DUBAI: For all its hydrocarbon wealth, the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region suffers from a fundamental scarcity, namely of underground renewable freshwater resources.
The region, one of the most water-scarce places on the planet, has some of the lowest water-availability levels on a per-capita basis.
Desalination dependence in the region is therefore high, even though desalination processes have a direct impact on the issue of sustainability and renewable-energy portfolios of these countries.
Data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) show that two-thirds of the water produced from seawater desalination in the region are, at present, from fossil fuel-based thermal technologies.
The rest is derived from membrane-based desalination, which relies heavily on electricity produced by burning natural gas.
Currently, the Middle East accounts for roughly 90 percent of the thermal energy used for desalination worldwide, with the UAE and Saudi Arabia at the helm.
To satisfy the drinking-water requirements of the region’s 400 million-plus people, a high reliance on non-conventional water resources such as desalination and the reuse of treated wastewater is “imperative,” Waleed Zubari, coordinator of the Water Resources Management Program at the College of Graduate Studies in Manama, Bahrain, told Arab News.
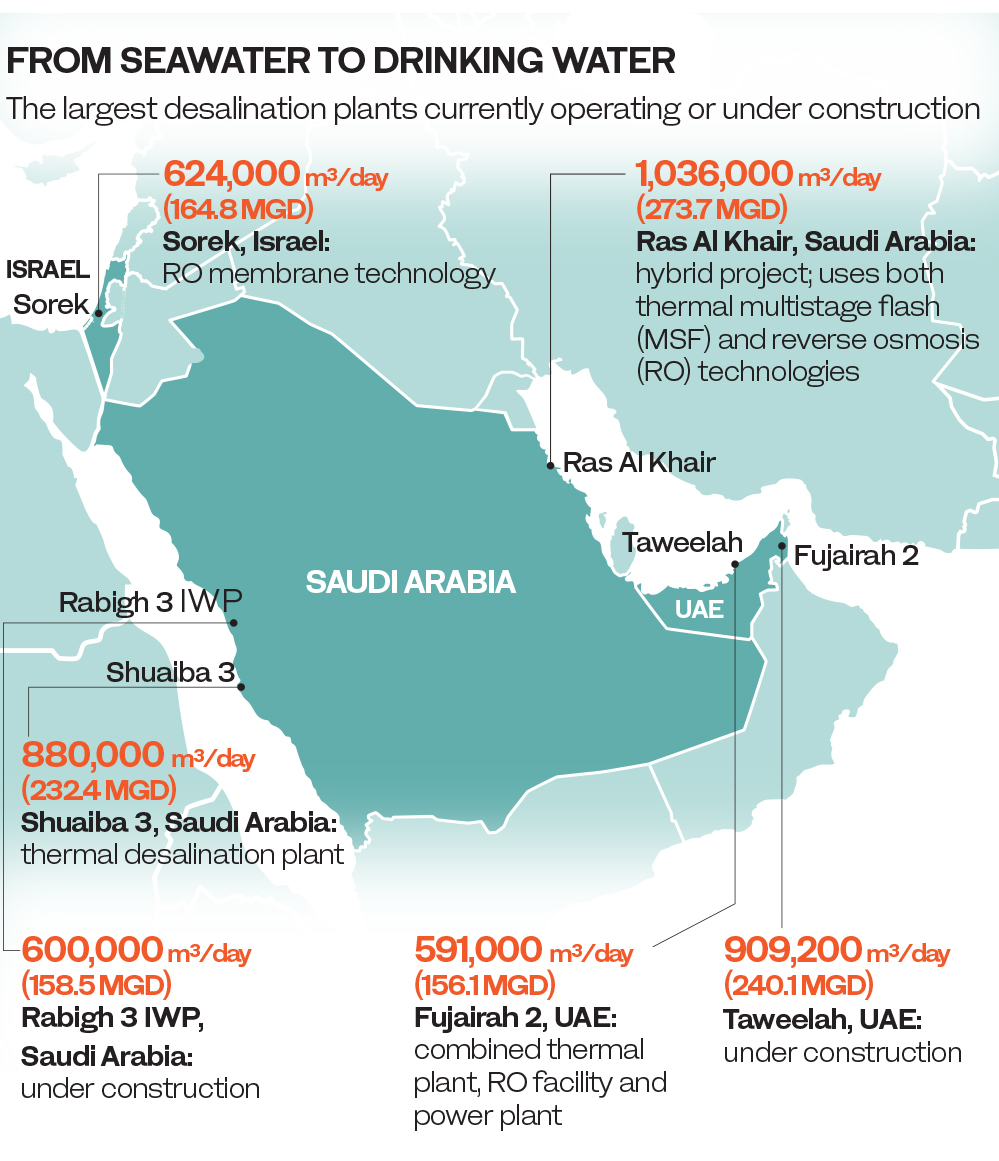
In fact, desalination becomes the only viable source for drinking water as the reuse of treated wastewater is increasingly being used for agriculture and landscaping, he said.
But the widely used desalination process based on fossil-fuel technology is an economic and environmental burden for countries with a high reliance on hydrocarbon revenues.
“Can we have sustainable water supply by desalination? Alternatively, can we have sustainable desalination?” asked Zubari.
Desalination, particularly co-production technologies that produce electricity and water as by-products, is an “energy intensive” process that claims at “alarming rates” a sizable portion of the energy resources in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, he said.
Despite a “tremendous decrease” in the cost of desalination over the decades, the practice is causing the fast depletion of the region’s energy resources and threatening the very source of some countries’ income, he added.
The way forward is to look beyond the deployment of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels to produce desalinated water.
FASTFACT
Desalinated water production in the Middle East is expected to grow almost 14-fold by 2040. (World Energy Outlook)
According to a special report in the World Energy Outlook series, “Outlook for Producer Economies,” for resource-rich economies “the high reliance on hydrocarbon revenues, coupled with the risk of fluctuations in prices, creates well-known pitfalls.”
However, the report noted, in response to changing conditions and the growing emphasis on renewables, “many major producers are displaying a renewed commitment to reform and economic diversification.”
The World Energy Outlook series examined six resource-dependent economies that are pillars of global energy supply: Iraq, Nigeria, Russia, Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Venezuela.
It assessed how the prospects for these major oil- and gas-producing economies will evolve in various scenarios by 2040.
The production of desalinated seawater in the Middle East, the report said, is projected to increase almost 14-fold during this period.
Globally, too, water desalination as a source of freshwater supply has become a major priority due to rapid population growth, poor water-management practices and global warming. The latter is believed to be decreasing annual rainfall by 20-40 cm.
To meet these challenges, there is “a concerted shift towards membrane-based desalination,” the report said.

Desalination, particularly co-production technologies that produce electricity and water as by-products, is an energy intensive process. (AFP )
Membrane-based technologies use electricity as the driver for desalination. For example, “reverse osmosis (RO) technologies” in membrane-based processes account for 60 percent of the capacity in Oman and roughly half the capacity in Saudi Arabia.
The Saudi state-owned Water and Electricity Co. is currently developing the Rabigh 3 project, which is expected to come on stream in 2021, with the potential to become one of the largest membrane-based seawater-desalination plants in the world.
The need of the hour, according to Zubari, is to achieve a degree of sustainability for desalination, which he said depends on countries “minimizing associated costs and maximizing desalination’s added value in the region.”
He believes this can be done through investment and ownership of desalination technologies, and urges governments to increase water conservation and decrease water waste and loss.
“One of the main options is the development of renewable energies to power desalination plants, particularly solar energy, in which the GCC countries have a comparative advantage,” Zubari said.
His view is seconded by Dr. Emad Yousef Alhseinat, assistant professor of chemical engineering at the UAE’s Khalifa University.
Energy sustainability is key to achieving sustainable desalination, said Alhseinat, adding that to achieve this objective, GCC countries have to diversity their energy sources to include renewable forms such as solar, wind and wave.
“And to get sustainable desalination processes, we need to invest in developing desalination technologies that are compatible with renewable energy,” he said.
According to Alhseinat, desalination processes, whether classified as thermal or membrane-based, require large amounts of energy to produce fresh water.
For example, “in RO processes, there is a need to reach a pressure of 50-80 bar to desalinate salty water,” he said, adding that this “high pressure” requires big pumps of water that consume large amounts of energy.
In short, he said, this process is “energy intensive, meaning high-cost, low-economic impact and high-carbon footprint.”
Another way to improve desalination in the region, added Alhseinat, is to allocate more investments to research and development in order to enhance the efficiency of current desalination plants.

This picture taken on December 11, 2019 shows a view of Jubail Desalination Plant at the Jubail Industrial City in Saudi Arabia's Eastern Province overlooking the Arabian Gulf. (AFP file photo)
“This can be done through adopting state-of-the-art optimization tools such as data mining and machine learning,” he said.
Applying artificial intelligence to analyze desalination data could also be a promising approach, according to Alhseinat.
Another important aspect of the desalination debate is its impact on the ecosystem. Injecting the hypersaline brine, or the waste stream of desalination plants, into the ground is harmful to the marine environment, particularly in the Arabian Gulf, said Alhseinat.
He believes a “zero-liquid discharge approach” could be developed to reduce the environmental impact.
Highlighting the dependence of the Middle East, indeed the world, on desalination technologies is the fact that there exist approximately 18,000 commercial desalination plants in operation internationally, with total installed production capacity of 86.55 million cubic meters per day (m3/day) or 2,870 million gallons per day (MGD).
“About 44 percent of this capacity (37 million m3/day) or 9,860 MGD is located in the Middle East and North Africa. Desalination in this region is projected to grow at a rate of 7-9 percent per year,” Alhseinat said.
While it may be the solution to freshwater shortage in the region, “so far there is no expectation of a direct economic value from it,” he added.
“Desalination in the GCC is contributing indirectly to the economic growth of the region even though it is considered as a cost in the countries’ energy bill.”
At the end of the day, Alhseinat said, ensuring the availability of freshwater is a must for any country to have sustainable economic growth.
*****
Twitter: @jumana_khamis




























