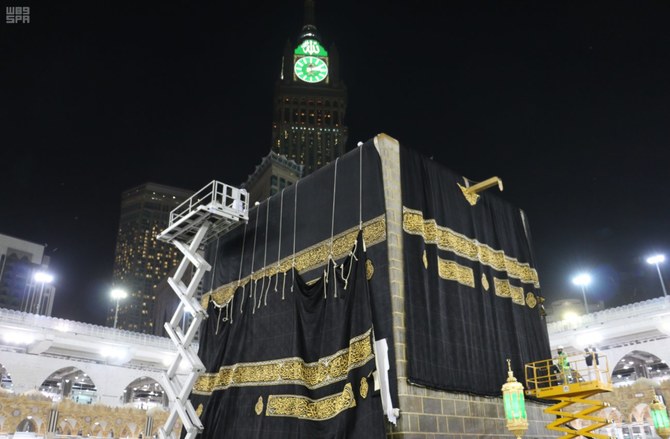
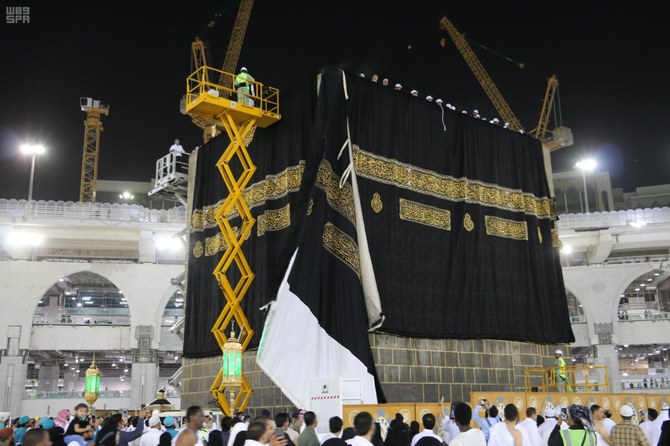
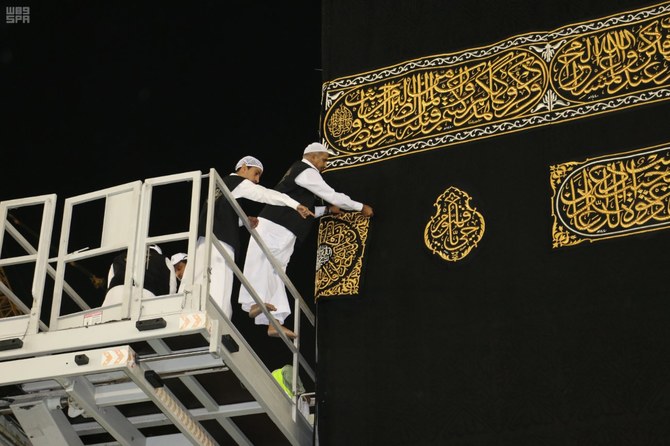
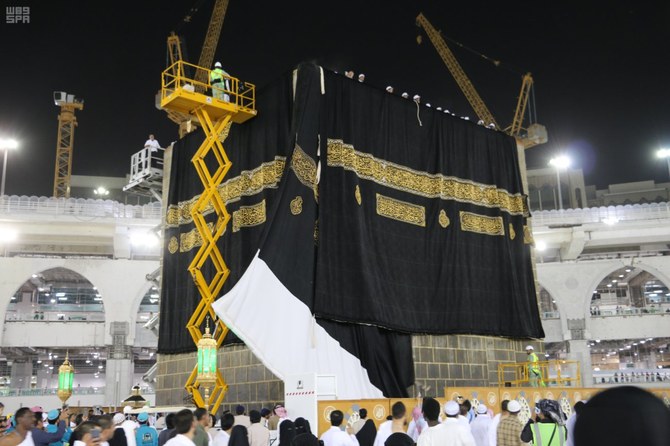
JEDDAH: In a tradition dating back centuries, a new black curtain, or Kiswa, is draped around the Kaaba in the Grand Mosque in Makkah once a year.
The fabric is made of high-quality silk, with verses of the Qur’an woven into it in the form of gold and silver thread running across the Kaaba’s belt.
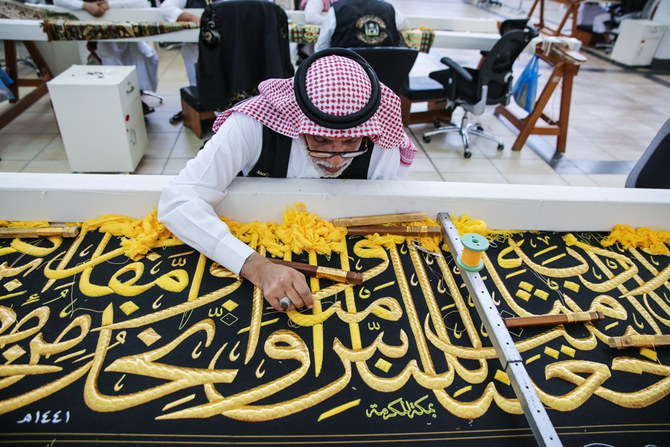
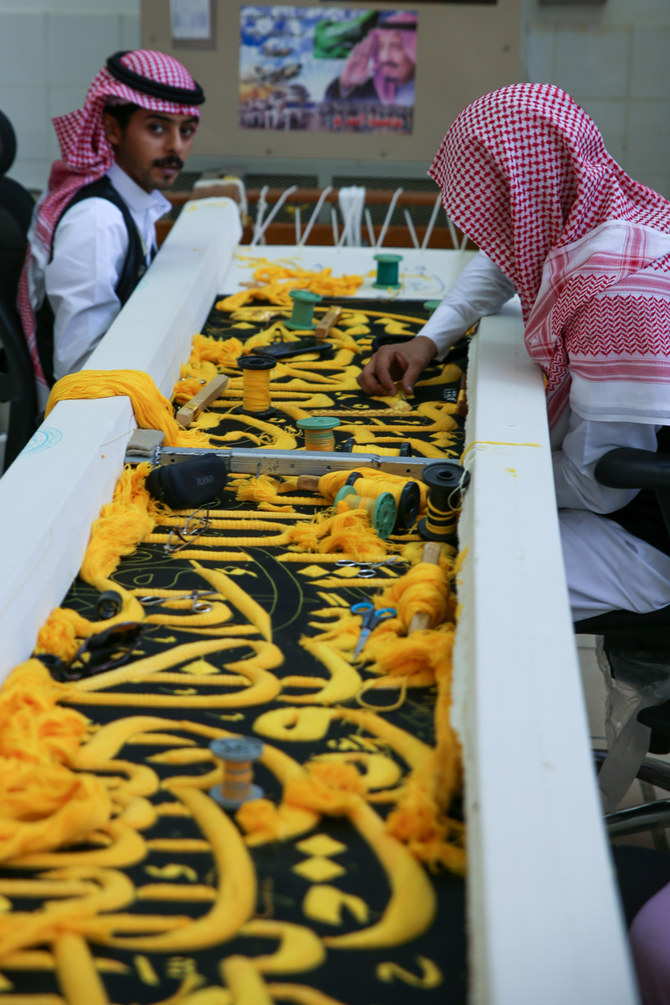
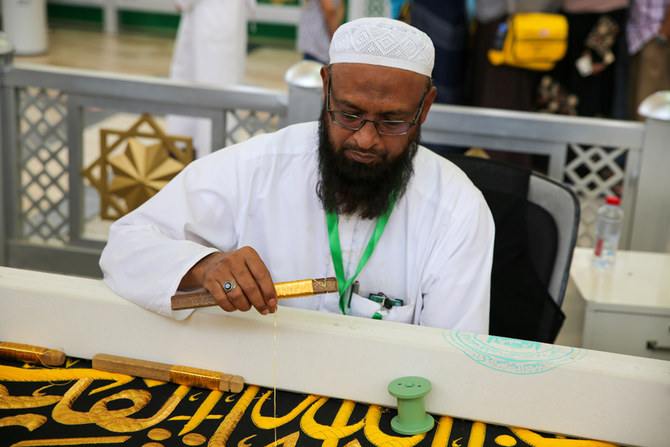
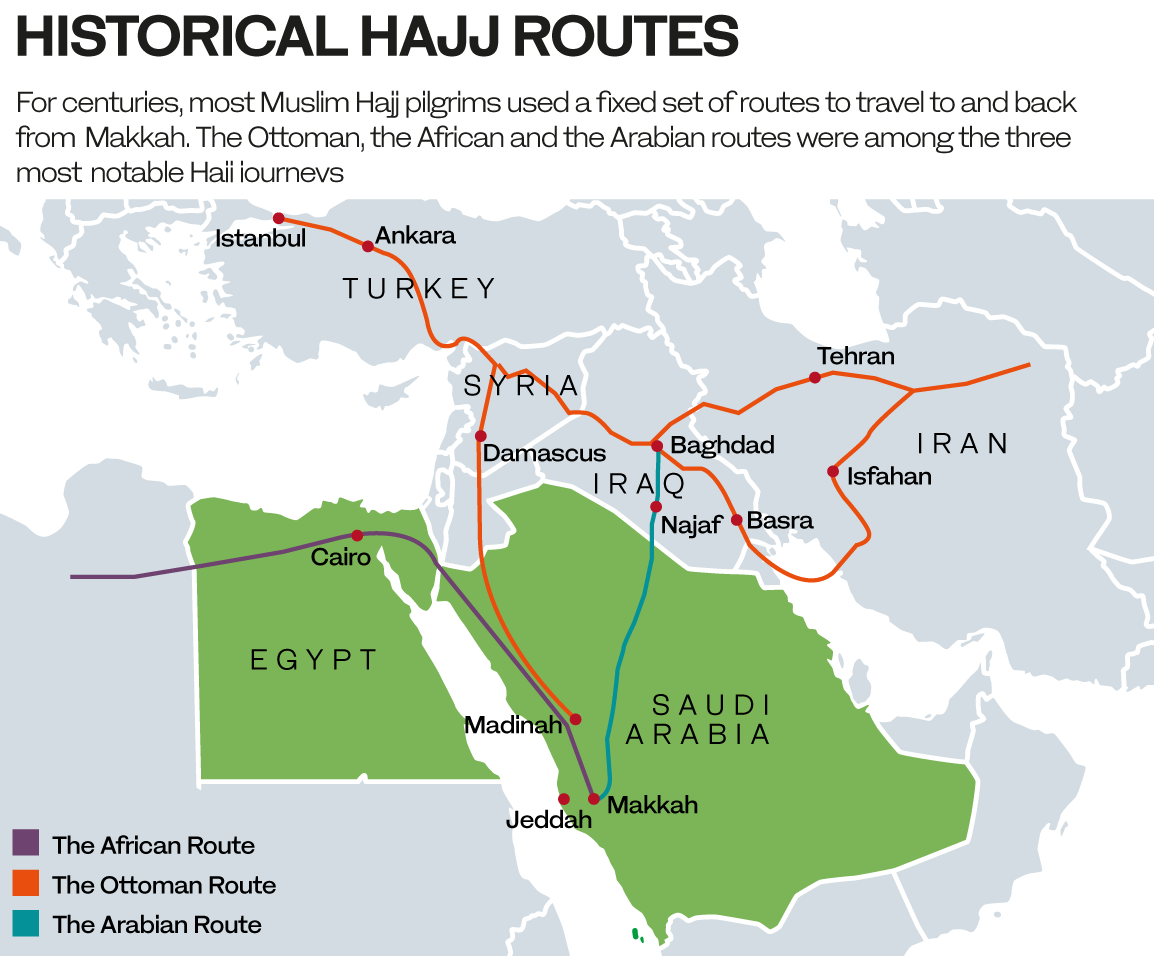
As pilgrims around the world begin their Hajj journeys, about 200 craftsmen of Saudi and other nationalities are engaged in producing the black curtain at the King Abdul Aziz Complex for Holy Kaaba Kiswa in Makkah.
They are dyeing, weaving, printing and manufacturing fabric pieces with great care and skill. Once perfumed and stitched to perfection, the finished silk curtain will be unveiled on the ninth day of the Islamic month of Dhu Al-Hijjah.
Before the establishment of the complex in 1926 by King Abdul Aziz, the Kiswa was supplied by different countries, most prominently Egypt.
A wide variety of fabrics and colors have been used through the centuries for manufacturing the Kiswa, a duty that is considered sacred.
From the writings of Arab historian Abu Al-Walid Al-Azraqi, it is known that Muslim Caliph Omar ibn Al-Khattab had the Kaaba draped with a light, white Egyptian cloth called Al-Qabbati, after sending a request to Amr ibn Al-Aas, governor of Egypt at the time, according to Egyptian history researcher Abdelmajid Abdel Aziz.
Uthman ibn Affan, the third caliph, ordered two Kiswas to be produced. The first, made of silk tapestry, was used to adorn the Kaaba on the first day of Hajj. The second, made from Al-Qabbati, was applied on the 27th day of Ramadan.
The tradition of annually draping the Kaaba with a new Kiswa continued for centuries, but the timing differed from one Islamic era to another.
During the Umayyad period, a new Kiswa was draped around the Kaaba on Ashura, the 10th day of the first month of Muharram.
It was replaced by another Kiswa at the end of Ramadan. The practice remained unchanged during the Abbasid period.
The rule of Abbasid Caliph Al-Ma’moon saw the Kaaba get a new Kiswa three times a year. The first was a red silk Kiswa on the first day of Hajj; the second was the white Al-Qabbati on the eve of the seventh Hijri month; and the third, made of white silk, on the 27th day of Ramadan.
Until 1192, the order to make the Kiswa always went to craftsmen who lived on an island in Tannis Lake (now known as Al-Manzila Lake) in Egypt’s northeast. Tannis bagged this coveted role by dint of its reputation as a textile-manufacturing hub.
But Salah al-Din — the first sultan of Egypt and Syria, and founder of the Ayyubid dynasty — ordered Tannis to be abandoned during the Christian Crusades. The manufacturing skills migrated to other parts of Egypt, notably Cairo.
The technology of the textile industry became more developed after the 13th century AD. The materials and techniques that began to be used ensured that a typical Kiswa did not wear out within a year.
During the Mamluk dynasty, Kiswa production became very expensive, forcing the sultan, Al-Nasir ibn Qalawun, to order Egypt’s governor to use the taxes from the villages of Bassous and Abul-Gheit for the purpose. But after many years, the tax revenue proved insufficient.
Later on, the cost of Kiswa production by the Egyptians was covered by an endowment created by Al-Nasir Ibn Qalawun.
During his rule, Sultan Soliman Al-Qanooni realized that the money from the endowment was insufficient, so he ordered the acquisition of seven villages in addition to three acquired in 1567 AD to create a dedicated revenue stream.
The proceeds from the 10 villages were then earmarked for manufacturing Kiswas for the Kaaba. This arrangement later proved to be the greatest contribution by Ottoman rulers.
Muhammad Ali Pasha, the Ottoman governor of Egypt from 1805 to 1848, ordered the expenses for making the Kiswa to be met by the state treasury.
This is how the historic Dar Al-Khoronfosh workshop came into existence in Cairo’s Al Gamaleya neighborhood.
In 1926, after the takeover of the Hijaz region, King Abdul Aziz ordered the establishment of a Kiswa factory in Makkah. The site was the Ajyad neighborhood near the Grand Mosque.
The present-day complex is located in Makkah’s Umm Al-Joud district. The black silk curtain is usually ready two months before the beginning of Hajj, when the keeper of the Kaaba, the Bani Shaiba family, formally takes possession of it.















































