LAHORE: In March, when Pakistan had reported less than 2,000 cases of the novel coronavirus, one of the country’s largest cancer hospitals cleared up its wards of non-essential traffic and propped up a makeshift camp in its parking lot.
Overnight, there were new rules. All incoming patients – old and new – had to be screened for fever and flu-like symptoms every single day. No one, not even the medical staff, was allowed inside the Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital (SKMCH) in Lahore without a thorough check-up.
Next, the building was divided into colored zones – red, yellow and green. Red was classified as a high-risk area, where a new, 50-bed isolation ward was rolled out for COVID-19 patients.
In a matter of days, the hospital took drastic measures on a war-footing to protect the most vulnerable – its cancer patients.
By mid-March, as the number of coronavirus cases gradually increased in the country, SKMCH, founded by Prime Minister Imran Khan in honor of his late mother, was already preparing for the worst. It paced through back-to-back surgeries that month, anticipating a countrywide lockdown.
The government announced a lockdown late in March, and within two weeks, the hospital had resumed operational procedures again. Nothing could be put on hold for too long. Even as COVID-19 continued to spread in Pakistan, officials told Arab News the hospital did not, for a single day, cancel chemo for its cancer patients, some of whom were young children.
“These days there is lots of testing, screening, cleaning and spacing out,” Dr. Muhammed Aasim Yusuf, the chief medical officer at the hospital, told Arab News. “It is all very labor intensive work.”
The hospital was launched in 1994 by the then retired cricketer Imran Khan who had yet to enter the political arena. It remains one of Pakistan’s most celebrated medical institutions and a benchmark for quality and efficiency in a country where health sector is in a shambles.
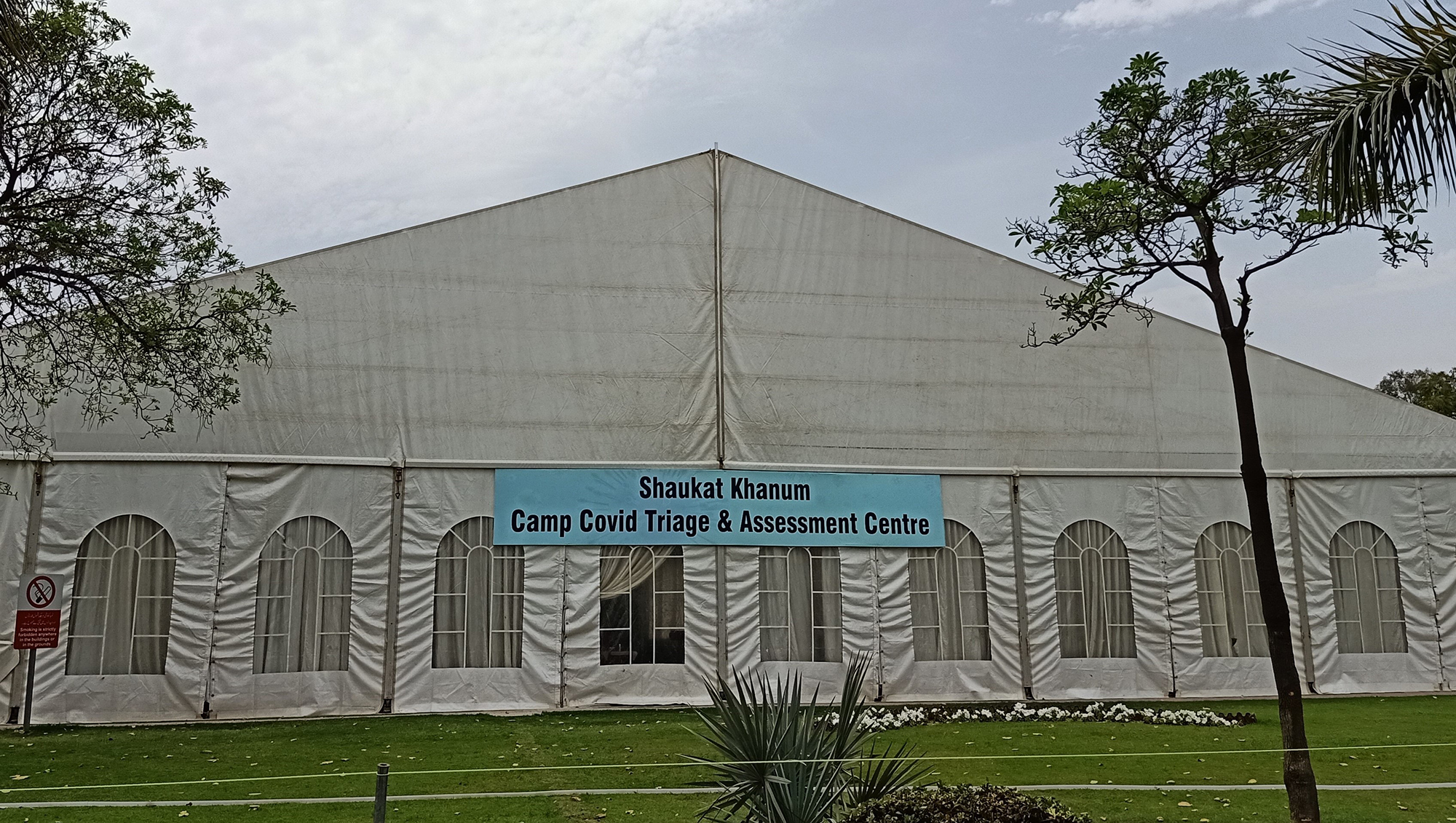

This is the undated photo of Camp COVID-19 that was recently set up in the parking area of the Shaukat Khanum hospital in Lahore to screen all patients entering the building. (Picture Courtesy: SKMCH)
Two decades later, however, it is in the midst of two battles – against cancer and coronavirus. And the struggle to save patients is only getting tougher by the day.
At its outdoor camp in Lahore, over 200 patients walk in every day. Around 40 percent of those feel they have COVID-19-like symptoms, say hospital staff.
The virus poses a greater health risk to those with weak immune systems, such as people receiving cancer care. According to the US-based National Comprehensive Cancer Network, a preliminary report from China showed that patients with cancer, who were later infected with COVID-19, have a three times higher chance of being put on a ventilator, admitted to an ICU, or of dying compared to patients without cancer.
Patients undergoing cancer treatment also have to make frequent hospital visits, which leaves them most exposed to the highly contagious illness.
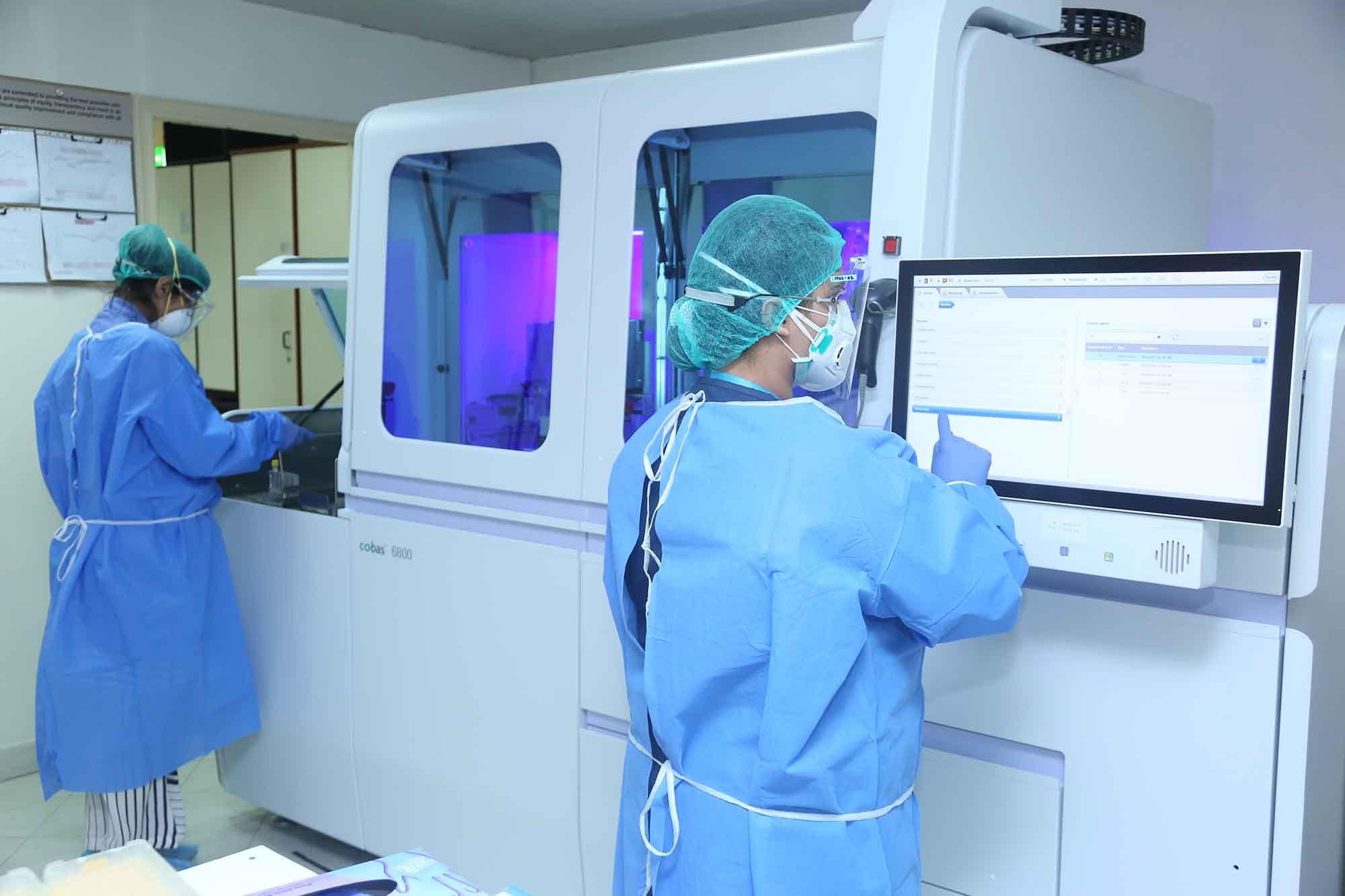
This undated pictures captures the view of the testing laboratory for coronavirus at the Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital. (Picture Courtesy: SKMCH)
At SKMCH, five people have died of the deadly disease, of which three were diagnosed with cancer, explains Dr. Aasim Yusuf. “For highly immunocompromised patients, the symptoms of [coronavirus] can also be masked,” he added. “So patients with very low immunity might not develop fever, for instance.” This makes it difficult for health care workers to detect the virus early on.
Inside the wards, pressure is only mounting on the over 3,000 hospital staff.
“Our staff is very stressed,” the chief medical officer said. “All our doctors and nurses are now working 13-hour shifts rather than the usual eight-hour ones.”
To date, 45 health care workers at the hospital have tested positive for COVID-19, reveals the doctor.
And SKMCH isn’t just caring for patients. It is also testing them for coronavirus, which has further increased the workload at its research center. Walk-ins at the hospital receive a free-of-cost diagnoses, while those who choose to be tested at its private laboratories, dotted around the country, have to pay.
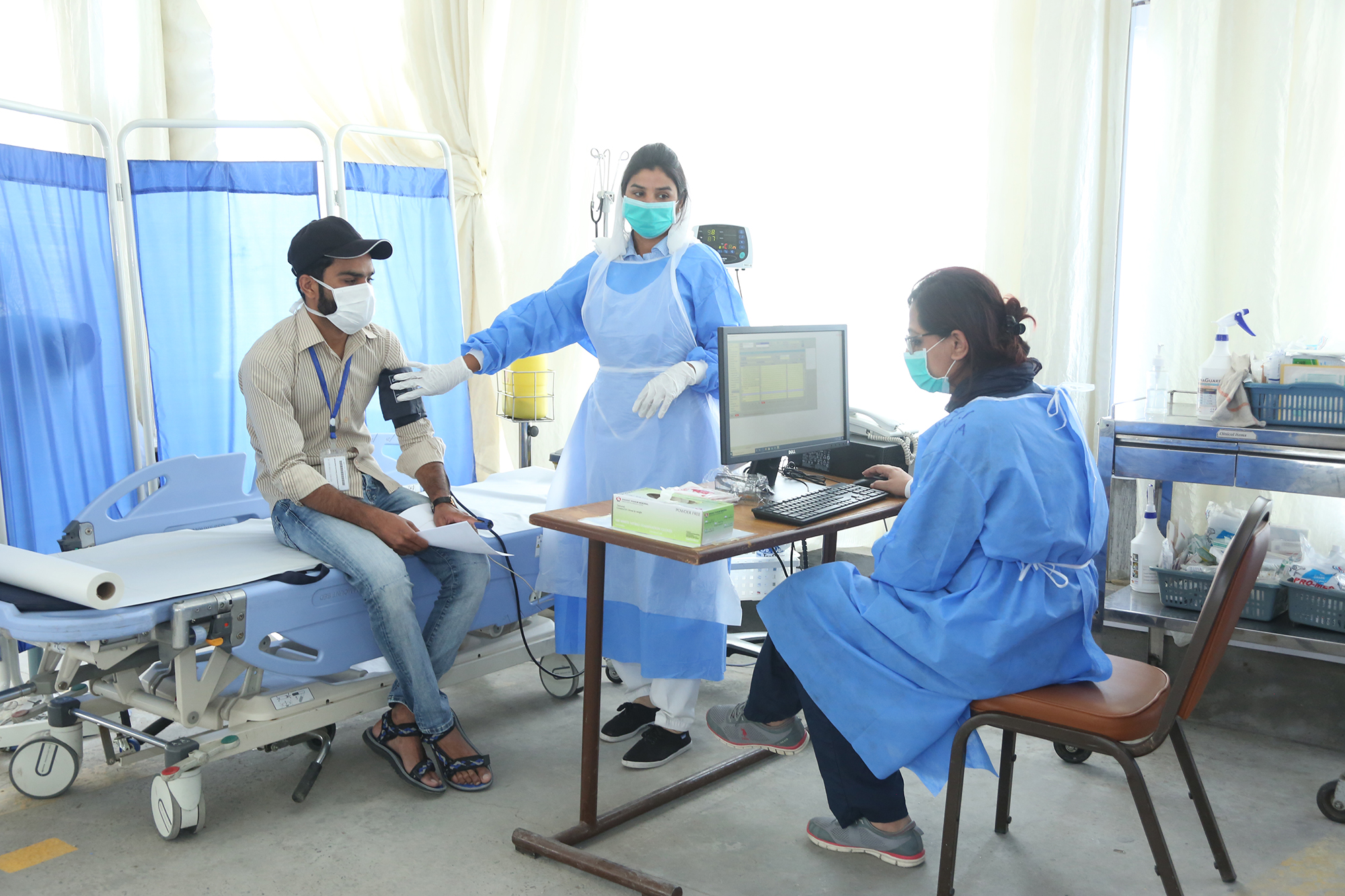

In this undated picture, nurses examine a patient at a temporary camp at the Shaukat Khanum Hospital in Lahore for coronavirus symptoms. (Picture Courtesy: SKMCH)
From late January to date, it has carried out over 5,200 tests from the Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa provinces, of which 88 percent were tested pro bono. Some of the test kits were provided by the federal government, nearly 2,300, while others were procured by the hospital on its own. As of now, the hospital has a testing capacity of 21,000 per day.
Built with the support of donations, the administration says that by testing some patients free of charge it is giving back to the country.
“We are a national institution,” Dr. Yusuf told Arab News. “We have been supported by the public for close to 30 years. It was our responsibility to step up and do what we can for [COVID-19] patients.”
Despite the emergency measures, there is one other problem.

This undated photo captures the general view of the Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital building in Lahore. (Picture Courtesy: SKMCH)
The hospital’s largest facility is in the city of Lahore, which is fast becoming the epicenter of the coronavirus in Pakistan, according to Punjab’s minister of health. A recent World Health Organization report on COVID-19 situation in Pakistan, dated May 1, notes that 26 percent of the total coronavirus positive cases were recorded in Lahore alone.
“These days you just don’t know what to expect when you walk into the hospital,” says Dr. Haroon Hafeez, the director quality and patient safety department. “Lahore is such a high-risk area now.”
Earlier, when the hospital started screening patients for coronavirus, they were given a questionnaire which included queries about international travel. But of late, with the increase in local transmission, over 80 percent in Pakistan, the questions have changed.
“Now we have altered our question forms to not just ask about symptoms but also if [the person] lives in Lahore. This is one of the biggest changes to have happened,” explained Dr. Hafeez.
Other doctors, too, expressed their concern.
“I’m fairly resigned to the fact that I’m going to catch the virus at some point. I think most of us at the hospitals are,” Dr. Yusuf said while sitting at his office in Lahore. “But at the end of the day our first priority is to protect our patients, who are the most vulnerable.”
















