KARACHI: A senior member of the ruling Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) government, which has been chasing PayPal Holdings Inc to start Pakistan operations, said the country was still in talks with the worldwide payments processor and “hopeful” it would launch services soon in the South Asian nation of 208 million.
As of this year, PayPal operates in about 200 markets and has 277 million registered accounts, allowing customers to send, receive, and hold funds in 25 currencies. Around 200,000 freelancers and over 7,000 registered small and medium enterprises (SMEs) would benefit if PayPal entered the Pakistani market.
The online payment industry is pegged to grow ten-fold to $500 billion by 2020, but last week, Senator Mian Mohammad Ateeq Shaikh told the Senate Standing Committee on Information and Technology that PayPal was afraid to enter Pakistan in the absence of laws to protect the company’s interests.
“The issue is under consideration, and we are hopeful [PayPal will enter Pakistan],” Muhammad Abdul Ghafar Wattoo, member of the National Assembly’s Standing Committee on Information Technology and Telecommunication, told Arab News.
PayPal, an Elon Musk-founded company, will allow Pakistani consumers to use the platform to shop online at some of the country’s most popular businesses. Merchants accepting PayPal will also be able to process both local and global payments through PayPal, getting access to the payment processor’s more than 218 million customers around the world and in Pakistan.
Industry insiders say one of the major bottlenecks to PayPal coming into Pakistan is a central bank-mandated $2 million license fee.
“For a company like PayPal, which earns between 2% to 3% on transactions, even a $100 million transaction a year could not justify a $2 million license fee,” Dawn reported this week.
Freelancer graphic designer Zoha Kaml Azmi said she was disappointed when she heard PayPal was refusing to start Pakistan operations.
“I had found a really good freelance site based in England but the client couldn’t pay me as I didn't have a PayPal account,” Azmi said. “I was very happy I could get myself registered on those freelance sites. PayPal is a global gateway that connects to the larger world. There are many freelance opportunities that I am missing because PayPal doesn’t exist in Pakistan.”
In the absence of PayPal or another internationally recognized payment gateways, Pakistani freelancers and SMEs have hacked other ways of providing services and being paid from abroad, according to the Secretary-General of the Pakistan Software Houses Association, Shehryar Hydri. Many SMEs and freelancers open accounts abroad through their relatives or friends and receive payments there, he said.
“From the government’s point of view, this is a major leakage in the system when people are forced to keep their money abroad,” Hydri said.
Pakistani technology company owners say Paypal launching operations in Pakistan could also solve the problem of stuck up payments abroad.
“Mostly clients in the US and Europe use PayPal,” said Mashal Amir, who heads Octopus Private Limited, a call center. “Whenever they float the project online they attach the conditions of having a PayPal account as well for payment. In Pakistan’s case, we miss opportunities due to non-existence of the facility and due to the payments remaining stuck for many years.”
He added: “The clients often question why they should open new account just for us on other networks when entire world works on PayPal.”
SM Arif, a financial and banking technologist, said the presence of global players like PayPal would allow access for Pakistani freelancers and companies to international markets.
“Otherwise it looks like they are operating in isolation,” Arif said. “To deal with foreigners in the international market you show the world that a conducive environment exists in your country. The big player boost the confidence of all players in that market. It makes you a part of the global economy, the world.”
Pakistan still ‘hopeful’ online payment giant PayPal will play ball
Pakistan still ‘hopeful’ online payment giant PayPal will play ball

- Around 200,000 freelancers, 7,000 small and medium enterprises will benefit if PayPal started operations in Pakistan
- Last week, a parliamentary committee said PayPal was afraid to enter Pakistan in absence of laws to protect company’s interests
‘Strive for peace’: Saudi Arabia seeks de-escalation of Pakistan-India tensions

- Riyadh urges neighbors to resolve disagreements through diplomatic channels, strive for stability and peace for their people and region
- Tensions have surged following attack on tourists in Indian-administered Kashmir that New Delhi blames on Pakistan, which denies the charge
ISLAMABAD: Saudi Arabia has expressed concern over heightened tensions between nuclear-armed neighbors Pakistan and India amid exchanges of fire along their disputed border separating Kashmir and fears of an Indian military incursion, state news agency SPA reported on Wednesday.
Relations have plummeted following a deadly attack on tourists in Indian-administered Kashmir on Apr. 22 that New Delhi has said Pakistan was involved in. Islamabad denies the charges. Fears have risen since that India may conduct limited airstrikes or special forces raids near its border with Pakistan.
Pakistan’s information minister said on Tuesday night the country had “credible intelligence” India intended to carry out military action against it in the “next 24-36 hours on the pretext of baseless and concocted allegations of involvement in the Pahalgam incident.”
“The Kingdom appealed to both nations to de-escalate, avoid further escalation, resolve their disagreements through diplomatic channels, uphold the principles of good neighborliness, and strive for stability and peace for the welfare of their people and region,” SPA said.
Meanwhile United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres spoke separately on Tuesday with Pakistan’s Prime Minister Shebaz Sharif and India’s Foreign Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar.
“The Secretary-General also expressed his deep concern at rising tensions between India and Pakistan and underscored the need to avoid a confrontation that could result in tragic consequences. He offered his Good Offices to support de-escalation efforts,” UN spokesperson Stephane Dujarric said.
The US State Department has also said Washington was in touch with both India and Pakistan while urging them to work toward what it called a “responsible solution.”
In public, the US government has expressed support for India after the attack but has not criticized Pakistan.
Since the attack, in addition to soldiers shooting over the Line of Control frontier that divides disputed Kashmir between the two nations, India and Pakistan have announced tit-for-tat diplomatic measures that included cancelation of visas and a recall of diplomats.
New Delhi also suspended a crucial water-sharing treaty with Islamabad and ordered its border shut with Pakistan. In response, Pakistan has closed its airspace to Indian airlines.
Kashmir is disputed between India and Pakistan since 1947, with both ruling it in part but claiming it in full.
Pilgrims begin arriving in Madinah as Pakistan launches Hajj flights operation

- Over 89,000 pilgrims will travel under the government’s scheme, traveling to Makkah and Madinah via 342 flights
- Pilgrims from Karachi and Islamabad are availing Makkah Route Initiative designed to streamline immigration process
ISLAMABAD: Pakistani pilgrims who will perform the annual Hajj pilgrimage this year under the government scheme began arriving in Madinah this week as Pakistan kicked off its 33-day-long Hajj flight operation.
Over 89,000 pilgrims will travel under the government’s scheme, departing for Makkah and Madinah via 342 flights, with the last one departing from Pakistan on May 31. The first Hajj flights departed from Islamabad, Lahore, Karachi and Quetta for the Saudi city of Madinah on Tuesday.
“First flight carrying 393 pilgrims from Islamabad landed at Prince Mohammad bin Abdulaziz International Airport,” Radio Pakistan reported on Wednesday.
“The intending pilgrims were transported to their residences in special buses. Later, they were warmly received at their hotels and presented flowers, chocolates, dates and refreshments as per Saudi cultural traditions.”
The pilgrims from Karachi and Islamabad availed the Makkah Route Initiative, which is designed to streamline immigration processes by enabling pilgrims to complete official travel formalities at their departure airports. Initially tested in Islamabad in 2019, the program was later expanded to Karachi, benefitting tens of thousands of Pakistani travelers. This saves pilgrims several hours upon arrival in the Kingdom, as they can simply enter the country without having to go through immigration again.
Around 50,500 Pakistani pilgrims will travel to Saudi Arabia under the initiative this year. The scheme was launched in 2019 by the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah and has been implemented in five countries: Pakistan, Malaysia, Indonesia, Morocco and Bangladesh.
Besides those using the government scheme, 23,620 Pakistanis will also perform Hajj through private tour operators.
The total quota for pilgrims granted to Pakistan for 2025 was 179,210, which could not be filled.
Traditional Swati rice dish finds new life at Pakistani valley’s roadside eatery

- Restaurant owner Nasar Khan began preparing warjale as a hobby, turned it into a business after strong demand
- Labor-intensive dish prepared with begumi rice grown in Swat and mixed with naturally occurring bitter wild greens
SWAT: At a small mudbrick, hut-style restaurant in Pakistan’s picturesque Swat Valley, customers are showing up to try a traditional delicacy: warjale.
A local version of vegetable rice served with clarified butter, yogurt, cheese, milk, fresh cream and sometimes with the sauce of chicken meat, warjale, an old regional dish, is being kept alive as the main attraction at the Kawdareen Traditional Restaurant (KTR) in Mingora city.
Known for its scenic landscape of mountains and trees and cultural heritage and archaeological sites, Swat attracts thousands of visitors every year.
Many now seek out Khan’s modest eatery to experience a taste of the valley’s traditional cuisine, especially warjale, which is made from a special rice called begumi, named after a noblewoman, Begum Bilqees Effandi, who had brought the rice variety’s seeds from Afghanistan in 1949 and cultivated it in the Bagh Dherai area of Swat for the first time.
“I had another business, this was my hobby but God gave me a chance and made this a business out of my hobby,” Nasar Khan, the 60-year-old owner, told Arab News at the restaurant which he started six years ago to revive traditional foods from the valley and introduce them to young people.
“I had in mind that our traditional food should be commercialized so that the youth who don’t know about it should get a sense of it, that was the main aim.”
Khan said he served nearly all the traditional foods of Swat, such as warjale, khare, a popular dish made with lamb, tomatoes, garlic and minimal spices cooked in a traditional karahi pan, as well as saag, which is cooked mustard or similar bitter wild greens.
A warjale meal was typically served with desi ghee, fresh cream and a yogurt-based drink called lassi. A portion for two people costs around Rs1,000, less than $1, while a three-person meal costs around Rs1,300.
Cooking warjale was a labor-intensive task, Khan explained.
“Warjale is cooked in a specific kind of saag, which can’t be cultivated but grows naturally,” he said. “The locals then pluck it and cut it in a special way … People of upper Swat call it chukan and those who live in the lower part call it warjale.”
Khan said warjale’s distinct flavor derived from ingredients that could only be sourced in Swat’s environment.
“The soil of Swat is fit for growing [Begami rice], which needs cold weather, fresh water and an environment like this,” he said.
Tourists visiting the restaurant vouched for the unique taste.
Izhar Zeb Yousafzai, a computer science lecturer visiting from Timergara, said he first heard about KTR online:
“We saw some videos about this restaurant on social media. We had a day off today, so we came here with friends ... Warjale was their specialty and we got a chance to eat it after a long time. When we gave it a try, we found its taste delicious.”
Asad Khan, a 28-year-old resident from Besham in Shangla district, said he had come to Swat for sightseeing before he heard about the restaurant and the dish.
“Warjale is the traditional food of Swat,” he said. “The way it is cooked and then presented with desi ghee, it has an exceptional taste, we can’t explain it.”
Pakistan air force’s ‘timely’ response compels four Indian jets to retreat — state media

- APP says Indian Rafale jets conducted patrolling within Indian geographical boundaries near de facto LoC border
- Minister says Islamabad had “credible intelligence” New Delhi intended to launch military action within 36 hours
ISLAMABAD: A “timely” response by the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) had “forced” four Indian Rafale jets to retreat after payrolling near the two nations’ de facto border, state-run Associated Press of Pakistan reported on Wednesday, as a top minister said Islamabad had “credible intelligence” New Delhi intended to launch military action within 36 hours.
Tensions have surged between the nuclear-armed neighbors following a deadly attack on tourists in Indian-administered Kashmir on Apr. 22 that New Delhi has said Pakistan was involved in, which denies the charges. Fears have risen since that India may conduct limited airstrikes or special forces raids near its border with Pakistan.
Since the attack, in addition to shooting over the Line of Control frontier that divides disputed Kashmir between the two nations, India and Pakistan have announced tit-for-tat diplomatic measures that included cancelation of visas and a recall of diplomats. New Delhi also suspended a crucial water-sharing treaty with Islamabad and ordered its border shut with Pakistan. In response, Pakistan has closed its airspace to Indian airlines.
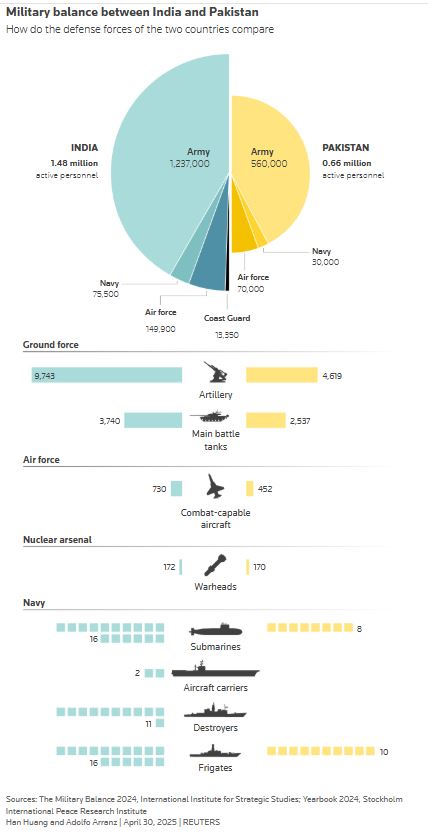
“On the night of April 29/30, four Indian Rafale jets conducted patrolling within Indian geographical boundaries” near the LoC, APP reported, saying PAF “immediately” detected the jets.
“A timely and swift response by the Pakistan Air Force forced four Indian Rafale jets to retreat … The Pakistani armed forces remain fully prepared and alert to give a befitting response to any aggression from India.”
Late on Tuesday night, Pakistan’s Information Minister Ataullah Tarar said Pakistan had “credible intelligence” India was planning military action against it in the “next 24-36 hours on the pretext of baseless and concocted allegations of involvement in the Pahalgam incident.”
The statement came after Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Tuesday reportedly authorized his country’s armed forces to respond to the latest attack in whatever way it deemed fit.
India has in recent years significantly enhanced its air combat capabilities with the acquisition of Rafale fighter jets from France. In 2016, India procured 36 Rafale jets for its air force, all of which have been delivered and are operational.
India also signed a $7.4 billion agreement with France this month to purchase an additional 26 Rafale jets — 22 single-seaters and four twin-seaters — for its navy, with deliveries expected by 2030.
India and Pakistan both claim Kashmir in full and rule it in part since 1947.
Pakistan urges simpler climate finance for vulnerable nations at Geneva forum

- Environment Minister Musadik Malik says global development not possible without climate justice
- He says Pakistan is highly climate-vulnerable despite contributing less than 1 percent to global emissions
ISLAMABAD: Pakistan’s Environment Minister Musadik Malik on Wednesday urged the international community to ease access to climate finance for vulnerable nations, saying Pakistan contributes less than one percent to global emissions but remains among the hardest hit by climate change.
Speaking in Geneva at a UN Capital Development Fund session on the sidelines of the Basel, Rotterdam and Stockholm (BRS) Conventions, Malik said developing countries like Pakistan face mounting climate threats despite minimal emissions and need more support from global financial institutions.
The BRS conventions are multilateral environmental agreements which focus on hazardous chemicals and waste management.
“Pakistan is among the countries most severely affected by climate change,” the Pakistani minister said, according to an official statement, adding this was despite the fact that it “contributes less than one percent to global carbon emissions.”
“The federal minister emphasized the need to simplify climate finance support,” the statement continued.
Malik reaffirmed Pakistan’s commitment to the Paris Agreement, a legally binding international treaty aimed at limiting global warming to below 2°C.
He said Pakistan was actively pursuing its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), with a focus on green growth, renewable energy and sustainable water systems.
Pakistan has faced recurring heatwaves, droughts and devastating floods.
In 2022, unprecedented monsoon rains left a third of the country submerged, killing about 1,700 people and leading to over $35 billion in infrastructure damage.
Pakistan also played a leading role in establishing the global loss and damage fund for climate-hit countries, though the mechanism has yet to become fully functional.
“Global development is not possible without climate justice,” Malik said, as he appealed for effective cooperation from international financial institutions for developing countries.










