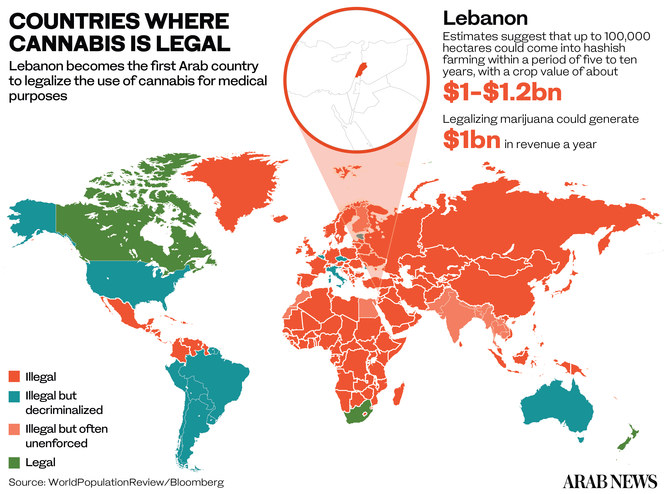
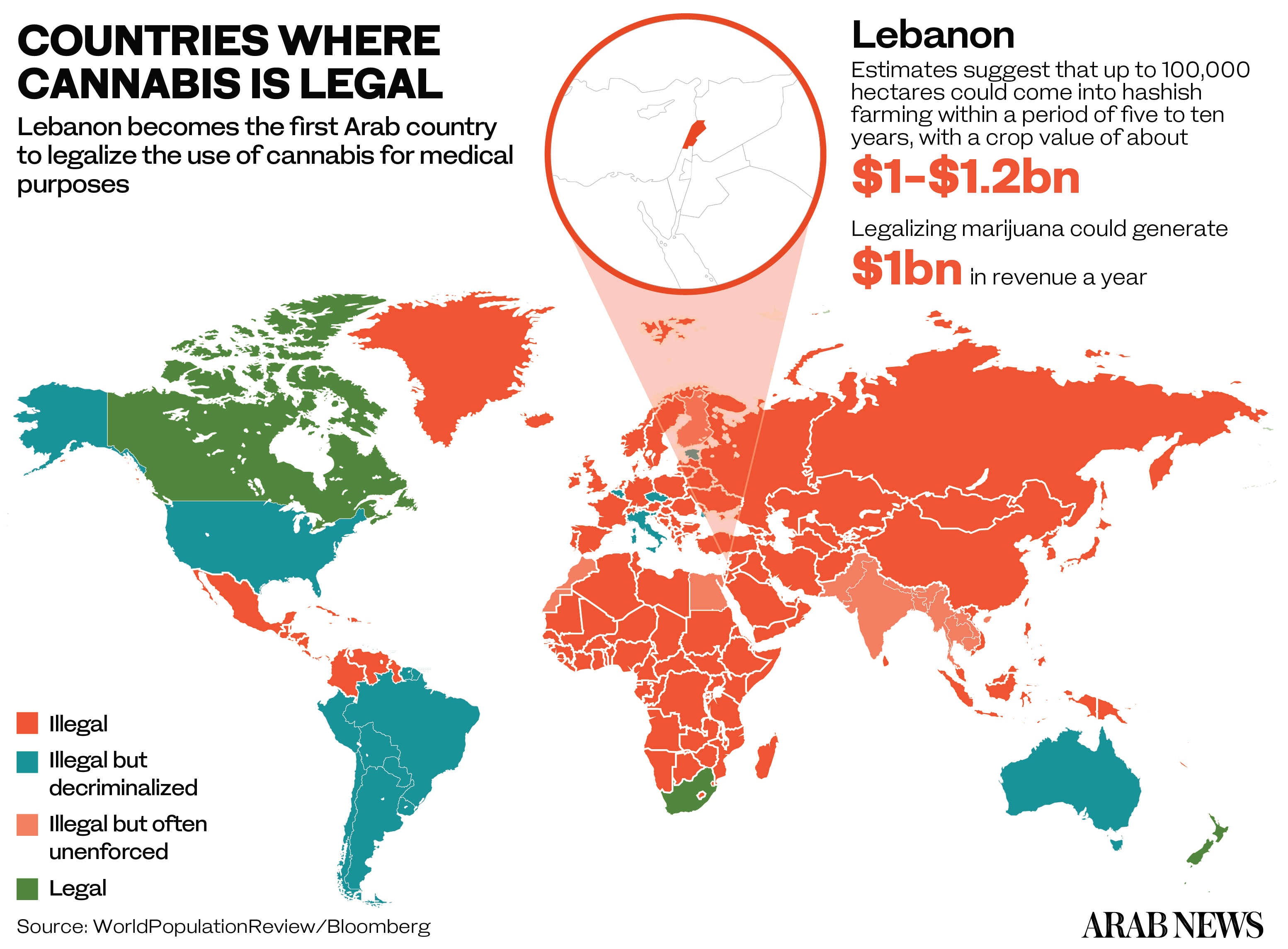
DUBAI: The international media’s blanket coverage of the COVID-19 pandemic was interrupted on Tuesday by breaking news about Lebanon becoming the first Arab country to legalize cannabis for medical and industrial use.
Experts from different fields have welcomed the decision in light of Lebanon’s manifold problems compounded by the coronavirus crisis — but with big caveats.
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the cannabis plant used primarily for recreational or medical purposes.
Until now, Lebanon had banned the growth, sale and consumption of cannabis, even though legalization of production had been recommended in the past.
However, attitudes began to shift after the US consulting firm McKinsey & Company touted the legalization of cannabis in a study on how the government could revitalize the economy.
In 2018, the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) ranked Lebanon in the world’s top five producers of cannabis.
Last year, Raed Khoury, Lebanon’s minister of economy, said medicinal marijuana exports could generate $1 billion in annual revenue for Lebanon.

A supporter of cannabis legalization demonstrates outside of the Charleston Gaillard Center ahead of the Democratic presidential debate on February 25, 2020 in Charleston, South Carolina. (AFP/File Photo)
For a country with one of the highest debt-to-GDP ratios in the world, the industry’s potential for revenue generation can hardly be glossed over.
Among those expressing guarded optimism is Dr. Nasser Saidi, a former chief economist at the Dubai International Financial Center who was Lebanon’s minister of economy between 1998 and 2000.
The move to legalize marijuana for medical use makes a great deal of sense for Lebanon, he said, noting that the country has long been a producer of hashish.
“In particular, the crop has helped the poorer areas of Lebanon, mainly the Bekaa Valley, and allowed agriculturalists to survive because many of their other crops aren’t necessarily exportable,” Saidi told Arab News.
“For the more traditional crops like potatoes, beetroot, olives and others, there is a lot of competition, whereas for hashish there is much less competition.
“Lebanon can build its reputation as a source of quality hemp. Medicinal marijuana in particular can be an important high-value export product.”
Saidi draws a parallel between Lebanon’s decision to decriminalize cannabis production, manufacturing and its use with the policies of some advanced industrial countries.
Pointing out that the US and Canada have legalized use of marijuana, hemp and hashish without any negative fallout, he said: “There is no reason why Lebanon should not be able to successfully and securely decriminalize hashish.”
Saidi’s guarded optimism is echoed by Cyril Widdershoven, a director at Verocy, a Dutch consultancy which advises on investments, energy and infrastructure risks and opportunities in the Middle East.
He believes conditional legalization could be a step towards taking out the middlemen and halting the illegal trade.
“If this is meant to be the main target, some support should be extended to the decision,” Widdershoven said.

A file photo taken on July 23, 2018 shows workers cultivating plants at a cannabis plantation in the village of Yammouneh in Lebanon's eastern Bekaa Valley. (AFP/File Photo)
“For a government, it can be very positive as it will bring, if properly regulated, additional taxes and income. Some amount of crime will get checked, though not all.”
Nevertheless, Widdershoven said much will revolve around how Lebanon defines “medical purposes.”
He said: “Is medical use the real objective or is it just a legal option to introduce cannabis in the open, without coming into conflict with other laws and regulations?”
According to Widdershoven, “income from taxes is obviously a potential benefit, but Lebanon will need to introduce a system that can control and manage production, transport, sale and taxation.
“Without it, cannabis legalization for medical and industrial purposes is going to give rise to a semi-legal grey area.”
Similarly, Saidi, who served as vice governor of the Central Bank of Lebanon for two terms, said the new law should not amount to control of the business by Lebanese politicians.
“Hashish growers are afraid that legalization means the industry will come under the control of a government-licensing administration or body, which could then be open to abuse, corruption and clientelism,” he told Arab News.
“They will tell you they fear that licensing will be monopolized by politicians and their cronies, enabling the latter to control the production, distribution and export of hashish — to the detriment of the growers.”
Saidi said legalization should mean decriminalization with a light regulatory structure but not a strict licensing system.
“You cannot, in a country with Lebanon’s corruption levels, institute a system for the farming, manufacturing and distribution of hashish that can be monopolized by the state or captured by a corrupt political class and its cronies,” he said.
“The government can play a role in terms of ensuring the quality of medicinal hashish, particularly for export purposes, and monitoring for statistical, public-health and taxation purposes. But I would not favor a strict physical licensing system.”
Saidi sees a lot of hype surrounding the economic dividend of cannabis legalization.

A cannabis plant is seen during the opening of a cannabis (marijuana) clinic at the Department of Development of Thai Traditional and Alternative Medicine in Bangkok on January 6, 2020. (AFP/File Photo)
According to one estimate, up to 100,000 hectares could come into hashish farming within a period of five to 10 years, with a crop value of $1 billion to $1.2 billion.
But Saidi does not see income from the crop as something that can put Lebanon’s public finances on a sustainable footing.
“We should allow producers to switch crops away — from low value-added crops like potatoes and sugar beet — to go into hashish, (as) it would help some of the poorest of the poor in Lebanon who eke out a subsistence income from agriculture,” he told Arab News.
“But it’s not a problem solver for the Lebanese government.”
Said added: “You can impose a tax, which is fine. Hashish consumption could be subject to VAT for local consumption to generate revenue for government, or to a production tax at a low rate.
“But again, I am not in favor of a licensing system to raise revenue because of the potential of corruption and bribery.
“Effectively, a licensing system would mean a highly inefficient regime for the benefit of politicians at the expense of growers. Licensing would become another form of political clientelism.”
An expert on Lebanon’s recreational drugs trade, who asked to remain anonymous, told Arab News that cannabis legalization was smart from the standpoint of Lebanon’s parlous economic situation and public finances.
However, he added, making cultivation of the plant legal is one thing while enforcement of the law without fear or favor is quite another.
He pointed out that Lebanon is the third-largest exporter of hashish after Afghanistan and Morocco, accounting for six percent of the world’s illegal supply of the drug, according the UNODC in 2012.
“This has made many people in Lebanon rich and powerful, specifically in the Bekaa Valley, where most of the cannabis is grown,” he said.
He wonders whether legalization will open opportunities for newcomers to enter the business or further enrich the players and politicians who control the business.
The anonymous expert said that he was unsure of the contours of a long-term strategy to decriminalize cannabis inside Lebanon for commercial purposes.
“These are basic questions that must be addressed if the legalization move is to make a positive impact on the economy,” he said.
Citing the tobacco industry as a cautionary tale, he said all Lebanese producers are required to sell only to government-approved authorities that produce and sell cigarettes, such as the Régie Libanaise des Tabacs et Tombacs.
“The risk is that the same situation could arise with cannabis. An element of corruption can completely wipe out the positive impact,” he said.
In his opinion, the Lebanese government wants a piece of the pie with the global legal cannabis market tipped to reach $103.9 billion by 2024.
“One can only hope that the Lebanese government transforms cannabis cultivation into a diversified income stream, with scope for local industries such as medicine, pharmaceutical, textile, wellness, and even tourism to flourish,” he said.
“But all this may be too much to ask given previous the government’s track record in other sectors.”
---------
THE BIGGEST CANNABIS PRODUCERS AND CONSUMERS
Mexico: Medical marijuana was legalized in 2017. The legalization of the drug for recreational purposes is expected to take place by April 30, 2020. According to Arcview and BDS, recreational marijuana sales in Mexico are expected to reach $582 million by 2024, with an additional $441 million in medical spending, for a combined $1.02 billion.
United States: Marijuana is legal in 11 states for adults over the age of 21 and legal for medical use in 33 states. The US marijuana industry’s economic impact is predicted to reach $77billion by 2022, according to Marijuana Business Factbook, while studies estimate the industry will produce at least 330,000 jobs by 2022.
Canada: In 2018, Canada become the second country in the world to implement legislation to permit a nationwide marijuana market. By the end of August 2019, cannabis inventories across the country had reached almost 400 tons. In total, 5,884,055 packaged units of cannabis were sold across the country for medical and non-medical purposes in 2019.
Paraguay: The principal producer of cannabis in South America legalized cannabis for medicinal use in 2007. However, the proposed framework for implementing a medicinal cannabis industry was not approved until 2018. That year the government opened licensing opportunities for businesses looking to cultivate cannabis for medicinal purposes in the country. The Senate also approved a separate bill permitting the personal growth of cannabis for medical use, provided users present authorized certificates.
Jamaica: Since decriminalizing marijuana in 2015, Jamaica now allows citizens to grow up to five cannabis plants, while the possession of two ounces or less has been downgraded to a petty offence. According to the US State Department, Jamaican farmers cultivate 15,000 hectares of cannabis every year. The government has also granted licenses to farmers who want to grow cannabis for medical, therapeutic or scientific purposes.
Morocco: According to a report released by the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Morocco remains the world’s largest producer of cannabis, producing over three times more than the next highest contender, Moldova. The report suggested that cannabis production in the country has continued to grow, showing an increase from 35,653 tons in 2016 to 35,703 tons in 2017.
Nigeria: Nigeria has the highest cannabis usage worldwide with 20 million users. It is estimated that 20.8 million people in Nigeria consume the illegal commodity every year in a market estimated at $15.3billion. Two reports have stated that Nigeria has the highest rate of cannabis use in the world with 19.4 percent of its population over the age of 15 consuming the drug in 2019, and at least 12 percent consuming it monthly.
United Kingdom: The country was declared the world’s largest producer and exporter of medical cannabis by the UN’s International Narcotics Control Board in 2018. According to the International Narcotics Control Board (INCB), 95 tons of marijuana was produced in the UK in 2016 for medicinal and scientific use, accounting for 44.9 percent of the global total. The cannabis-based medicine ‘Sativex’ accounts for a significant proportion of UK legal cannabis production and is available on prescription.
Afghanistan: Over 10 years ago, Afghanistan was the largest supplier of cannabis, estimated at 1,500-3,500 tons a year, according to a UNODC report. Between 10,000 and 24,000 hectares of cannabis are grown every year in Afghanistan, with major cultivation occurring in 17 out 34 provinces.
India: In 2019, buyers in Delhi and Mumbai purchased 38.3 tons and 32.4 tons of cannabis respectively, despite the drug being illegal in these cities, according to data released by the Berlin-based data firm ABCD. Cannabis is sold at Rs315 per gram in Delhi and Rs329 per gram in Mumbai, which are the cheapest rates globally, says the report. In 2017, Uttarakhand became the first Indian state to allow farmers to cultivate hemp plants for industrial purposes. The drug is believed to have been sold and consumed across the country for decades.