DUBAI: D-Day looms for the world’s biggest state sponsor of terror, as the US is set to reimpose sanctions against Iran on Sunday. The move could be the final nail in the coffin of a flawed nuclear deal that emboldened Iran’s actions in the region, according to experts who commended US President Donald Trump’s decision to walk away from the ill-fated agreement.
The 2015 nuclear deal, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), saw Tehran agree to curtail its nuclear weapons program in return for the lifting of sanctions. However, on May 8 this year, Trump announced his decision to end US participation in the plan, describing it as “disastrous” and “defective at its core.” In doing so, he acknowledged that it failed to curb Iran’s ballistic missile program and address its provocative regional activities in Syria, Yemen, Lebanon and Iraq.
Moments after announcing the US would pull out of the deal, Trump signed a fresh two-part set of sanctions against Iran and warned countries against pursuing any cooperation with Tehran on its controversial nuclear weapons program. The second part of those sanctions — designed to reduce Iran’s exports of oil to zero — comes into effect on Monday.
Iran is the third-largest producer in the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). Additional sanctions that kick in on Monday directly target countries that buy oil from it by blocking them from access to US markets and financial institutions.
Iran’s biggest energy buyers, including China and US allies such as India, Turkey and South Korea, are working to get around the sanctions or make up the shortfall elsewhere.
Dr. Dalia Dassa Kaye, director for the Center for Middle East Public Policy at the RAND Corporation, told Arab News that the sanctions “will work in inflicting more pain on Iran.”
Dr. Sanam Vakil, senior consulting research fellow at Chatham House for the MENA region, said there had been early indications that the original deal was flawed.
“The deal was not comprehensive enough, did not include Iran’s regional activities and it had a shorter time frame than many people wanted,” she said.
The heart of the nuclear deal, negotiated over almost two years by the Obama administration, was that Iran would curb its nuclear program in return for the relaxation of sanctions that had crippled its economy.
But after coming to power, Trump described the agreement among the five permanent members of the UN Security Council and Germany — known as P5+1 — as a “horrible, one-sided deal that should have never, ever been made,” rejecting claims that the Iranian regime desired only a peaceful nuclear energy program.
Vakil said the agreement was sold as a transactional deal that many thought would lead to “transformational changes in Iran’s behavior.”
“However, Iran’s regional policy has always been detached from its nuclear program,” explained Vakil. “There is no correlation between sanctions and the commitment to the nuclear deal and Iran’s commitment to its regional allies. Actually, while Iran entered into the agreement, it also entered into the Syrian war.”
However, Vakil believes that it is possible another nuclear deal “will be back on the table,” providing it addresses Iran’s state-funded terror. “I think the deal will try to address all the outstanding issues that the US has raised. What is clearly important is a compromise. The original nuclear deal was not enough of a compromise for President Trump. The next (deal) will have to be a compromise to all parties.
“The US has issued 12 demands as a launchpad for negotiations, and Iran’s regimes around terrorism in the region will be included in those discussions. This is not just an Iran issue, this is a regional and international issue, and if the US wants to get involved in a long-term concession with Iran, it is going to have to take its regional activities into account.”
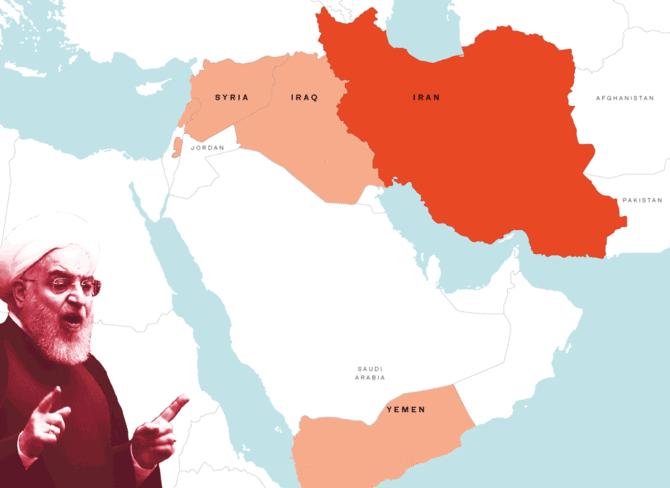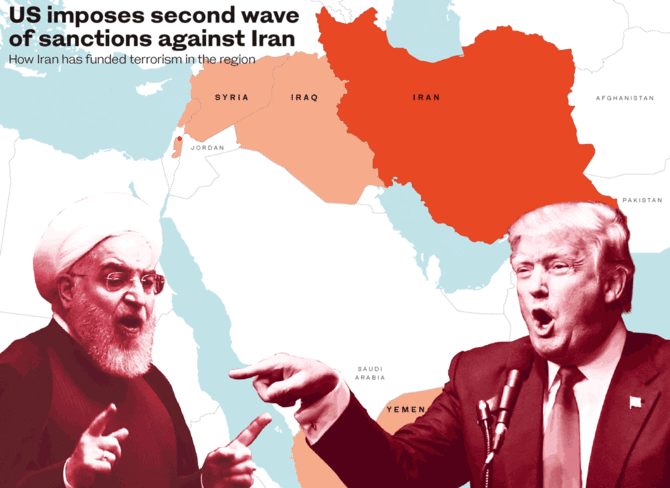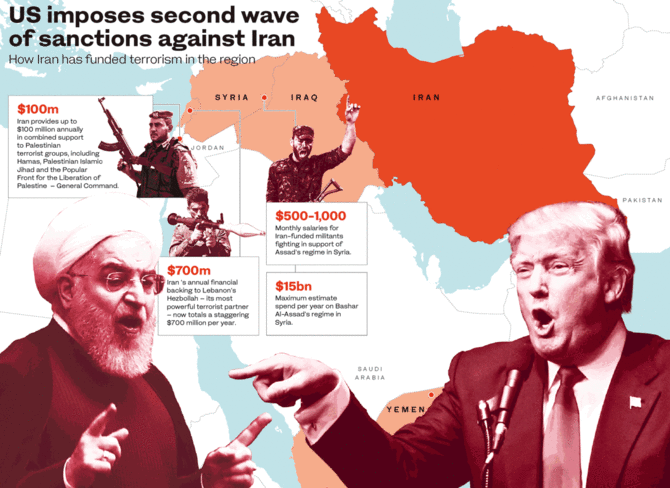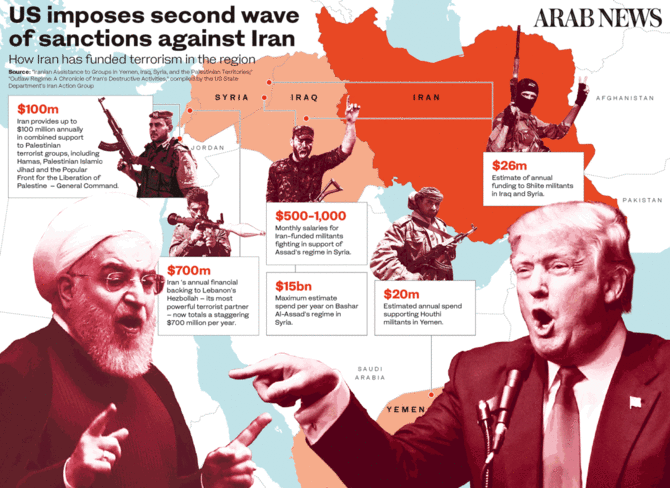
A report, “Outlaw Regime: A Chronicle of Iran’s Destructive Activities,” compiled by the US State Department’s Iran Action Group and released in September, highlights Iran’s terror campaign in the region, including providing funding, training and weapons to the Lebanese Hezbollah, Hamas, Palestine Islamic Jihad, Kata’ib Hezbollah in Iraq and Al-Ashtar Brigades in Bahrain.
Beyond these US-designated terror groups, Iran has provided weapons and support to Shiite militant groups in Iraq, the Houthis in Yemen and the Taliban in Afghanistan.
Iran’s annual financial backing to the Lebanese Hezbollah now totals a staggering $700 million. Since the end of the 2006 Israel-Hezbollah conflict, Iran has supplied Hezbollah with thousands of rockets, missiles and small arms. Hezbollah now has more than 100,000 rockets or missiles in its stockpile. Iran also provides up to $100 million annually in support to Palestinian terrorist groups and, since 2012, has spent hundreds of millions of dollars aiding the Houthis.
Harris Breslow, an associate professor with the department of mass communication at the UAE’s American University of Sharjah, told Arab News that Trump’s argument has always been that the JCPOA did not cover Iran’s behavior in the region.
“The agreement just covered nuclear weapons activity, so, as a result, some people argued that Iran saw this as an opportunity to do whatever it wanted, as long as it didn’t involve nuclear weaponry,” said Breslow.
Robert Satloff, executive director of the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, has highlighted many core problems of JCPOA — firstly, that it was sold, in part, as a way for Iran to recoup billions of dollars in lost sanction revenue.
“From the beginning there was a real fear that the Iranians would divert large sums to their destabilizing regional ambitions and terrorist proxies. In the past two years, that has certainly been the case, with Tehran expanding its ballistic missile program and extending its regional influence by channeling funds and weapons to Hezbollah, the Houthis and thousands of Shiite militia traveling from as far away as Afghanistan to fight in Syria and Iraq,” he said.
Satloff said a secondary issue was Iran’s ballistic missile program. “Given that the Iranians are exploiting a loophole that the Obama administration permitted in the relevant UN Security Council resolution to plow ahead with developing missiles potentially capable of delivering nuclear weapons, it is wholly false for advocates of the deal to argue that the JCPOA has halted, frozen or suspended Iran’s nuclear-weapons program. Such a program has three main parts — development, weaponization and delivery — and ballistic missiles are an integral part of that. Critical aspects of the program are moving ahead, deal or no deal.”
The Foundation for Defense of Democracies has identified as many as 23 ballistic missile launches by Iran since the end of the July 2015 nuclear deal.
Satloff also said one of the biggest flaws in the JCPOA was the expiration of all restrictions on Iran’s enrichment of nuclear material 15 years into the agreement.
Breslow said, optimistically, the sanctions would lead to the P5+1 re-examining Iran’s terror campaign in the Middle East.
“Trump is trying to steer the global agreement from America,” he said. “He wants to negotiate a better deal. However, the realistic may say this will make Iran hard-line. Whether a new deal is revisited, and revisited in a way where there is a better deal on the table, remains to be seen.”