KARACHI: Last Tuesday, Dr. Naseem Salahuddin, the head of the Rabies Free Pakistan (RFP) project, woke up to discover that months of work put in by her team to vaccinate and neuter stray dogs in Karachi had been summarily wasted.
Overnight, municipal authorities in an upscale neighborhood in southern Karachi had killed at least 50 strays Salahuddin’s team had treated. And this was not the first time this had happened.
Authorities estimate the citywide operation has so far culled thousands of dogs but do not have a full count for all six districts that make up Karachi city.
“You work from dawn to dusk, put in your best effort, spend time and resources and they kill the dogs without any reason — it’s like being stabbed in the back,” said Salahuddin, who heads RFP, a project of Karachi’s Indus Hospital.
The periodic culling of dogs by shooting or using poison tablets hidden in food is common in Pakistan and has unnerved both animal rights activists and citizens, but officials in Sindh province, of which Karachi is the capital, say it is necessary because packs of wild strays pose a threat to residents.
In Pakistan, up to 5,000 people die each year of rabies, according to infectious disease experts. Anti-rabies vaccines, mostly imported from neighboring India, seem to be in perennial short supply at Karachi hospitals.
A stray dog walks past auto-rickshaws parked alongside a street during a government-imposed nationwide lockdown as a preventive measure against the COVID-19 coronavirus, in Karachi, Pakistan, on April 7, 2020. (AFP /File photo)
Rabies is a neglected disease in Pakistan, with scant data available, although the cases of dog bites are rising, doctors and officials said.
Around 150 patients come to Karachi hospitals daily with dog bites, doctors said. Last June, the Sindh health department said there were almost 70,000 dog bite cases reported between the months of January and May. Indus Hospital treated over 7,000 cases of dog bites last year and said it had already treated 4,000 cases this year. Dr. Seemin Jamali, executive director of Jinnah Hospital, the largest health facility in Sindh, said the hospital had treated 6,000 patients for dog bites between January and July.
Street animals, particularly dogs, are often a part of the urban landscape in developing countries like Pakistan. In Karachi, a megacity of over 15 million, it is common to see strays lurking in public parks, guarding street corners and howling in neighborhoods at night. Joggers say they have to carry stick to pry dogs away, and cyclists keep stones in their pockets to throw at chasers.
Malik Fayyaz, the chairman of the district municipal council in southern Karachi, confirmed that authorities were killing, as well as sterilizing, dogs due to a rising number of complaints from residents.
He said a vaccination and spaying project the council had started in collaboration with Indus Hospital had stalled due to the coronavirus pandemic, and culling strays was thus currently the only option.
Another program launched last year in Karachi’s district central, the largest municipal cooperation in the city, had also stalled.
Rehan Hashmi, the central district council chairman, said dogs had to be taken off the streets even if that meant euthanizing them. Authorities would stop killing dogs, he added, if there was a program that could vaccinate and spay “100 percent stray dogs.”
“Saving a human life is more important than saving the life of a dog,” Hashmi said.
In August 2016, the district council of south Karachi killed 800 stray dogs, pushing lawyer Muhammad Asad Iftikhar to file a petition in the Sindh High Court. Last December, the court finally directed authorities to stop culling animals and instead to neuter and vaccinate them. But cull tactics continue.
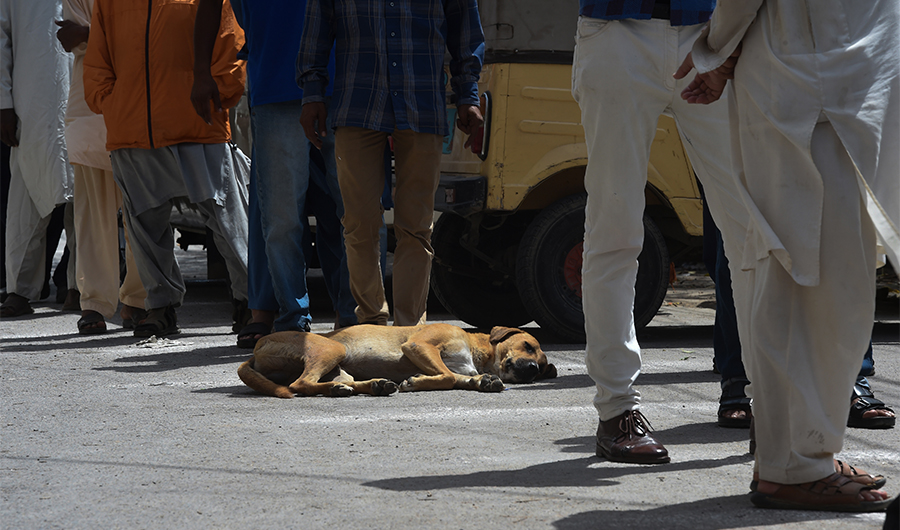

A stray dog rests on a street as people line up maintaining social distancing to buy groceries from a governmental subsidised shop during a government-imposed nationwide lockdown as a preventive measure against the spread of the COVID-19 coronavirus, in Karachi, Pakistan, on April 8, 2020. ( AFP/ File Photo )
Last month, the Ayesha Chundrigar Foundation (ACF), which has recused and neutered over 6,000 stray animals in Karachi in the last seven years, filed a petition in the Sindh High Court after hundreds of dogs the organization had vaccinated and spayed were found dead. Many of the dogs were given poisoned food, the Foundation said, and were found with their legs tied to other dogs so they could not run away or seek help as the venom took effect.
The ACF petition, which is yet to be heard in court, seeks a uniform policy by the government to curb the spread of rabies and contain rising stray populations in Sindh instead of sentencing dogs to death.
In Pakistan, the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act of 1890 was amended in January 2018 to include fines and punishments for animal abuse. The law does not provide a ‘holistic approach’ toward animal welfare, rights activists say, and needs to be replaced with new legislation recognizing animals as sentient beings that need protection and care.
Indeed, animal welfare advocates say Pakistan has never made a priority of pushing responsible animal control policies, including spaying and neutering, which would have helped avoid the current problems.
“Killing dogs is not only inhumane but ineffective also,” said Aftab Gauhar, a project manager at RFP, which operates across Karachi and has vaccinated nearly 24,000 dogs, and neutered and spayed over 3,500 since 2018. He said rising dog populations and rabies infections could be tackled with sterilization, mass vaccination drives and community engagement to teach people how to behave around strays.
There are currently a number of charities in Karachi who cruise the city treating sick dogs and taking healthy ones to shelters for vaccinations and sterilizations before depositing them back exactly where they were found: on the streets.
Ayesha Chundrigar, who founded ACF, said strelization could lead to a 50 percent fall in the number of strays within a year.
“Stray dogs should be neutered and left to live in their natural habitats, which are the streets,” she said.
In an emotional video message posted online last month after hundreds of ACF rescues were found dead, Chundrigar said:
“We [ACF] are about to complete seven years next month. It has really been a hard seven years. We feel grieved. We have no success to show. Because all of our success stories are dead.”
She added: “We can’t take it anymore. They [municipal authorities] win. We’ve fallen apart, trying like absolute fools in this lawless city of millions. Can’t do it anymore. We’re tired and hopeless.”
But speaking to Arab News, the animal welfare advocate said she was hopeful concerned citizens and civil society groups would help lead to change.
“People are now realizing that we have been very cruelly treating animals in this country,” she added. “I believe that change will occur.”















