AMMAN: Will the summer of 2020 see Israel make good on its threats to annex more parts of the West Bank and the Jordan Valley? If the US-Israeli coordination on President Donald Trump’s Middle East peace plan since January is any indication, the answer could very well be “yes.”
Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, during the election campaign in September 2019, said Israel will annex the Jordan Valley and impose its sovereignty over West Bank settlements for security concerns in the long run.
Around half a million Israeli settlers live in the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, according to Israeli sources.
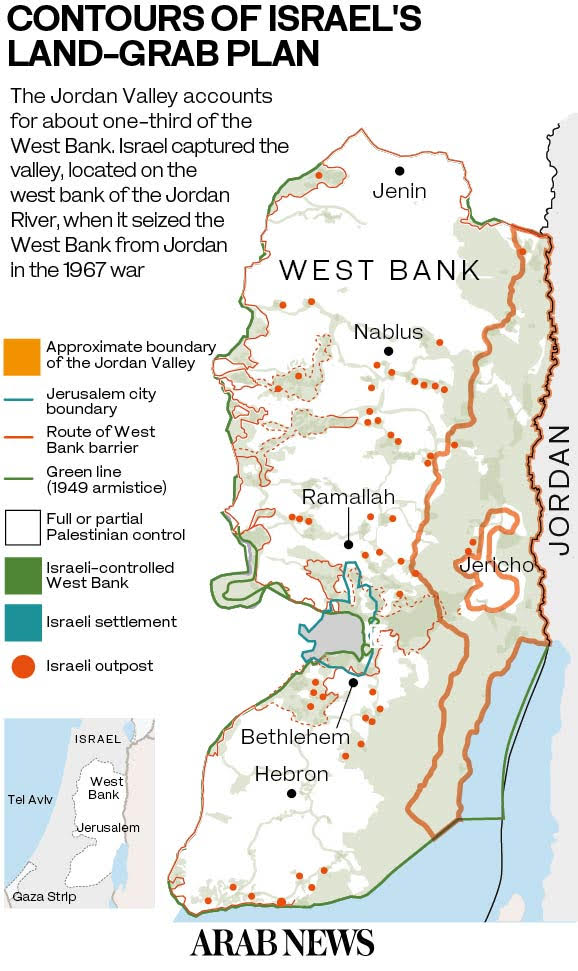
UN data show there are 31 Jewish-only settlements built in the Jordan Valley, most of which are agriculture-based, with around 8,000 settlers. Since its occupation in 1967, Israel has set up some 90 military posts in the area and forcibly evicted around 50,000 Palestinians.
Netanyahu’s declaration found support in Washington as the White House announced its much-talked-about “Vision for Peace, Prosperity and a Brighter Future for Israel and the Palestinian People.”
With Netanyahu at his side and no Palestinians in the room, Trump and his son-in-law cum senior advisor, Jared Kushner, outlined last year a detailed plan that envisioned a demilitarized Palestinian entity without East Jerusalem and the Jordan Valley (with the exception of the city of Jericho). It showed all Israeli settlements and the north Dead Sea as part of Israel.
According to the Trump Peace Plan — mockingly dubbed the “deal of the century” — three land plots in the Negev desert were to be granted to Palestinians as part of a unilateral land swap.
The idea of annexation of Palestinian territories has been an integral part of Israeli planning since the June 1967 war. Shortly after Israel occupied the West Bank (including Jerusalem) and Gaza in the war, it began the process of a takeover.
The Israeli government of 1967, headed by Levi Eshkol of the Labor Party, carried out the first annexation, less than three weeks after the occupation. On June 27, 1967, the Israeli Knesset, its national legislature, decided that the “law, jurisdiction and administration of the State of Israel government shall extend to any area of ‘Eretz Israel’ it so orders.”
Therefore, Israeli law extended to cover all parts of East Jerusalem, giving civilians a legal status different from those in the rest of the Occupied Territories.
According to Khalil Tafakji, director of the Arab Studies Society in Jerusalem, the annexation and its justification took root in the first weeks of the occupation after the 1967 war. “Once they annexed East Jerusalem, they eyed other parts to incorporate with Israel,” he said.
Israel drew up many plans under its various leaders, including the Yigal Allon Jordan Valley plan, Ariel Sharon’s separation plan and Avigdor Lieberman’s plan of people exchange, said Tafakji.
“All these plans have been aimed at unpopulated lands, in true commitment to Zionist principles of wanting land without people. Ultimately, these plans, like the current one by Netanyahu, are meant to deny the Palestinians their statehood,” he told Arab News.
Israel’s initial annexation attempts were incorporated into what is known as the Allon Plan. Yigal Allon, who was an army general turned minister shortly after the 1967 war, suggested annexing most of the Jordan Valley, from the river to the eastern slopes of the West Bank hill ridge; East Jerusalem; and the Etzion bloc, a cluster of Jewish settlements located directly south of Jerusalem.
In Allon’s plan, the remaining parts of the West Bank, containing most of the Palestinian population, were to become Palestinian autonomous territory or would return to Jordan, including a corridor to Jordan through Jericho. Jordan’s King Hussein rejected the plan.
Israel’s annexation plans for the Jordan Valley and the northern Dead Sea area, according to Tafakji, “encompass over 30 per cent of the occupied West Bank.”
In 1993, under the Declaration of Principles signed between the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) and the state of Israel at the White House, the West Bank was divided into three areas: Area A under Palestinian control; Area B under Palestinian control and Israeli security control, forming about 22 percent of the West Bank; and Area C under full Israeli control, consisting of over 60 percent of the West Bank’s 5,655-square-kilometer area.
Israel’s expansionism could mean imposing its control over the entire eastern part of the West Bank and cutting off all geographical contiguity with the rest of the territory, says Tafakji.
“The annexation is aimed at exploiting large agricultural areas and allowing Israel to invest in them, building more settlements and legalizing settler outposts, and not for security reasons as it claims, because it already has a peace agreement with Jordan,” he said.
A big stumbling block in Israel’s plans for further annexation is the Palestinian city of Jericho in the West Bank. According to Khaled Ammar, author and film producer and a long-time Jericho resident, during the historic negotiations of the Oslo Accords (1993 and 1995), Palestinian leader and PLO Chairman Yasser Arafat insisted that the first leg of the Israeli army withdrawal should include all of Gaza and the Jericho governorate.
In the wake of the Oslo agreements, the Palestinians wrested back administrative control of Jericho from the Israel security over what is listed as Area A in the city as well as in the nearby water-rich Jordan Valley town of Ouja, which has a sweet water spring.
For Palestinians, the Jordan Valley, which is located in the east of the West Bank on the border with Jordan, is a vital and integral part of their future state due to its strategic location and fertile lands.
“Not only is Jericho the bridge city to Jordan and to the rest of the world, Jericho and its population have become a thorn in Israel’s side as it tries to take the land without its people,” Ammar told Arab News. The Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics lists the population of Jericho governorate at 52,000 Palestinians.
Though the July 1 deadline for annexation is now said to be neither “sacred” nor urgent, Israel’s intent has drawn global concern. According to a post by the BBC, the Israeli plans “could result in some 4.5% of Palestinians in the West Bank living in enclaves within the annexed territory.”
The Israeli human rights group B’Tselem said that Israel has declared about 20 percent of the area as natural reserves, taken over large areas in the north of the Jordan Valley to build the separation wall, and used 56 percent of its area for military purposes.
A Palestinian government settlement watchdog said that any annexation would leave 19 communities in the Jordan Valley, home to 3,700 Palestinians, at risk of forced displacement or being disenfranchised.
Netanyahu, however, has said that Israeli sovereignty will not be applied to Palestinians in the Jordan Valley, and reports say the same exclusion will be extended to Palestinians in other annexed parts of the West Bank. Given Israel’s past record, there is little assurance to be found in this statement.
Twitter: @daoudkuttab



































