MAKKAH: All Muslims dream of making Hajj at least once in their life. Saudi authorities are getting ready to host nearly 2 million pilgrims who have received their Hajj permits and are about to make their dreams come true. Each year the Saudi government provides facilities and services to enable pilgrims to perform their rituals with ease and tranquility.
Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques, King Salman, recently inaugurated the Guests of God Service Program, which features more than 130 initiatives, including management of Saudi archaeological and cultural sites to enrich pilgrims’ experience. Over 100,00 security personnel are expected to oversee this year’s Hajj to ensure pilgrims safe access to the holy sites.
More than 32,000 health specialists will provide health care services to this year’s Guests of God. Pilgrims will receive necessary vaccines at entry checkpoints to ensure their well-being. The Health Ministry delivered more than 360,000 polio vaccine doses and 480,000 influenza and meningitis vaccine doses to domestic pilgrims and residents of Makkah and Madinah last Hajj season. The ministry has made 180 hospital and medical centers ready to serve pilgrims.
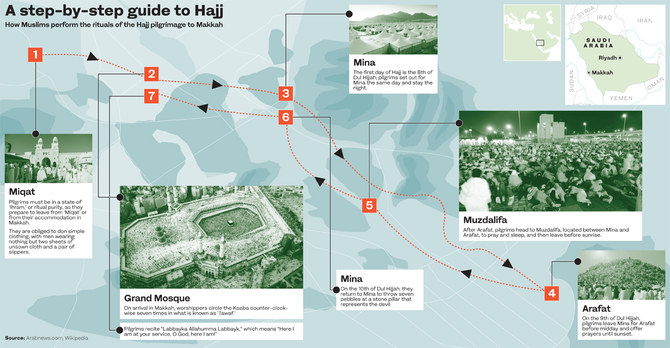
1. MIQAT
Hajj begins with Ihram (state of ritual purity) for all pilgrims. Pilgrims start their Hajj at a Miqat. There are five Mawaqeet (plural of Miqat) before they can reach Makkah. There they wash, wear their white clothes (Ihram), pray and make the intention to make their Hajj (niyyah), before getting to Makkah. They start making Talbiah (saying: ‘Labbaika Allahuma Labbaik’) .
Allah made Makkah a sacred and hallowed city that hosts His house, so it shouldn’t be entered except in a specific manner which implies glorifying God and surrendering to Him. Therefore, the Almighty ruled that anyone wanting to visit His glorified House for Hajj or Umrah must enter the state of Ihram from specific places that he is not permitted to pass without Ihram.
The Mawaqeet surround the boundaries of Makkah from north, south, east and west, and are on the path of pilgrims who come from all over the world.

2. GRAND MOSQUE
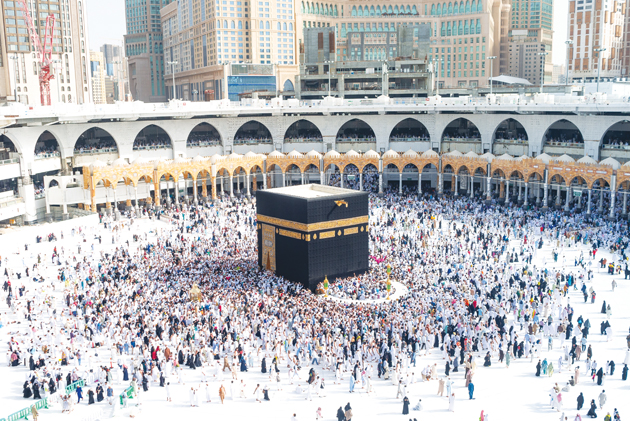
When pilgrims reach Makkah, they head to the Holy Mosque and circle Kaaba seven times (Tawaf), starting with the Black Stone. They walk counter-clockwise so that the Kaaba stays on their left. This is the Tawaf of Umrah for those performing the Tamattu Hajj (rites of Hajj and Umrah), and the tawaf of the arrival for those performing the Ifraad type (only performing the rites of Hajj) or Qiran type (performing the rites of Hajj and Umrah, also known as minor Hajj; this type doesn’t require animal sacrifice). Pilgrims are then required to pray next to the Ibrahim site when they complete seven circles.
Afterwards, they undertake Sa’e, which means “seeking” or “ritual walking.” This rite consists of walking seven times between the hills of Safa and Marwah, which are to the south and north of the Kaaba, respectively. Originally, this was done outdoors, but today the path is enclosed in a gallery. Pilgrims recite prayers, including:
“O Allah! I intend to perform seven rounds of Sa’e between Safa and Marwah to please You. Make it easy for me and accept it from me.” All rituals performed in the Grand Mosque are done barefoot.
After completing Sa’e, those performing the Tamattu type of Hajj shave their heads twice — once after the previous rites and again after the animal-sacrifice ritual. Men have their hair either completely shaved or trimmed, though shaving is preferred. However, a man may not want to have his head shaved completely during the Umrah if he plans to complete the Hajj rites in the next few days, which also include shaving. Women do not have their heads shaved, but instead cut a lock of hair or have their hair trimmed. After hair-cutting, Umrah is complete and the restrictions of Ihram are lifted.
Pilgrims can return to their normal activities. However, if a pilgrim is performing the second and third type of Hajj; Ifraad or Qiran, then the hair-cutting ritual is delayed after the animal-sacrifice part.

3. MINA
On the first day of Hajj (eighth day of Dhu’l-Hijjah), pilgrims head to Mina, near Makkah, where they spend the rest of the day, which is known as the Day of Tarawiyyah. Here, the Saudi government provides amenities, including thousands of air-conditioned tents offering temporary housing for pilgrims. On the first night, no major rituals take place, so pilgrims spend their time praying and reflecting with other pilgrims. In Mina, men and women stay in separate tents, which are located adjacent to each other.

4. ARAFAT
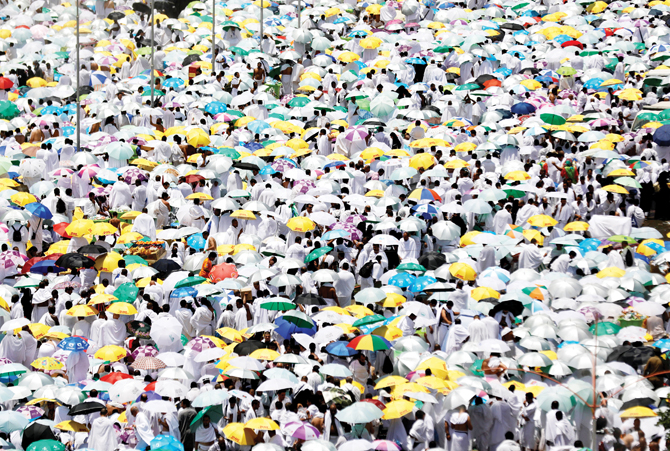
On the second day of Hajj (ninth day of Dul Hijjah), pilgrims travel to nearby Mount Arafat. Pilgrims complete Dhuhr (noon prayer) and Asr (afternoon prayer), and stay there supplicating the Almighty and asking Him for forgiveness and mercy until the sun sets.
It was narrated that the Prophet said: “Hajj is Arafa.” It is the day of Dua’a (supplication) and Dhikr (remembrance of Allah), on which Allah prides His Angels on His pilgrims and forgive them.
The Prophet is reported to have said: “When the day of Arafa comes, Allah descends to the heavens and prides the angels on His servants. He says: ‘Look at my servants; they came to Me from every valley, unwashed and uncombed. Be witness that I have forgiven them.”
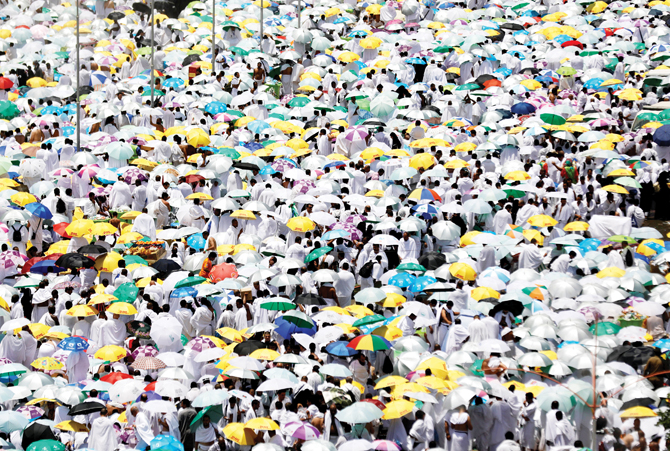

5. MUZDALIFAH
After sundown, pilgrims head quietly to Muzdalifah, between Mina and Arafat. There, they offer an evening prayer to God (Maghrib and Isha) and spend the night sleeping on the ground beneath the open sky. In the morning, pilgrims gather pebbles, which they will use in the stoning ritual later in the day. They spend the night in Muzdalifah as the Prophet — peace be upon
him — did until dawn. However, it is permissible to leave Muzdalifah after midnight.
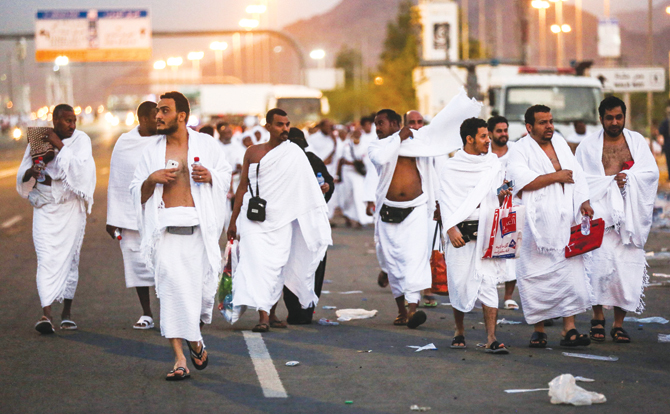

6. MINA AGAIN
Before the sun rises, pilgrims head back to Mina to take part in a ceremony meant to symbolize stoning the devil. Pilgrims throw seven consecutive pebbles at a special stone monument called the Jamrat Al-Aqabah. This ceremony can be crowded, tense and emotional. The elderly, children, sick and injured are discouraged from taking part. Instead, they may perform this later in the evening, or have a friend or confidant perform the ritual on their behalf. After stoning, men shave their heads while woman cut some of their hair. This is called the minor (Tahallul), which removes all the limitations of Ihram, except sexual intercourse.
After the stoning ritual, it is necessary to offer an animal sacrifice to God. In the past, each pilgrim did this individually; however, today, it is much more common for pilgrims to simply purchase a sacrifice voucher. After selling vouchers, qualified personnel will sacrifice a lamb for each pilgrim (or a camel for every seven pilgrims), butcher the animals, package the meat, and ship it to Muslim communities worldwide to feed the poor.
Animal sacrifice can be done at any point on the 10th, 11th, or 12th day of Dhul-Hijjah. This ritual commemorates Prophet Ibrahim’s readiness to sacrifice his son, before he was replaced by a lamb, and symbolizes the believers’ submission to God. The meat is shared out, especially among the needy.
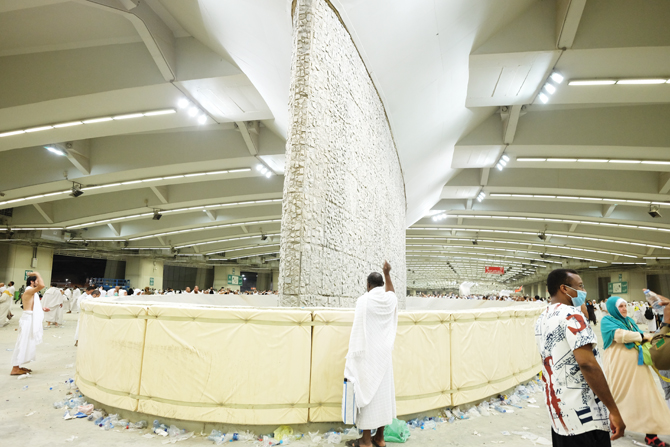

7. GRAND MOSQUE
Pilgrims then go to the Haram to make Ifadah Tawaf, followed by Sa'e if they have not made the Sa’e after the Arrival Tawaf.
Worshippers return to Mina to spend the three nights of Tashreeq and throw the pebbles. It is recorded that the Prophet slept all three nights in Mina and did not rush into leaving. However, if someone wishes to leave early, he should throw the pebbles on the 12th day and leave Mina before sunset. If the sun sets before he leaves, he must sleep the third night in Mina. But if he proceeds to leave Mina and the sun sets on his way out, but he has not left Mina yet, he does not have to stay the night.
Just as in the Umrah, the Hajj requires pilgrims to perform the Tawaf and Sa’e rituals at the Kaaba and the nearby hills. The rituals are performed essentially identically to the way they are performed during the Umrah, but it is strongly recommended that these ceremonies be done only after the stoning, sacrifice, and hair-cutting rituals. After completing the Tawaf and Sa’e, pilgrims are released from their state of Ihram and may resume the activities that were previously prohibited. At the end of their third day, pilgrims return to Mina and spend the night there in prayer.