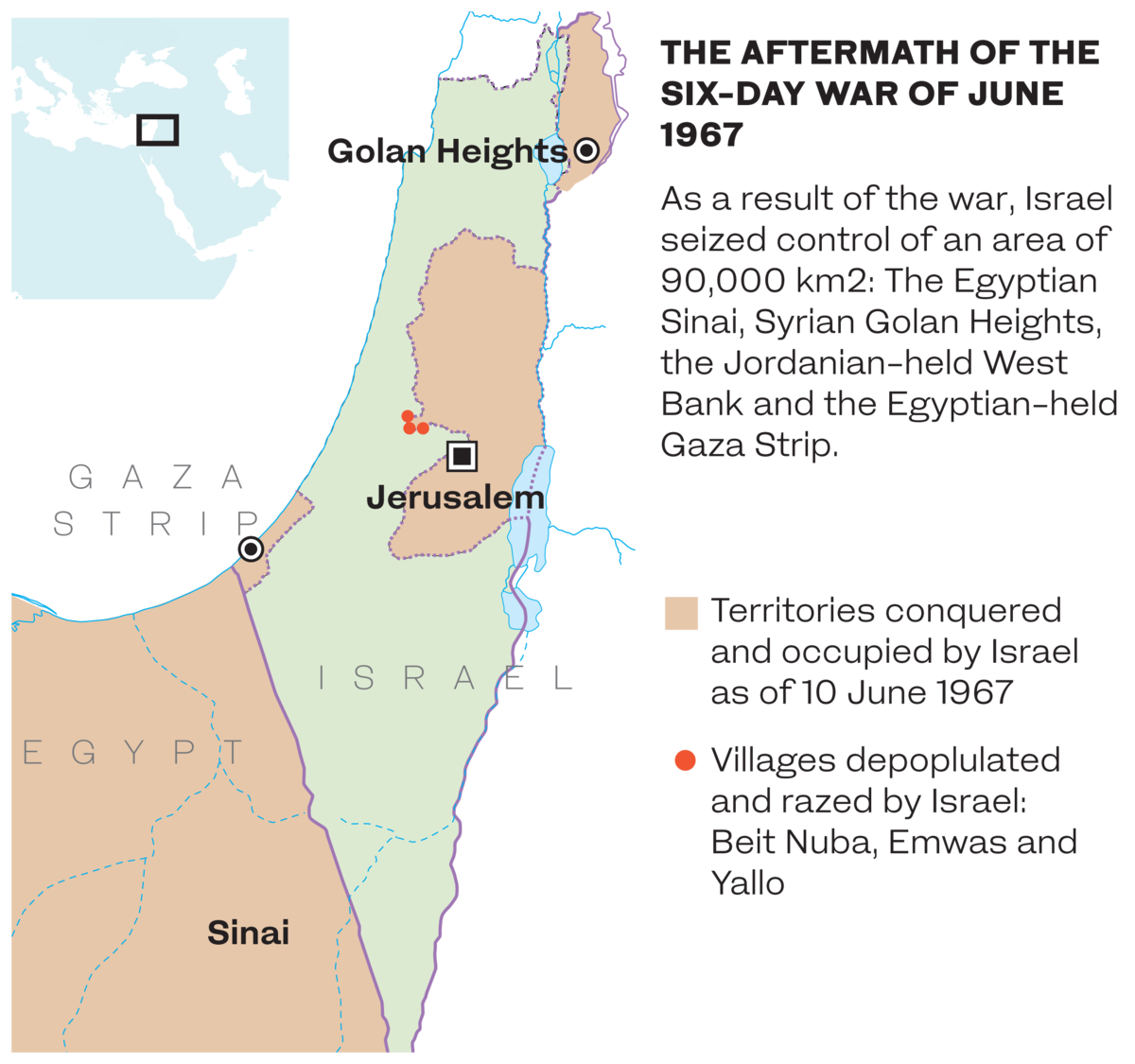
The aim of the conference was to establish lasting peace for the land in accordance with UN resolutions and international legitimacy.
Co-sponsored by the US and the Soviet Union, this conference was designed to follow up the Egypt-Israel treaty by encouraging other Arab states to sign their own peace deals with Israel.
The conference eventually led to the signing of a peace treaty between Jordan and Israel in 1994. In the meantime, the Palestinian negotiators continued their covert negotiations with their Israeli counterparts until they eventually announced the Oslo agreement.
Jordan’s leadership continues to reject any talk of any form of confederation between Jordan and Palestine before an independent Palestinian state becomes a reality.
King Abdullah has repeatedly said that the people of the countries and no one else can decide a confederation between the two states. He also stressed that as long as Israel continues to occupy the Palestinian territories, there will be no peace or security not only in the region but also in the whole world.

























