BEIRUT: Lebanon is celebrating its centennial as a modern state with a fading recollection of the landmarks that stood a hundred years ago.
The exception is the Residence des Pins (Pine Residence), the home of the French ambassador in Beirut, which witnessed the establishment of Greater Lebanon on Sept. 1, 1920, and has remained steadfast against the country’s subsequent turmoil.
Other urban markers of that era either became extinct from natural factors and social development or were destroyed during the Lebanese Civil War. Whatever little was preserved perished in the explosion at the Port of Beirut less than a month before Lebanon’s centennial.
The houses of Beirut’s neighborhoods tell the stories of various epochs. During the first two decades of the 20th century, Beirut was a modest city centered around a tiny natural port, its inhabitants not exceeding 10,000 people.
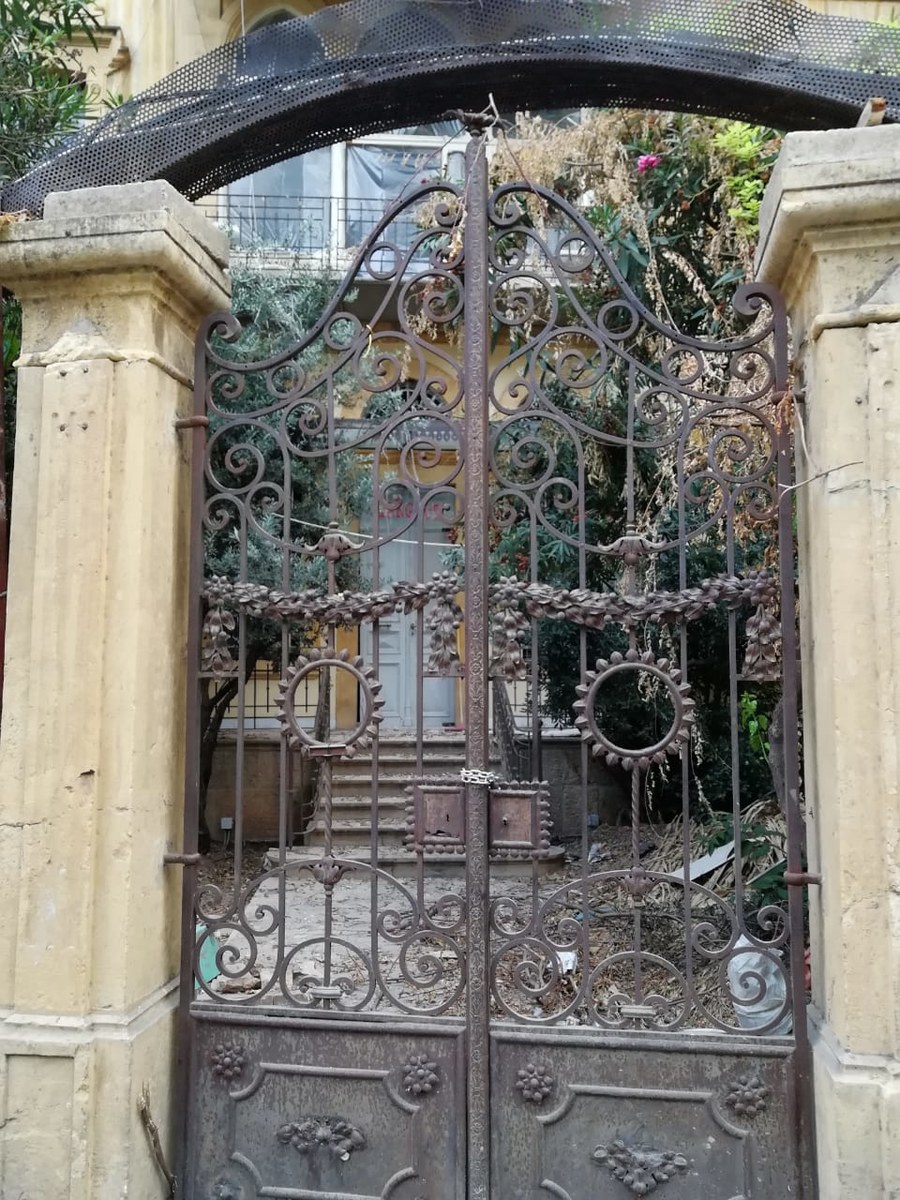

A wrought iron gate on Mar Mikhael Street. (AN Photo/Najia Houssari)
The city was surrounded by a wall bearing many gates, which closed early each day. The names of these gates — such as Bab Idriss, Asour Gate, and Bab Al-Burj — still resonate, although the walls and gates are no longer standing.
“Beirut did not start to develop until the end of the third decade of the 20th century, when the West began showing an interest in cities on the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea, including Alexandria, Haifa, Beirut, Mersin and other Ottoman ports that were ready to receive commodities,” said architect Rahif Fayad, 84.
The role of Beirut’s port quickly grew and resulted in the rise of a new mercantile class in the city and Mount Lebanon, Fayad explained.
“The city’s population boomed and had to expand beyond its walls to neighboring areas, which led to it becoming a modern, open city.”
Most buildings during that period were constructed with sandstone excavated from Beirut sand rocks. These old stones can still be seen in Spears Street, the wall of the American University of Beirut, and many of Beirut’s old houses that are still resisting the two forces of modernity and destruction.
The stones were covered with a layer of limestone or cement to protect them from seasonal climatic effects. Houses consisted of one or two floors and were surrounded by a garden, often overlooking the sea, so that family members could live safely, without coming into contact with the surrounding neighborhood.
The facade of these houses consisted of three arches, with a red-sloped brick roof. This style was widespread in Beirut and other coastal cities throughout the eastern Mediterranean and served specific social needs. The inner courtyard was covered with a roof and became known as “Al-Dar” (living room), which was surrounded by bedrooms, a kitchen, and a dining room. This was the typical house of Beirut’s rising mercantile bourgeois class.

A window with marble decorations in Susuk Palace. (AN Photo/Najia Houssari)
The houses were constructed by professionals — designers and construction workers educated in Europe and the US. The architecture was of the finest quality and fit in well with the surrounding environment, as local materials and expertise were used.
Italian architects were hired to design such places as the Sursock Palace, located on the eponymous street bearing the name of this aristocratic family.
With the large number of new arrivals, Beirut expanded and saw its port boom.
In 1920, with the declaration of Greater Lebanon and the beginning of the French Mandate era, colonialists introduced wide streets, modern transportation — such as tramways and cars — and an insatiable, consumerist lifestyle. They tried to fashion public places in the heart of historical Beirut, but some of these collided with the ancient churches and mosques present in the area.
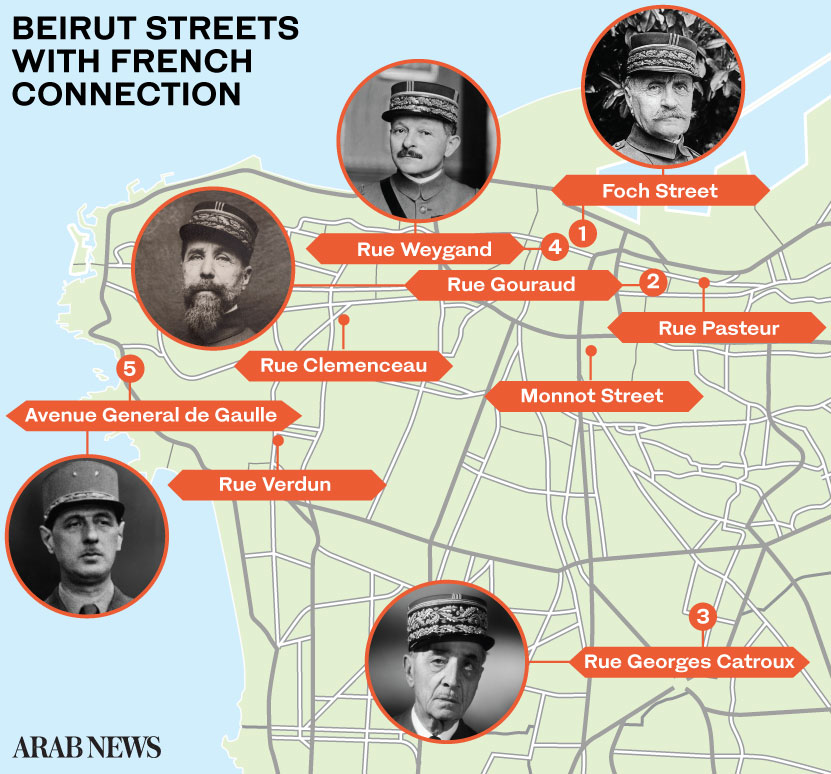
Colonialists also introduced Haussmannian architecture, which entailed dividing the façade of a building into three vertical parts that would be adopted into contiguous buildings, forming the facade of a whole street. This design is best featured in Maarad, Foch, Allenby and Wegan Streets, and other orthogonal streets north of the Beirut Municipality Building.
This design can also be seen in areas relatively distant from the historical heart of Beirut, including Spears, Al-Kantari, May Ziadeh, Gemmayzeh, all the way to the Sursock area in Achrafieh.
“Beirut was the link between East and West, and this is depicted in its architecture since the French Mandate, which introduced new stylistic elements without relinquishing Islamic characteristics,” architect Fadlo Dagher said. “This blend of modern and Islamic elements is best expressed in the architecture of the Beirut Municipality building, which reflects both Ottoman and French architecture.
“This building was designed by the Greek-Lebanese engineer Youssef Aftimus (1866-1952), who began its construction during the Ottoman era and finished it during the French Mandate.”
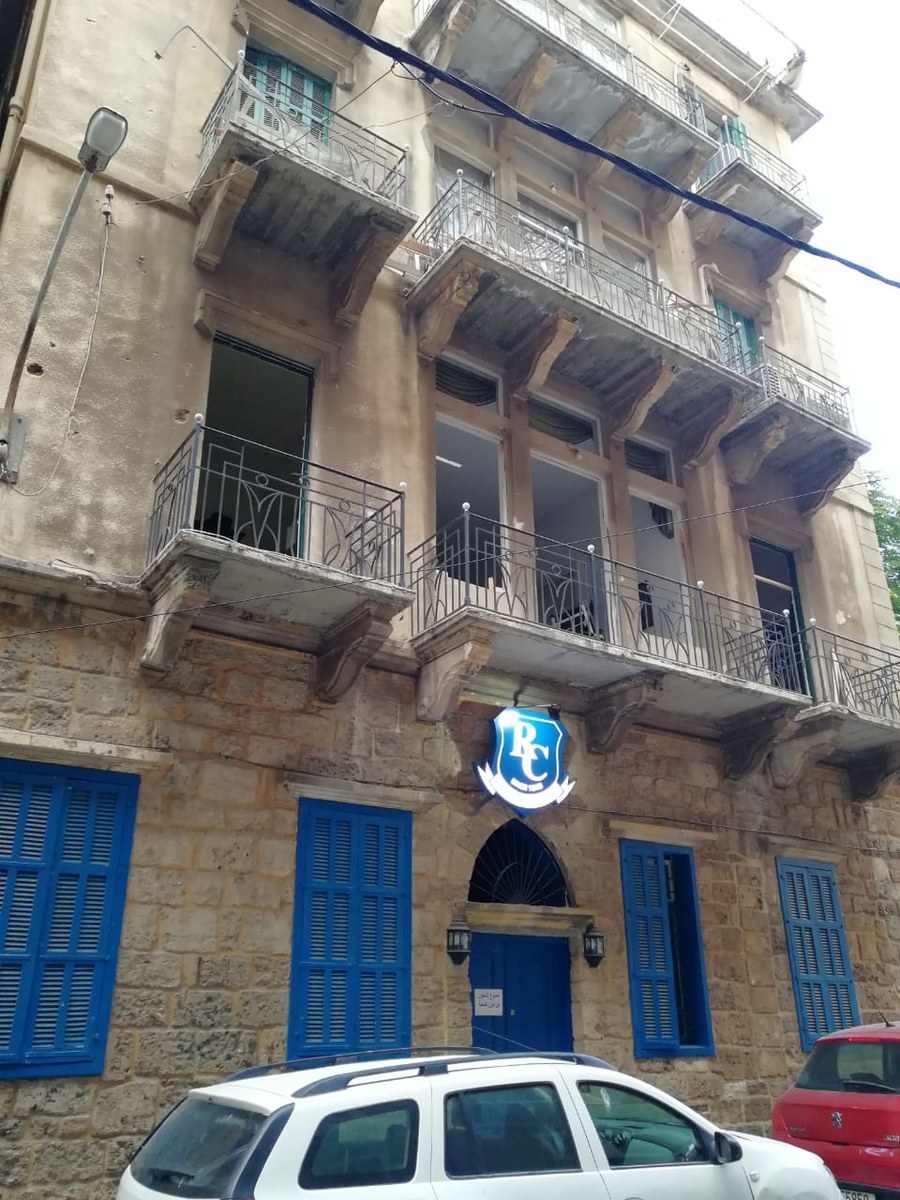

A building in Jemaizi with marble balconies. (AN Photo/Najia Houssari)
Beirut’s architectural identity, in Dagher’s words, “reflects the city’s openness to everybody.”
How is it that some palaces and buildings are still standing after 100 years?
“Prior to the Mandate era, Ottoman construction depended on wood to build roofs,” Dagher said. “In 1925, cement was introduced, and brick claddings were replaced with iron, reinforced concrete, or cement.
“During the Ottoman period, balconies were made of marble, but during the Mandate era they were replaced with verandas with three walls, exposed on one side to winds blowing over Beirut. It is pleasant to spend the evening on them.”
As these balconies were roofed, Dagher added, people would be protected from the sun during summer and rain during winter.
“It is noteworthy that terraces were always built on the northern side, in order to not be exposed to the sun,” he said. “They were usually ornamented with oriental and Western designs.”
The Mandate period witnessed a shift from single-family homes to multi-story buildings for commercial investment, Dagher explained.
“With the introduction of cement, buildings became five stories high, with each floor divided into two apartments, while the ground floors were left for shops,” he said. “New social groups came to live in these buildings, adopting the Western economic, social and cultural lifestyle, away from the independent houses surrounded by gardens.”
Lebanon’s independence in 1943 led to the further growth of Beirut. The city adopted modern, vertical architecture and the international style. Later, this would lead to uneven development, and the “Beiruti bourgeois house” would become engulfed by asymmetric iron and cement buildings and towers. Beirut’s ties to the sea withered away.
With the explosion that shook the city on Aug. 4, the Lebanese discovered how fragile and easily damaged their city was. They were also disappointed to discover that the city was not easy to evacuate in case of natural or man-made disasters.
According to a survey by specialized committees, 360 heritage buildings dating back to the period between 1860 and 1930 were partially or fully damaged by the explosion at the port.
“The restoration of these buildings, with their wooden ceilings, renowned decorations, marble balconies and carved windows, primarily requires a political decision to preserve the architectural memory of the city,” Dagher said.
“These are two or three-story buildings and palaces, while the building system in Beirut allows the construction of buildings as high as 13 stories. Many investors are showing interest in buying these damaged, forgotten buildings in order to replace them with tall ones and erase our heritage.”
Twitter: @najiahoussari































