MISSOURI: As Turkey carries out almost daily attacks on impoverished Kurdish regions in neighboring Syria and Iraq, keeps its own elected ethnic Kurdish MPs indefinitely imprisoned, and coerces Iraqi Arab and Kurdish authorities to act as its local police, it is hard to remember that August marks the centenary of a pact in which provision was made for a Kurdish state.
The Treaty of Sevres, signed on Aug. 10, 1920, essentially laid out the Ottoman Empire’s terms of surrender following the First World War. The treaty, which included signatories from Britain, France, Italy and the Ottoman Empire, promised religious and ethnic minorities in Turkey various safeguards to protect them and their rights.
With regard to the Kurds, the treaty stated: “If within one year from the coming into force of the present Treaty the Kurdish peoples within the areas defined in Article 62 shall address themselves to the Council of the League of Nations in such a manner as to show that a majority of the population of these areas desires independence from Turkey, and if the Council then considers that these peoples are capable of such independence and recommends that it should be granted to them, Turkey hereby agrees to execute such a recommendation, and to renounce all rights and title over these areas.” (Kurdistan Section III Article 64)
Under the leadership of Mustafa Kemal (who later came to be known as Ataturk), remnants of the Ottoman army organized military resistance to the terms of the treaty. Convinced that they were fighting to save the sultanate and caliphate, and promised recognition and self-governance in the new Turkey, most Kurdish tribes joined with Ataturk during what came to be known as Turkey’s War of Independence.
The Ataturk-led resistance to Sevres proved successful, and the treaty was replaced in 1923 by the Treaty of Lausanne. Ataturk’s representatives in Lausanne insisted on stipulations regarding minority rights in the new treaty, however, wherein Turkey only recognized “non-Muslims” as minorities, specifically the Jewish, Greek and Armenian communities. Turkish representatives in Lausanne rejected the concept of ethnic minorities in Turkey, thereby also refusing to entertain cultural, linguistic or other minority rights for such groups.
With the loss of its holdings in Europe and Arab lands, as well as genocidal campaigns against Christians in Ottoman lands, the Kurds stood out as Turkey’s only remaining significant minority in 1923.
The refusal of Turkish diplomats to recognize ethnic minority rights in Lausanne was thus squarely aimed at the Kurds. Their policy formed the first step in betraying earlier promises of recognition and self-governance to the Kurds who participated in Turkey’s War of Independence.
Under a Muslim sultanate and caliphate, Kurds (the large majority of whom are Sunni Muslim) could have expected an equal place. It thus made sense for Kurds to join Turks in fighting for these two institutions in 1920. But Ataturk abolished the sultanate in 1923 and the caliphate in 1924, replacing them with a secular nation-state concept imported from parts of Europe.
Taking his cue from France in particular, Ataturk then went about trying to make the Turkish state and nation completely co-terminous, meaning that only a Turkish ethnic national identity would be permitted in the new Turkey. Kurdish language, culture, music, names and any other manifestations of Kurdish identity were promptly outlawed.
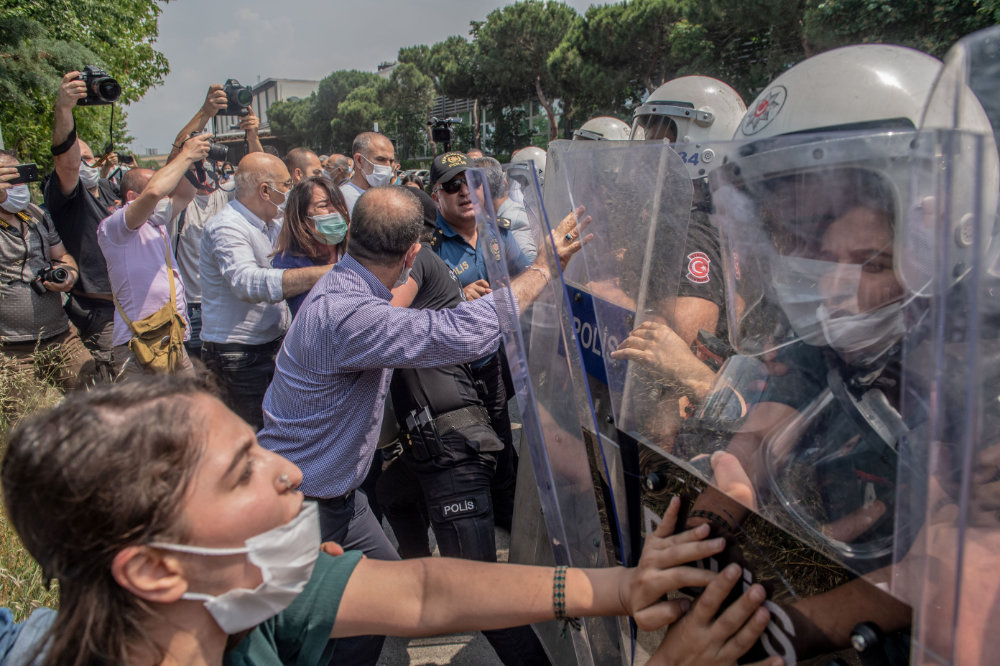

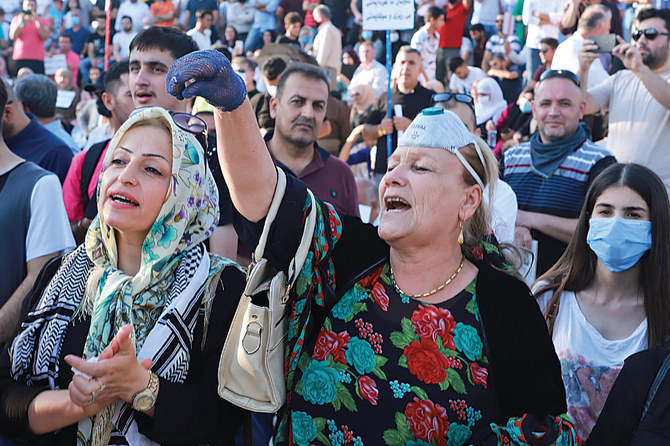
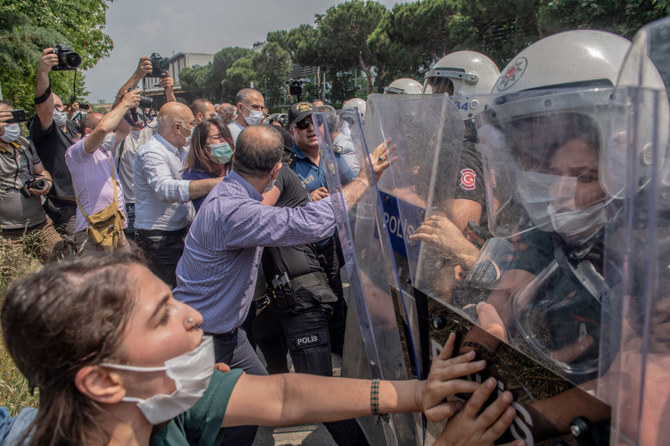
Demonstrators clash with Turkish riot police during a "March for Democracy" called by Kurdish People's Democratic Party (HDP) in Istanbul on June 15, 2020. (Photo by BULENT KILIC / AFP)
The Kurds unsurprisingly revolted against the secularization and Turkification of the new state in 1925 and 1927-30. These revolts and numerous subsequent ones were all brutally suppressed.
The 1937-38 suppression of the Kurdish revolt in Dersim (renamed Tunceli by Turkish authorities) is recognized by many as a genocide, with 10,000-30,000 killed, including civilians hiding in caves who were murdered with poison gas or burned alive by Turkish forces.
When Kurdish unrest began manifesting itself in Turkey again in the 1960s, one right-wing Turkish nationalist periodical warned the Kurds to “remember the Armenians” — a somewhat ironic choice of rhetoric given Turkish nationalists’ refusal to admit that the Ottomans ever committed genocide against the Armenians of Anatolia, whose numbers fell from some 2 million in the Ottoman Empire on the eve of the First World War to almost nothing after 1915.
With the exception of Turkey’s 1974 intervention in Cyprus, the Turkish armed forces seemed to specialize in only one thing since the creation of the Turkish Republic: Suppressing Kurds. Apart from Cyprus and participation in the Korean War and the 1991 Desert Storm campaign in Iraq, the Turkish military’s only significant operations in the 20th century involved counterinsurgency against Kurds.
Most of the military campaigns took place in Turkey itself, but from the 1980s onward the Turkish military also frequently conducted cross-border raids into Iraq to chase after guerrillas of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK). And so it continues to this day.
Turkey’s invasion and occupation of Afrin in northern Syria in 2018 was aimed at PKK-aligned Syrian-Kurdish groups there. The October 2019 Turkish invasion and occupation of parts of northern Syria east of Afrin had the same objective.
Although no significant attacks from Kurdish forces in Syria into Turkey had occurred since the onset of the Syrian civil war in 2011, Turkey claimed a need to occupy and establish “buffer zones” in northern Syria. The Turkish invasions seriously threatened Kurdish-led operations against Daesh in Syria.
Although one might not know it from the scant media coverage, almost weekly Turkish strikes in Iraqi Kurdistan, with remarkably similar rhetoric about necessary “buffer zones,” have been ongoing for several years. The most recent series of operations (dubbed Claw-Eagle and Claw-Tiger) this year have seen Turkish ground troops deployed to the area, in addition to Turkish bases already present in Iraqi Kurdistan since the mid-1990s.

The Treaty of Sevres was signed on Aug. 10, 1920. (Supplied)
The maneuvers in the summer of 2020 also seemed to be conducted in cooperation with Iranian forces, with Turkish airstrikes against fighters of the Free Life Party of Iranian Kurdistan (PJAK), an Iranian-Kurdish party aligned with the PKK.
Recently, a Turkish drone strike killed two high-ranking officers of the Iraqi army who were meeting with PKK militants in northern Iraq after clashes between the two. Both Baghdad and Erbil, the seat of the Kurdistan Autonomous Region of Iraq, have repeatedly protested against Turkey’s violations of Iraqi sovereignty, but to little effect.
Turkey claims a right to defend itself and act against the PKK presence in Iraq or PKK-aligned Kurdish groups in Syria. If the mere presence of such groups, especially in the very mountainous and difficult-to-control territory along the border, justifies invasions and occupations of Arab territories, a similar logic could in theory be used by Israel or the US to target Palestinian Hamas leaders hosted in Ankara and Istanbul today, to say nothing of Arab countries whose Islamist critics have extensive propaganda campaigns operating from Turkish soil.
The official Turkish approach of the last 100 years seems rather like a policy of opposing Kurdish self-government “even if it’s in Alaska,” as a popular Turkish joke goes. When Turkey invaded northern Syria in 2018 and 2019, one justification offered by Turkish leaders was that they did not want “to see Syria become another northern Iraq.” By this, they meant Kurdish autonomy in Iraq, of course.
One-hundred years after the Treaty of Sevres, it looks like “le plus ça change, le plus c’est pareil.”
• David Romano is Thomas G. Strong Professor of Middle East Politics at Missouri State University.




























