DUBAI: Founded 72 years ago, with its headquarters in the Swiss city of Geneva, the World Health Organization (WHO) is responsible for promoting global public health, keeping the world safe and serving the vulnerable.
But as the new coronavirus disease (COVID-19) ravages the US and many other countries after originating in China and killing thousands there, the UN agency finds itself at the center of a heated argument, with both its credibility and financial health on the line.
Last week, US President Donald Trump fired the opening salvo when he announced he was going to halt US funding to the WHO pending further evaluation.
At more than $400 million, Washington’s contribution provided 15 percent of the WHO’s 2018-19 budget. By contrast, China, the second largest economy in the world, gave about $86 million during the same period.
The UN agency, which has 194 member states, stands accused by Trump of “severely mismanaging and covering up” the spread of the coronavirus, and of having failed in its basic duty.
In response, Dr Tedros Ghebreyesus, the WHO director-general, said the impact of a withdrawal of US funding will be reviewed and the help of the agency’s partners sought to fill “any financial gaps” and ensure “uninterrupted work.”
“The WHO is not only fighting COVID-19,” he said. “We’re also working to address polio, measles, malaria, Ebola, HIV, tuberculosis, malnutrition, cancer, diabetes, mental health and many other diseases and conditions.”
Ever since the epidemic appeared in China, Ghebreyesus, an Ethiopian microbiologist and the first non-physician and African in the role, has become the WHO’s public face, in the same way that Dr. Anthony Fauci, the US immunologist and long-time director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, has become “America’s doctor.”
However, simmering tension between the WHO and influential Republican lawmakers has put Ghebreyesus in an awkward position, with calls being made by policy pundits for his resignation.
Trump of course is hardly the first public figure to blame the WHO of failing to adequately assess the outbreak when it first emerged in the Chinese city of Wuhan.
Among the many actions of the WHO that have raised eyebrows is a tweet on Jan. 14 claiming that preliminary Chinese investigations had found “no clear evidence of human-to-human transmission” of the coronavirus.
WHO experts were not allowed to visit China and investigate the epidemic until the total confirmed cases in the country had crossed the 40,000 mark on Feb.10.
So, did the WHO cover up for China? Dr. Theodore Karasik, a senior advisor at Gulf State Analytics in Washington DC, feels both the WHO and China could have undoubtedly done a better job.
“Speed and efficiency are two words that were not practiced at the beginning of the outbreak,” he told Arab News, alluding to the WHO’s many contentious public statements and tweets during the initial stage of the pandemic.
“Not only was the WHO behind the curve because of its refusal to describe COVID-19 as a pandemic, but China is also at fault (for) attempting to cover up the extent of the outbreak.”
He said China “absolutely” should have restricted travel sooner, but other countries as well should have taken preventive measures.
“There is plenty of blame to go around,” Karasik said. “Once again the world is reacting instead of being proactive.
“Funding for the WHO is key at the moment because of the global health emergency. Bureaucratic problems can be taken care of after the crisis is over.”
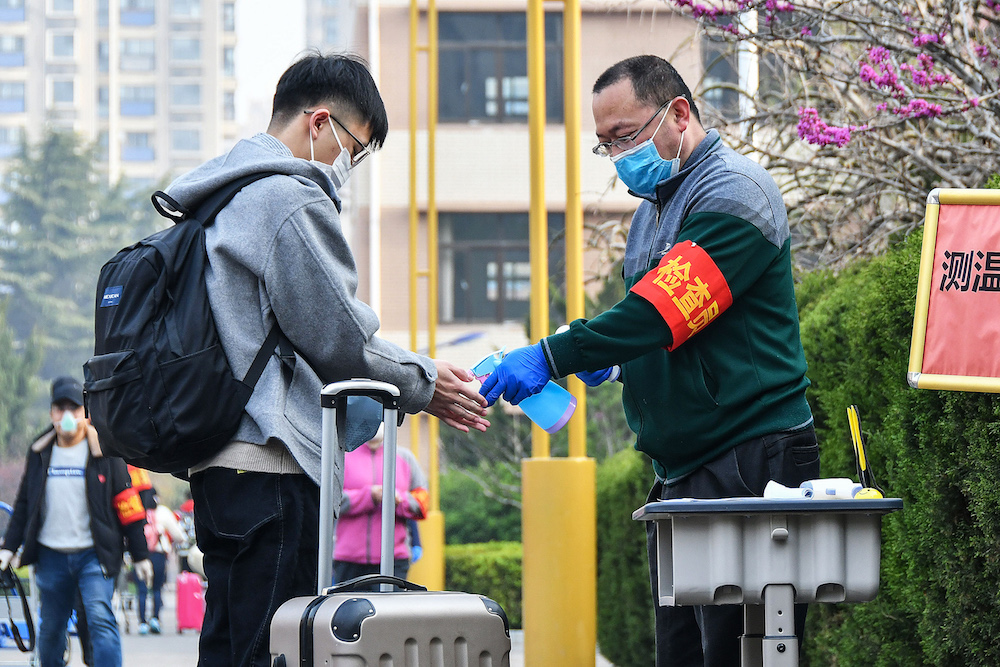

A staff member checks the body temperature of a student at the entrance of a school as students return to school after the term opening was delayed due to the COVID-19 coronavirus outbreak. (AFP)
Once that time arrives, Karasik said, the world could focus on how to restructure the WHO, how to define a pandemic and how to make the UN agency more efficient.
Whether US politicians are willing to hold their fire until the coronavirus storm has passed is an open question, though.
Michael Singh, managing director of the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, said there was a firm consensus in the US capital that China failed to act on early indications of a brewing outbreak, and even took steps to suppress the information.
“While other governments were also slow in marshaling their responses, China’s failure is singular in that it may have cost the world the chance to avert this pandemic altogether by halting the virus spread before it began,” he told Arab News.
“There is far less agreement in Washington and internationally, however, regarding to what extent the WHO should share any blame apportioned to China, though certainly the WHO did itself few favors with its frequent, florid praise for Beijing in forums like the WEF (World Economic Forum) and elsewhere.”
But is cutting WHO funding the best choice at this point of time for the US?
In Singh’s opinion, what is needed is a critical assessment of the WHO’s performance in addressing the COVID-19 outbreak in China and a determination of what reforms Washington and other donors should demand in light of the pandemic.
However, he added: “It will be difficult to gain international support for this amid the pandemic, when most governments — including key US allies whose support would be needed for such an effort — are focused first and foremost on halting the virus’ spread and mitigating its economic impact.”
Indeed, many experts are questioning the wisdom of Trump’s decision to cut funds to the WHO just when it has issued an appeal for $675 million to help battle the pandemic.
“It is unfair to blame one side or the other before an investigation is carried out into the matter,” said Ahmed Al-Astad, a scientific adviser at TRENDS Research & Advisory, an Abu Dhabi-based think tank.
“It is difficult to believe that the WHO covered up, even though it may have been slow to respond. This pandemic caught everyone by surprise, and it is this lack of preparedness that should be blamed.”
But should the WHO have supported travel restrictions much earlier than it did?
In Al-Astad’s view: “The US, China, the WHO, and a lot of other countries around the world were caught unprepared. The blame game seems to be more out of frustration than any concrete evidence.”
As the pandemic continues to cause global havoc, in hindsight “travel restrictions (in China) should have been implemented a little earlier,” according to Al-Astad.
“That would have really helped considering the tremendous amount of connectivity around the world today and there is no other way to stop the spread of this virus. Even if this was done a week earlier, things could have been different.”
While China could have done a better job, the virus quickly spread far and wide, and some countries, especially in Europe, could not prepare themselves adequately, according to Al-Astad.
“I don’t think it would have made much difference if some of these countries learned two weeks or a month before China revealed the details,” he told Arab News.
“On the other hand, there are examples of countries that reacted quickly and saved their people from a major health crisis.
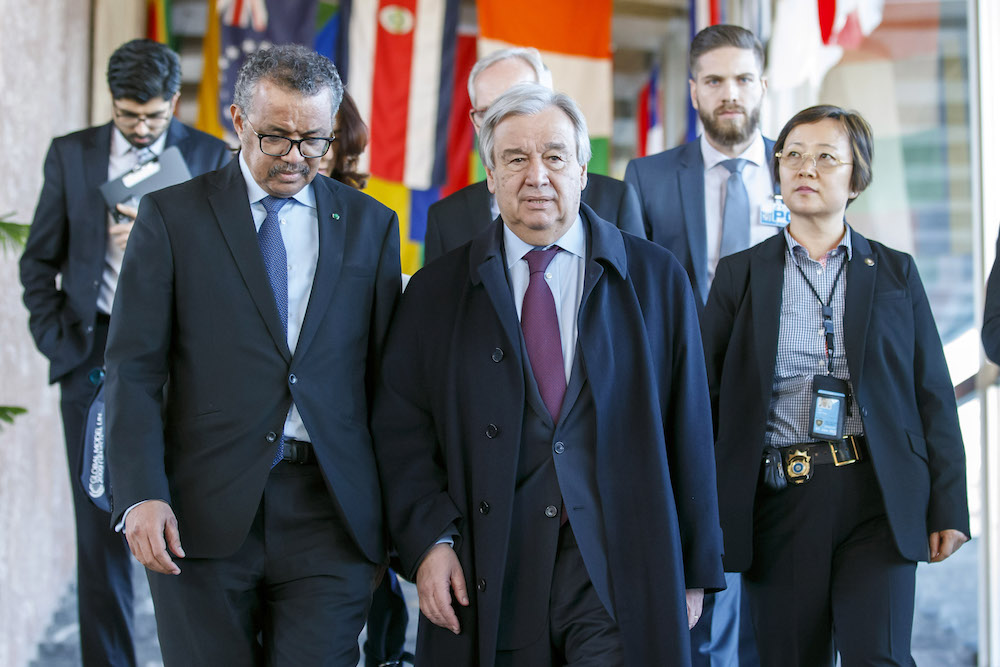

Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus (L) Director General of the World Health Organization (WHO) and UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres (R) arrive to attend an update on the situation regarding the COVID-19. (AFP)
“The UAE, for instance, imposed a lockdown in time and prevented the virus from spreading very rapidly.”
Whatever the best course of action may be, Al-Astad said cutting funding to the WHO could push it “deeper” into China’s grip.
“The WHO is a global body and its performance, or lack of it, should not be seen from the prism of one country’s reaction,” he said.
“The need of the hour is to strengthen the funding and resources of the WHO, not the other way round.”