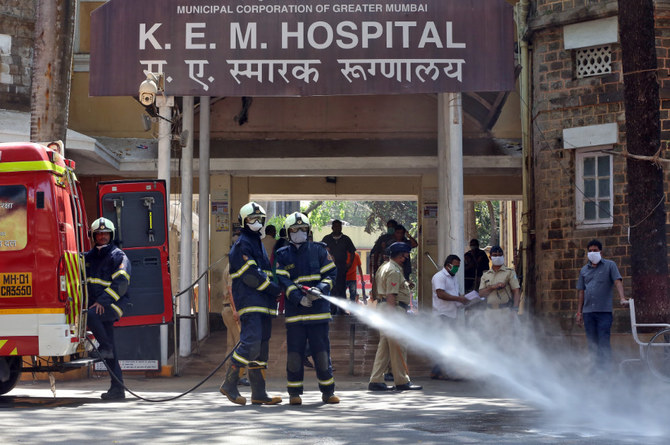
BENGALURU, India: As the coronavirus pandemic grips the world, a curious datum has emerged from the Indian subcontinent, where the world’s biggest national curfew is now in force.
India, the world’s second-most-populous country — and consistently, despite improvements, at the bottom of many global health indices — is doing better than 40 countries and a ship by the number of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infections, according to the latest World Health Organization (WHO) data.
Yes, a ship. On March 26, India’s official tally of confirmed cases reached 649 (with 13 deaths). That is fewer than the 712 cases reported in February on the Diamond Princess, a British cruise liner, and fewer than Saudi Arabia or even tiny Luxembourg.
The reason for this anomaly: India is just not testing enough of its 1.3 billion people. As of March 24, fewer than 22,000 Indians had been tested, or 16 per million, compared with 6,551 per million in South Korea, 4,917 per million in Italy or 244 per million in the US.
INNUMBERS
- 1.3 BILLION - India’s population
- 22 ,000 - Indians tested
- 649 - Confirmed cases
No one believes that India has 649 infections, not even its conservative government, which insists, contrary to the WHO, that there is no community transmission of the disease.
Cases are now doubling every five days and matching global trajectories. One recent prediction from a team of eight mostly government scientists says widespread community transmission “may take anywhere from a minimum of 20 days to a few months to be visible.”
But there is little question that the pandemic is unfolding, and India knows it: The largest global lockdown of any country began on March 22 and was scheduled to run 21 days.
A national curfew has grounded domestic and international flights and stopped all metro services, public transport and trains.
Thousands, perhaps millions of daily-wage workers frantically trying to reach home after Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the curfew were stranded, as trains and buses ground to a halt. Many started long treks on foot, trying to walk a few hundred miles home.
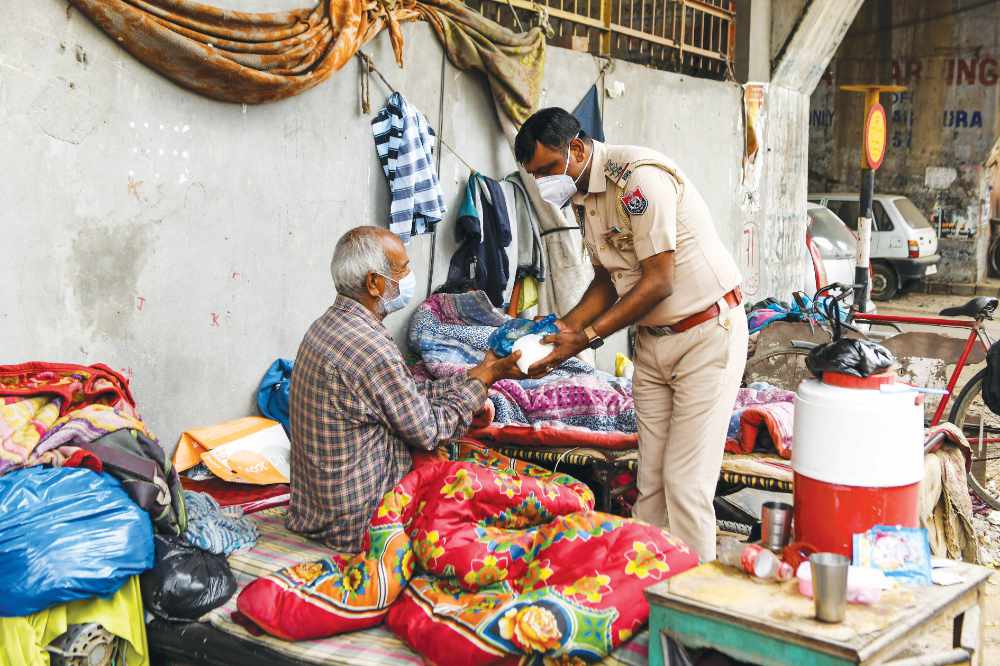

Police in Amritsar distribute food during the first day of a 21-day lockdown. (AP)
Aid workers and community organizers urged the government to start income-support schemes, open stadia and halls, and provide free food to the poorest, whose daily incomes have stopped.
But aside from a few states that have organized support programs, most of those stranded have been left to fend for themselves.
“India faces a formidable challenge not just in flattening the curve of infections, but also in sustaining a long halt to activities that keep millions employed and coping with a rapid increase in pressure on its weak medical infrastructure,” Ramesh Venkataraman, a private equity investor and former McKinsey & Co. partner, told Arab News.
“The government should welcome any offers of help, especially from the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) bloc, with whom New Delhi enjoys strong diplomatic, trade and strategic ties,” he added.
“India’s recovery, stability and continued economic expansion are of vital interest to the oil-exporting Gulf countries.”
For now, the great danger is that at the current infection rate, which counts only confirmed cases, India is poised to have one of the world’s largest burdens of a highly infectious disease that has no known cure.
One worst-case estimate says up to 300 million to 500 million Indians could be infected (the best-case scenario by the same expert is 200 million).
The numbers depend on whether India will follow the path of South Korea, which leveled the curve and held down deaths despite a high infection rate, or Italy, where the pandemic is raging with no signs of abating.
No Indian expert believes the South Korean model of aggressively identifying and quarantining the infected will work in a chaotic nation where testing is not expanding fast and people have routinely been jumping quarantine and infecting thousands — if not millions —since the first case was reported on Jan. 30.
The good news is that the large majority of these infections may be mild, but that will still leave 10 million with severe illness, said Ramanan Laxminarayan, director of the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy, a think-tank based in Washington DC.
Laxminarayan told an Indian TV network that this level of life-imperiling infections could perhaps be handled if they occurred over a year.
The challenge is that these infections are likely to be concentrated over a period of weeks —and that is not something India can handle.
Health officials and doctors take part in a hospital drill in Allahabad. (AP)
At the best of times, India’s health care system is in crisis. The country spent about 1.28 percent of its gross domestic product on health in 2018.
Saudi Arabia, by contrast, spent 5.74 percent in 2016, and the global average was 5.99 percent.
Up to 75 percent of primary health care in rural areas comes from what are officially called “informal-sector providers,” which means by those unqualified to dispense medical care, either under indigenous or allopathic systems. In other words, quacks.
As the COVID-19 pandemic plays out, India’s shortcomings will take many more lives. The most severe infections are likely to require intensive care and ventilators, which are in critically short supply in the country.
There is no accurate nationwide count, but ballpark estimates of ventilators range from 30,000 to 80,000.
“Even if we’re now able to procure or produce a large number (of ventilators) overnight, making sure they’re functional and operated properly is a huge challenge,” said Manoj Mohanan, associate professor of public policy, economic and global health at Duke University.
He is currently on a year-long sabbatical in India, where he continues to assist several states on issues related to health policy.
“An overarching problem though is that we just aren’t prepared to deal with the epidemic once it starts off in rural areas (where more than 800 million Indians live),” Mohanan told Arab News.
“(If) the common presenting symptoms of COVID-19 (cough, fever, shortness of breath) show up at these providers, we’ll face a ‘damned if they do, damned if they don’t’ problem.”
If any country has extra resources to help India at this point, said Mohanan, getting personal-protection equipment (PPE) would be top of his list because it is tangible and can be done.
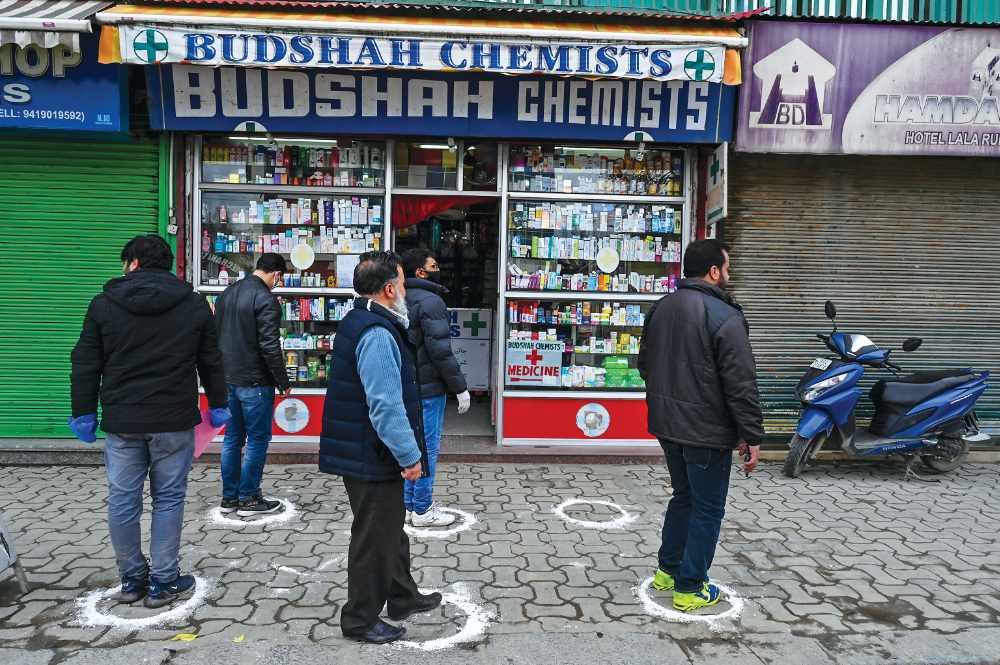

People stand on designated areas to maintain social distancing as they queue outside a medical store in Srinagar. (AFP)
Second would be supporting efforts to develop low-cost ventilators, successful deployment of which will require large-scale training and hand-holding to make these effective.
“One of the problems with disasters is a lot of people want to donate equipment or goods/supplies, but there’s no appetite to support staffing, maintenance and operation of the equipment (especially if it was given by someone else),” said Mohanan.
Doctors and other health workers are already reporting shortages of PPE — including hazmat suits and the highest-quality N95 masks — thanks in great part to government delays in stopping exports and ramping up production, despite warnings and alerts from manufacturers, experts and the WHO.
India’s third big requirement will be mobile intensive-care units, which are particularly important because of their scant presence in rural areas.
The poorest Indians will also require income support, as the economy endures a massive shock thanks to the 21-day curfew, during which millions will lose daily-wage jobs and migrant workers will return home.
“It will be months before their income streams are back,” said Mohanan. “The economic consequences of this crisis will be felt long after the virus is contained.”





























