ISLAMABAD: Nuclear-armed rivals India and Pakistan face their worst tension in years over the disputed region of Kashmir, with Islamabad saying they shot down two Indian warplanes Wednesday and captured two pilots. Pakistan immediately shut down its civilian airspace in response.
But how did the relations between these two Asian nations become so bad and what’s at stake in this rapidly worsening conflict that both sides say they want to de-escalate?
___
WHAT STARTED THIS LATEST TENSION?
On Feb. 14, a suicide car bomber attacked a paramilitary convoy on the Indian-controlled side of Kashmir in the Himalayas, killing more than 40 troops. The militant group Jaish-e-Mohammed, which is based in Pakistan, claimed responsibility for the attack. The suicide bomber was from Indian Kashmir. New Delhi long has accused Pakistan of cultivating such groups, something denied by Islamabad. India launched an airstrike on Pakistani territory early Tuesday that New Delhi called a pre-emptive strike against militant camps in Pakistan. India said its bombs killed a “very large number” of militants, while Pakistan said there were no casualties in an airstrike it described as being carried out “in haste.”
___
WHY IS THIS TENSION SO DANGEROUS?
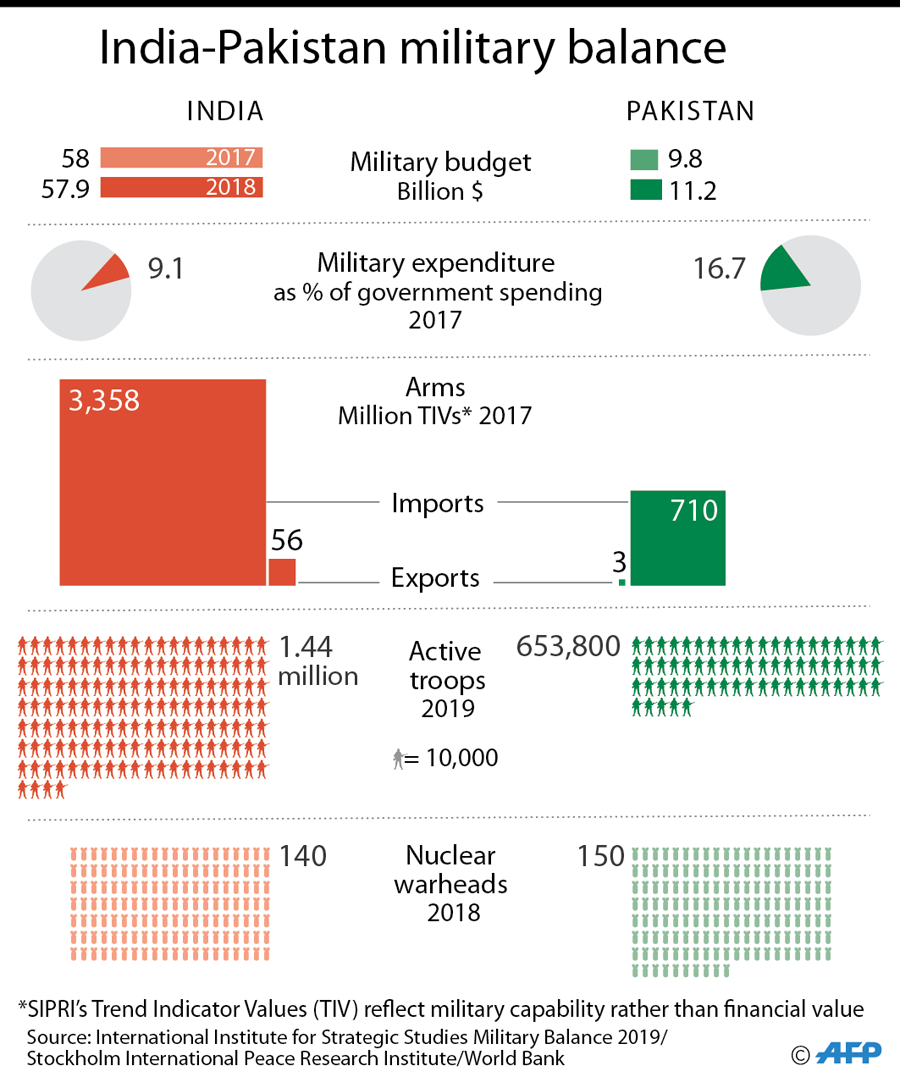
Both India and Pakistan are believed to possess more than 100 nuclear warheads each and have conducted atomic weapon tests. Both countries have test-fired nuclear-capable missiles. Pakistan also has refused to renounce a first-strike option with its atomic bombs should it feel outgunned in a conventional war. It takes less than four minutes for a missile fired from Pakistan to reach India. The Bulletin of Atomic Scientists warns that “computer models have predicted that the physical impacts of a nuclear exchange between India and Pakistan, or even a single strike on a large city, would be devastating . and would reverberate throughout the world.”

___
HOW DID THE DISPUTE OVER KASHMIR BEGIN?
When Britain granted independence to the region in 1947, it divided the Indian subcontinent into a predominantly Hindu India and mostly Muslim Pakistan. Some areas could decide their own fate. In Kashmir, the only Muslim majority area ruled by a Hindu monarch, its ruler decided against giving the population a choice. That started the first India-Pakistan war in 1947. The conflict ended in 1949 when a United Nations resolution established the Line of Control dividing Kashmir between the two nations and calling for a direct vote on which country should control it. That vote has never been held. Indian and Pakistan fought a second war over Kashmir in 1965.
___
WHAT HAS HAPPENED SINCE?
India and Pakistan fought a third war in 1971 over what was East Pakistan, which later became an independent Bangladesh. In 1999 and 2000, after Pakistan’s military sent a ground force into Indian-controlled Kashmir at Kargil, the two countries faced off and a worried world urged both to pull back from the brink of war, fearing it could escalate into a nuclear conflict. Even in times of relative peace the two nations readily engage in brinkmanship and aggressive rhetoric.
___
HOW DO THE MILITARIES OF INDIA AND PAKISTAN COMPARE?
India, home to 1.3 billion people, has a conventional army of about 1.4 million soldiers. Pakistan, with a population of over 200 million people, has about 650,000 troops. Both countries have spent billions developing conventional arms. Last year, Pakistan spent about $11 billion or about 3.6 percent of its gross domestic product on defense. India meanwhile allocated about $58 billion, or 2.1 percent of its GDP on defense, according to the International Institute for Strategic Studies. India’s ballooning military spending has propelled it to the world’s fifth-biggest defense spender, surpassing the United Kingdom, according to the IISS.
_
__
HOW IS PAKISTAN REACTING?
Pakistan, which has a history of military coups and strong-arm rule from those tied to its intelligence services, has largely reacted to this conflict through its civilian government. Foreign Minister Shah Mahmood Qureshi took the lead to condemn the airstrike Tuesday, painting India as an aggressor who would suffer repercussions, without elaborating. Qureshi also accused Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi of playing with regional stability to get votes in upcoming national elections. Prime Minister Imran Khan has called for a joint meeting of Pakistan’s upper and lower houses of parliament. Public criticism of India has been loud across Pakistani media, with sporadic protests against New Delhi breaking out across the country.
___
HOW IS INDIA REACTING?
Indian government officials called the airstrike Tuesday a counterterrorism operation based on credible intelligence that another attack against India was imminent. The tensions could be a boon for Modi, whose Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party aims to maintain power in elections due by May. The airstrike appears to have temporarily insulated the Modi government from criticism about it failing to create as many jobs as pledged in the 2014 elections. Opposition party leaders have responded with support for India’s air force. Meanwhile, Modi earned points with the powerful Hindu nationalist social group, the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh, or RSS. RSS chief Mohan Bhagwat said Tuesday: “Truth and non-violence are fine, but the world understands the language of power.”
___
Associated Press writer Emily Schmall in New Delhi contributed to this report.
























