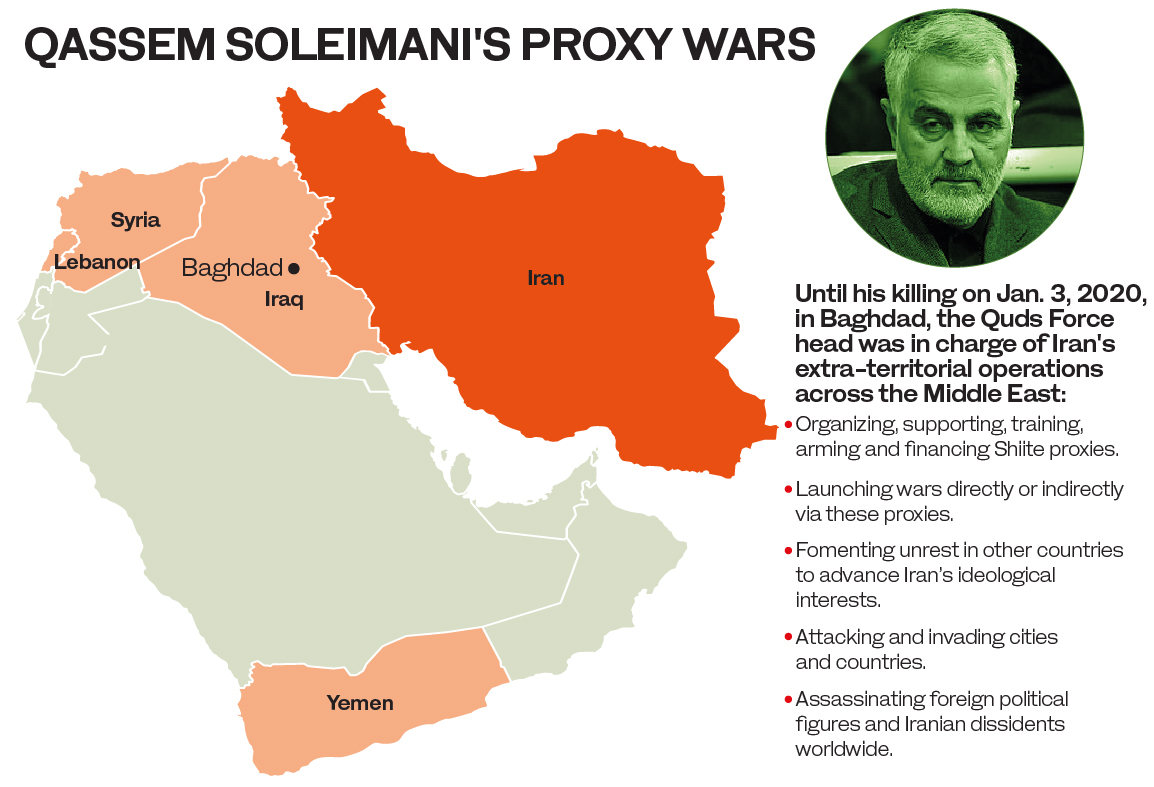
DUBAI: The US air strike that killed Iran’s top general Qassem Soleimani, 62, and six others as they traveled from Baghdad’s international airport early on Friday morning put an end to the two-decade career of the Middle East’s most dangerous man.
For the US, Arab countries and Israel, Soleimani was a shadowy figure in command of Iran’s proxy forces, responsible for fighters in Syria backing President Bashar Assad and for the deaths of American troops in Iraq.
When it came to authority, he was Iran’s second man after Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei. Being a staunchly loyal confidante to Khamenei, Soleimani developed great influence over foreign policy.
While many others in the ranks of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) have experience in waging the asymmetrical, proxy attacks for which Iran has become known, Soleimani was easily the most prominent general.
As the architect of Iran’s outsized military influence beyond its borders, he prioritized offensive tactics and operations over defensive ones, and rejoiced in taking overconfident selfies with his troops and proxies in battlefields in Iraq, Syria, Yemen and Lebanon.
The Iran nuclear deal of 2015, also known as JCPOA, provided financial, strategic and geopolitical opportunities for Soleimani. His greatest notoriety would arise from the Syrian civil war and the rapid expansion of Daesh in the Middle East. Iran, a major backer of Assad, sent Soleimani to Syria several times to lead attacks against fighters opposed to Assad and Daesh.
After 2011, Soleimani had declared that the unrest and uprisings in the Middle East and North Africa “provide our (Iran’s) revolution with the greatest opportunities ... Our boundaries have expanded, and we must witness victory in Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon and Syria. This is the fruit of the Islamic revolution.”
Taking advantage of regional unrest and instability, Soleimani and the IRGC’s elite Quds Force infiltrated top security, political, intelligence and military infrastructures in several countries and exercised control over which foreign leaders and politicians came to power.
BIO
Nationality: Iranian
Birth: March 11, 1957, in Qom, Iran
Occupations: Construction industry; utilities; military (IRGC)
Battle experience: Kurdish revolt after 1979; Iran-Iraq war 1980-1988
Proxy wars: Post-2003 Iraq; Syrian civil war; Lebanon; Yemen conflict
Death: Jan. 3, 2020, in Baghdad
The Quds Force also gave birth to many designated terrorist groups, including Asaib Al-Haq and Kataib Al-Imam Ali (KIA), which use horrific tactics similar to Daesh. KIA is known for showing videos of beheadings and burning bodies, and Asaib Al-Haq reportedly receives some $2 million a month from Iran.
Small wonder then, many people saw the blood of innocents — including Syrian, Yemeni, Lebanese, Bahraini and Iraqi children and women — on Soleimani’s hands.
Born on March 11, 1957, Soleimani was said in his homeland to have grown up near the mountainous town of Rabor. According to the US State Department, he was born in the Iranian religious capital of Qom.
Little is known about his childhood, though Iranian accounts suggest Soleimani’s father was a peasant who received a piece of land under the Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, but later became encumbered by debts.
By the time he was 13, Soleimani began working in construction, later as an employee of the Kerman Water Organization. Iran’s 1979 Islamic Revolution swept the shah from power and Soleimani joined the IRGC in its wake.
He deployed to Iran’s northwest with forces that put down Kurdish unrest following the revolution. Soon after, Iraq invaded Iran and began the two countries long, bloody eight-year war.
The fighting killed more than 1 million people and saw Iran send waves of lightly armed troops into minefields and the fire of Iraqi forces, including teenage soldiers. Soleimani’s unit and others came under attack by Iraqi chemical weapons.
After the Iraq-Iran war, Soleimani largely disappeared from public view for several years, something analysts attribute to his wartime disagreements with Hashemi Rafsanjani, who would serve as Iran’s president from 1989 to 1997.
But after Rafsanjani, Soleimani became head of the Quds Force. He also grew so close to Khamenei that the Supreme Leader officiated the wedding of the general’s daughter.
Soleimani oversaw the IRGC’s foreign operations and soon would come to the attention of Americans following the 2003 invasion of Iraq and the overthrow of Saddam Hussein.
In secret US diplomatic cables released by WikiLeaks, US officials openly discussed Iraqi efforts to reach out to Soleimani to stop rocket attacks on the so-called Green Zone in Baghdad in 2009.
At the peak of his power, Soleimani ruled over roughly 20,000 Quds Force members. However, it could also use forces from the IRGC and Basij in case of emergencies.
In addition, Soleimani technically commanded fighters from militias that Iran supported and helped create. He also hired fighters from many countries, including Afghanistan, to fight as proxies.
The Quds Force provided deadly, sophisticated bombs such as improvised explosive devices (IEDs) that killed many civilians and non-civilians, including Iraqis and Americans. In a 2010 speech, US Army General David Petraeus recounted a message from Soleimani he said explained the scope of Iranian’s powers.
“He said, ‘Gen. Petraeus, you should know that I, Qassem Soleimani, control the policy for Iran with respect to Iraq, Lebanon, Gaza and Afghanistan,’” Petraeus said.
The US and the UN put Soleimani on sanctions lists in 2007, though his travels continued.
In 2011, US officials also named him as a defendant in a Quds Force plot to allegedly hire a Mexican drug-cartel assassin to kill Adel Al-Jubeir, then Saudi Arabia's ambassador to the US.
Before Soleimani's luck ran out on Friday, he was rumored dead several times. Those incidents included a 2006 airplane crash that killed other military officials in northwestern Iran and a 2012 bombing in Damascus that killed top aides of Assad.
More recently, rumors circulated in November 2015 that Soleimani was killed or seriously wounded leading forces loyal to Assad as they fought around Syria’s Aleppo.
Soleimani’s actual killing followed a New Year’s Eve attack by Iran-backed militias on the US embassy in Baghdad. The two-day assault prompted Trump to order about 750 US soldiers deployed to the Middle East.
The breach at the embassy followed US air strikes that killed 25 fighters of the Iran-backed militia in Iraq, the Kataeb Hezbollah.
Iran has vowed to avenge Soleimani’s killing, with President Hassan Rouhani saying it would make Iran more decisive in resisting the US, and the IRGC claiming that anti-US forces would exact revenge across the Muslim world.
However, Randa Slim, non-resident fellow at Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced international Studies, believes retaliation now is easier said than done. She said in a tweet: “Iran will respond to US strike killing Soleimani. The only questions are: How soon, where & how?"
Slim herself offered an answer: “Soleimani was the principal linchpin in the Tehran-regional proxies space. With his demise, the reaction might take longer to organize and pull off.”






































