AL-MUKALLA, Yemen: Until the Iran-backed Houthi militia seized Yemen’s western port city of Hodeidah in late 2014, foreign and local experts had been regularly visiting a 45-year-old oil tanker moored in the Red Sea.
It was a practice that ensured that the FSO Safer, abandoned just a few kilometers off Yemen’s coast, did not touch off a disaster by exploding or sinking and spilling oil. But having witnessed the devastation caused by the Aug. 4 blast in Beirut and taken its lessons to heart, the Arab world cannot afford to ignore the imminent danger posed by Houthi stalling tactics.
Expressing concern about the condition of the vessel, Saudi Arabia has called for a meeting for Arab environment ministers on Monday. According to a statement issued on Sunday by Kamal Hassan, assistant secretary-general and head of the Economic Affairs Sector at the Arab League, the aim of the special session is to discuss ways and mechanisms to activate Resolution No. 582, which was adopted by the Council of Arab Ministers Responsible for Environmental Affairs in Oct. 2019.
The objective is to “find an appropriate solution to avoid an environmental catastrophe due to the failure to maintain the oil ship Safer anchored off the Ras Issa oil port in the Red Sea since 2015.”
When the Houthi militia gained control of Hodeidah, the FSO Safer was carrying 1.1 million barrels of oil, or almost half of its capacity, according to local officials. No sooner had the fighters tightened their grip on the city than technical experts fled the area, realizing that it had become too dangerous for them to stay on.
Over the past two years, the FSO Safer has attracted regional as well as international attention on and off, thanks in part to the regular appearance on social media of photos of rusting pipes and water leaking into the engine rooms, raising the specter of a floating powder keg.
INNUMBERS
45 Age of oil tanker FSO Safer
1.1m Barrels of crude oil in tanker
During the same period, Yemeni government officials, environmentalists and foreign diplomats have sounded the alarm over possible outcomes that could both exacerbate the humanitarian crisis in Yemen and take a heavy environmental toll on the Red Sea littoral states.
The UN has suggested sending a team of experts to Hodeidah to assess the damage to the FSO Safer, but the Houthi militia, who want to pocket the proceeds from sale of the oil, have rejected the proposal. The oil in the FSO Safer’s storage tanks was once estimated to be worth $40 million, but its value now may be less than half of that as crude prices have fallen a lot since the onset of the coronavirus pandemic, according to reports.
The internationally recognized government of Yemen has repeatedly accused the Houthi militia of using the decaying tanker as a bargaining chip, citing demands such as the resumption of salaries for public servants in areas under its control, removal of government forces from Hodeidah, and more relaxed inspection of ships bound for the port.
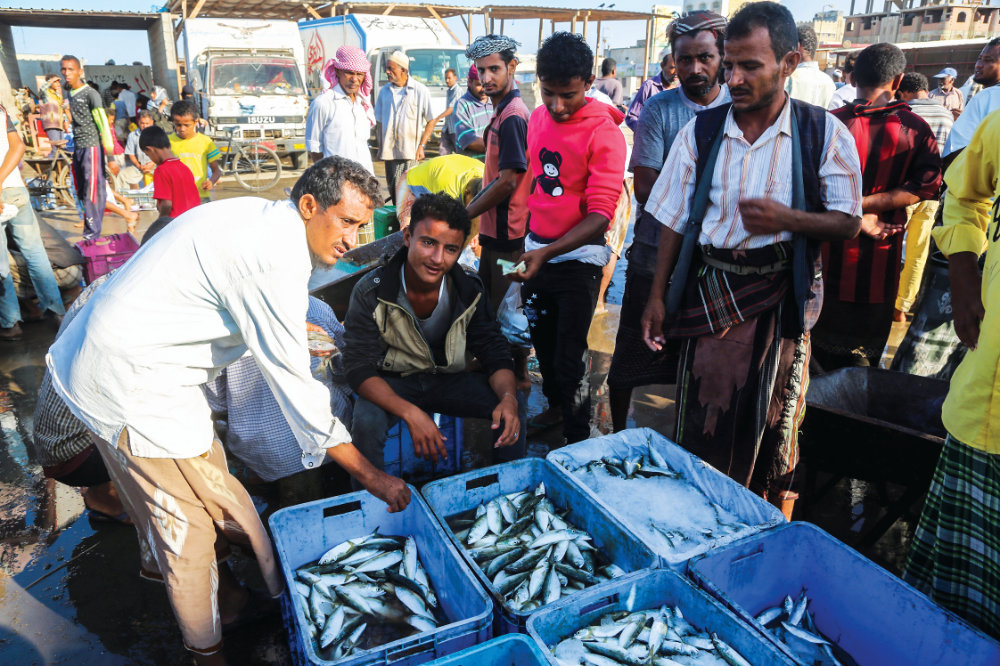

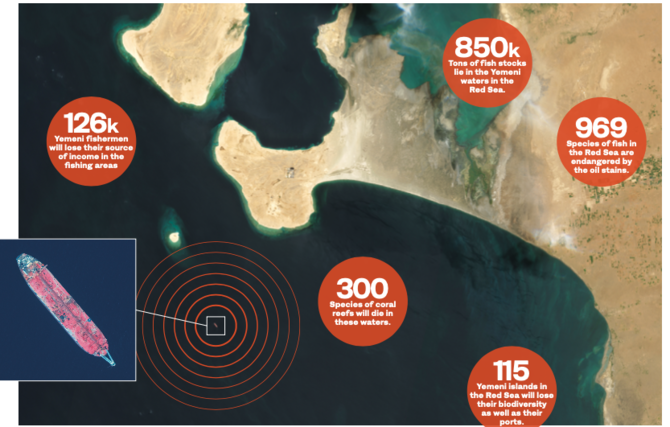
An oil spill would devastate the livelihoods of nearly four million Yemeni people, with fishing stocks taking 25 years to recover. (AFP)
In July, the government requested the UN Security Council to convene an urgent session to discuss the Safer issue amid concern that time was running out. In almost all their meetings with foreign envoys and diplomats, Yemeni officials bring up the matter of the tanker and the attendant risk of an environmental disaster in the Red Sea. For the past several months, Western and Arab diplomats, UN officials, aid organizations and experts too have underscored the urgency of breaking the deadlock in order to avert a human, economic and environmental catastrophe.
In July, the UN described the rusting tanker as a “ticking time bomb,” adding that the tanker’s cargo of oil could cause an environmental disaster four times bigger than the 1989 Exxon Valdez spill off Alaska. Last week, the UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres added his voice to the growing concern over the deadlock by appealing to the Houthi militia to give UN experts access to the oil tanker.
As for the Trump administration, its views were conveyed via a tweet by the US mission to the UN that said: “The US calls on the Houthis to cease obstruction and interference in aid ops and fuel imports. We urge the Houthis to cease their assault on religious freedom and to permit UN technical teams immediate, unconditional access to the Safer oil tanker.”
In comments in June, Michael Aron, the British ambassador to Yemen, said unless the Houthi leadership allowed experts to address the FSO Safer’s problems, the potential damage to the environment was far greater than that caused by the recent spillage of 20,000 tons of fuel in Russia’s Siberia. “The threat to the environment in the Red Sea is enormous, and will impact on all the countries who share this coastline,” he said.
Independent researchers too say the condition of Safer is deeply concerning. In a paper for the Atlantic Council in 2019 entitled “Why the massive floating bomb in the Red Sea needs urgent attention,” energy experts Dr. Ian Ralby, Dr. David Soud and Rohini Ralby said the potential consequences of an oil-tanker disaster in the area include an end to the two-year ceasefire in Hodeidah and an aggravation of Yemen’s humanitarian crisis.
“The risk of explosion increases by the day, and if that were to happen, not only would it damage or sink any ships in the vicinity, but it would create an environmental crisis roughly four and a half times the size of the Exxon Valdez oil spill,” the three scientists said. Other experts have speculated that just a stray bullet from an exchange of fire between rival factions could trigger off an explosion of the FSO Safer’s oil cargo.

Yemeni NGO Holm Akhdar says 126,000 people working in the fishing industry could lose their jobs in the case of a disaster.
“Even worse, given the complexity of this war, an errant bullet or shell from any one of the combatants could trigger a blast as large as Beirut’s August 4th disaster, prompting a historic oil spill,” Dave Harden, managing director of Georgetown Strategy Group, wrote in an op-ed in The Hill last month. He added: “Clean-up efforts would be daunting — given the insecurity of being in a war zone and the additional health risks from COVID-19.”
Similar concerns have been expressed by local government officials and fishermen in Hodeidah. Waleed Al-Qudaimi, deputy governor of Hodeidah, said that any spillage from the FSO Safer would create a humanitarian crisis as severe as the one caused by the Houthi insurgency.
“It (the oil spill) will add an additional burden that will affect Yemen for the next decades, deprive thousands of people of their jobs and destroy marine biodiversity in Yemeni waters,” he said. Al-Qudaimi appealed to the international community to keep up pressure on the militia to allow maintenance work to be carried out.
For a country reeling from a combination of conflict, humanitarian crisis, plunging currency and crumbling economy, repairs to an abandoned oil tanker off its coast might not carry the ring of urgency normally associated with a major disaster.
But now that the world knows what happened when Lebanese officials ignored warnings for years over a cache of highly explosive material stored in a Beirut port warehouse, the importance of resolving the FSO Safer issue cannot be overstated.
• Twitter: @saeedalBatati