ABU DHABI: On Wednesday, Kosovo marks the 10th anniversary of the landmark advisory opinion of The Hague-based International Court of Justice (ICJ) that the nation’s 2008 declaration of independence did not violate international law.
Kosovo’s riveting story, however, began a decade earlier. After politicians unsuccessfully waged a years-long peaceful struggle for greater autonomy or independence, the Kosovo Liberation Army launched an armed uprising against Serbian rule in the mainly Muslim Yugoslav province in March 1998.
This galvanized a disproportionate response from the Serb political establishment, which did not discriminate between ethnic Albanian Kosovar fighters and civilians, sending thousands of refugees into neighboring Albania and North Macedonia.
In response to the escalating violence by Yugoslav President Slobodan Milosevic’s forces, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) began airstrikes on March 24, 1999, against Serbian military targets.
That 11-week campaign caused many civilian deaths and massive infrastructure destruction but was viewed as a just war by Kosovar Albanians and much of the global commentariat.
After Yugoslavia accepted a peace proposal in June 1999, Javier Solana, the NATO secretary-general, ordered an end to the bombings. The UN Security Council adopted Resolution 1244, creating the UN-NATO joint interim mission in Kosovo, or UNMIK. The cessation of violence brought hope to Kosovars at a time of great despair, paving the way for a new reality and prompting a return of refugees.
After nine years under UN control, Kosovo declared independence through its Assembly on Feb. 17, 2008. Rejecting the declaration as illegal, Serbia sought the ICJ’s validation of its stance. The case of Kosovo became the first the court faced regarding a unilateral declaration of independence.
The ICJ delivered its advisory opinion on July 22, 2010, following several rounds of public hearings and written statements, including a three-part statement by UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
The ICJ concluded that “the adoption of declaration of independence of 17 February 2008 did not violate general international law, Security Council resolution 1244 (1999) or the Constitutional Framework adopted on behalf of UNMIK by the Special Representative of the Secretary-General,” and that “consequently the adoption of that declaration did not violate any applicable rule of international law.”
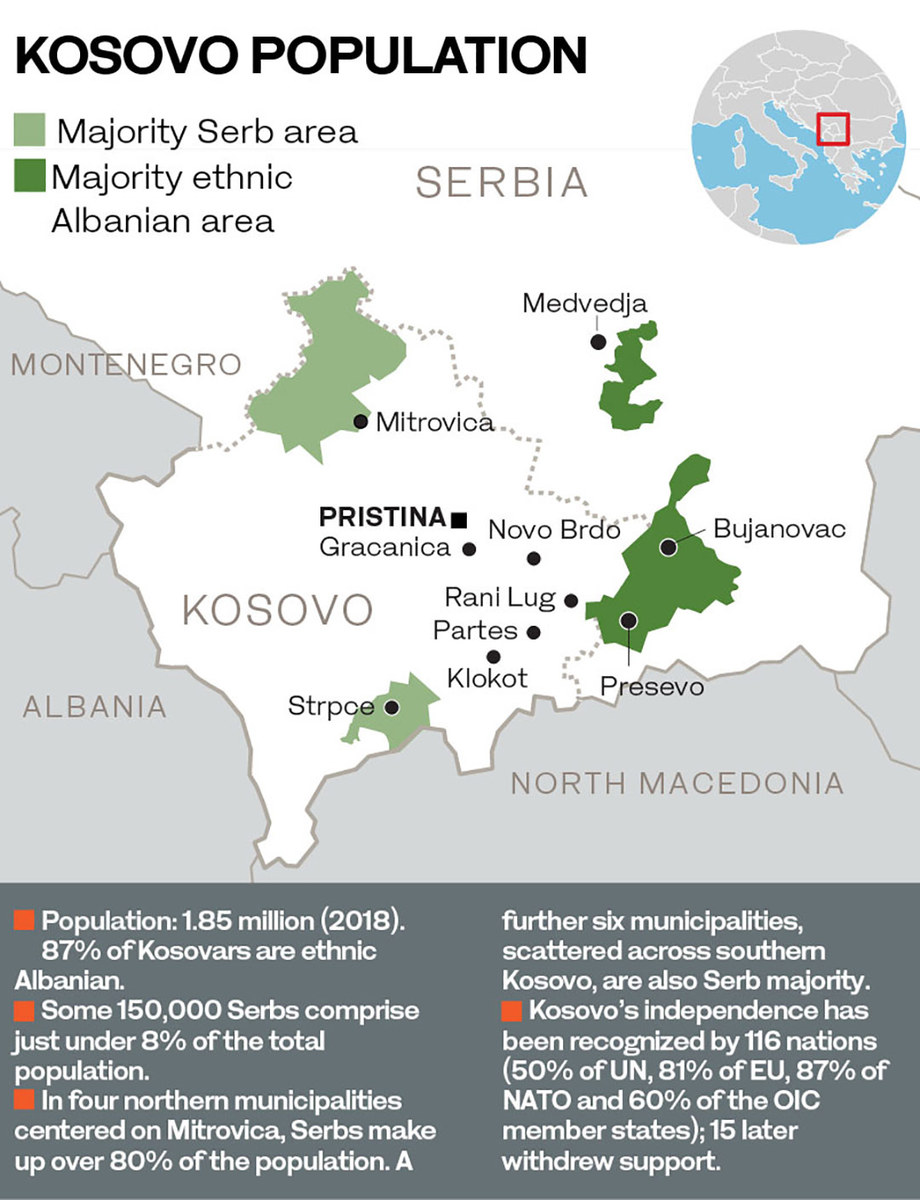
Although non-binding, the precedent-setting ICJ opinion provided key momentum to Kosovo’s foreign policy, resulting in 116 countries recognizing its independence over time.
The US, several EU member states and the Gulf countries recognized Kosovo’s independence early on. Saudi Arabia was among 35 states that submitted statements supporting Kosovo and later opened an embassy in Pristina. Russia, China and five EU member states, including Spain and Greece, do not recognize Kosovo.

Despite socio-economic setbacks and territorial disputes, Kosovo has made significant progress on the foreign-policy front. In 2013, Kosovo and Serbia entered into a dialogue under the Brussels Agreement, resulting in a series of negotiated settlements, including on border disputes, minority issues and car-license plates, among others. The ones implemented have improved lives on both sides.
While Kosovo is not a member of the UN or Interpol, it enjoys full membership of the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, which celebrated its 20th anniversary in the country last year. Kosovo also concluded its year-long chairmanship of the South-East European Cooperation Process.
Despite its tumultuous history, Kosovo enjoys good relations and close cooperation with its first neighbors, North Macedonia, Albania and Montenegro, according to Lulzim Mjeku, Kosovo’s ambassador to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Domestically, Kosovo has responded well to major challenges such as structural and youth unemployment. With an annual economic growth of more than 4 percent, it has partly succeeded in meeting the young population’s growing demand for education and jobs.
INNUMBERS
Kosovo War
- 13,000 Kosovar Albanian civilians killed by Serb forces.
- 20,000 Women raped.
- 3,000 Persons who went missing.
- 1 million People who fled ethnic cleansing campaign.
- 40% Infrastructure of Kosovo destroyed.
The steady economic progress, however, has been impeded by the COVID-19 pandemic. New cases have risen significantly since the beginning of June, totaling more than 5,000 confirmed incidences and more than 100 reported deaths as of mid-July.
Kosovo’s parliament elected a new government in early June after Prime Minister Albin Kurti’s administration collapsed in late March following a no-confidence vote prompted by its mishandling of the pandemic.
The new prime minister, Avdullah Hoti, has promised to reach a deal on continuing the Brussels-backed dialogue with Serbia.
Over the past decade, Kosovo has made steady progress in relations with countries in the Middle East. Starting in August, Kosovo and Saudi Arabia will jointly implement an agreement on avoidance of double taxation. Last year, Kosovo welcomed some 8,000 Saudi tourists.
Aiding Kosovo’s fight against COVID-19, the Muslim World League has sent valuable humanitarian assistance. The Kosovo embassy in Riyadh was able to organize a repatriation flight for 183 of its nationals living in Saudi Arabia.
Although some analysts believe that Kosovo has not adequately used the international momentum created by the ICJ decision, the country has made steady progress on key areas, while facing significant work ahead, especially on full normalization of relations with Serbia.
More broadly, Kosovo has set bold objectives, including membership of the UN, EU and NATO, with renewed commitment to continue exercising a responsible foreign policy regionally and globally.
-------------------------
Twitter: @eminaosmandzik






















