DUBAI: Near the town of Ras Al-Ain in Hasakah, in northeastern Syria, empty jerry cans were piled high on the roadside, where women and their restless children waited in the blistering heat for trucks to bring water to their parched community. Just a few days earlier, Turkish occupation forces had once again cut off the water supply from the Alouk pumping station, five kilometers away.
This critical facility normally supplies drinking water to nearly 1 million people in Hasakah. Without it, the province goes thirsty.
“We had no water for a month,” recalled Ahmed Zubair, 22, who works at a local phone shop. “Without water, we can’t protect ourselves against the coronavirus disease (COVID-19). This is a reason for the spread of disease, because there’s not enough water for cleaning, only for drinking. This is a danger for children and for society in general.”
Xelil Osman, a local delivery driver, said: “We were delivering water to the people with trucks. The water situation is really bad, and we always worry it won’t be enough for the people. If there is water, we deliver it. But if there is none, we have nothing to deliver.”
It was no accident of fate that water had to be delivered by road to tens of thousands of Kurdish residents in Ras Al-Ain and surrounding areas in Hasakah for nearly four weeks since Aug. 13.
In October last year, Turkey and its Syrian rebel proxies launched their self-proclaimed Operation Peace Spring, targeting the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) in northeastern Syria. The SDF is mostly made up of members of the People’s Protection Units, which Turkey considers a terror group because of its ideological connection to the Kurdistan Workers’ Party, whose armed struggle since 1984 for greater Kurdish rights evolved into an insurgency over time.
The SDF had spearheaded the US-backed coalition campaign against Daesh in northern Syria, destroying the militants’ last holdouts in Deir ez-Zor in March 2019. However, in a “betrayal” that stunned coalition partners and shocked the US foreign-policy establishment, Washington did nothing when Ankara launched a massive assault on the SDF in October 2019, forcing it to withdraw from its positions along the Turkey-Syria border.
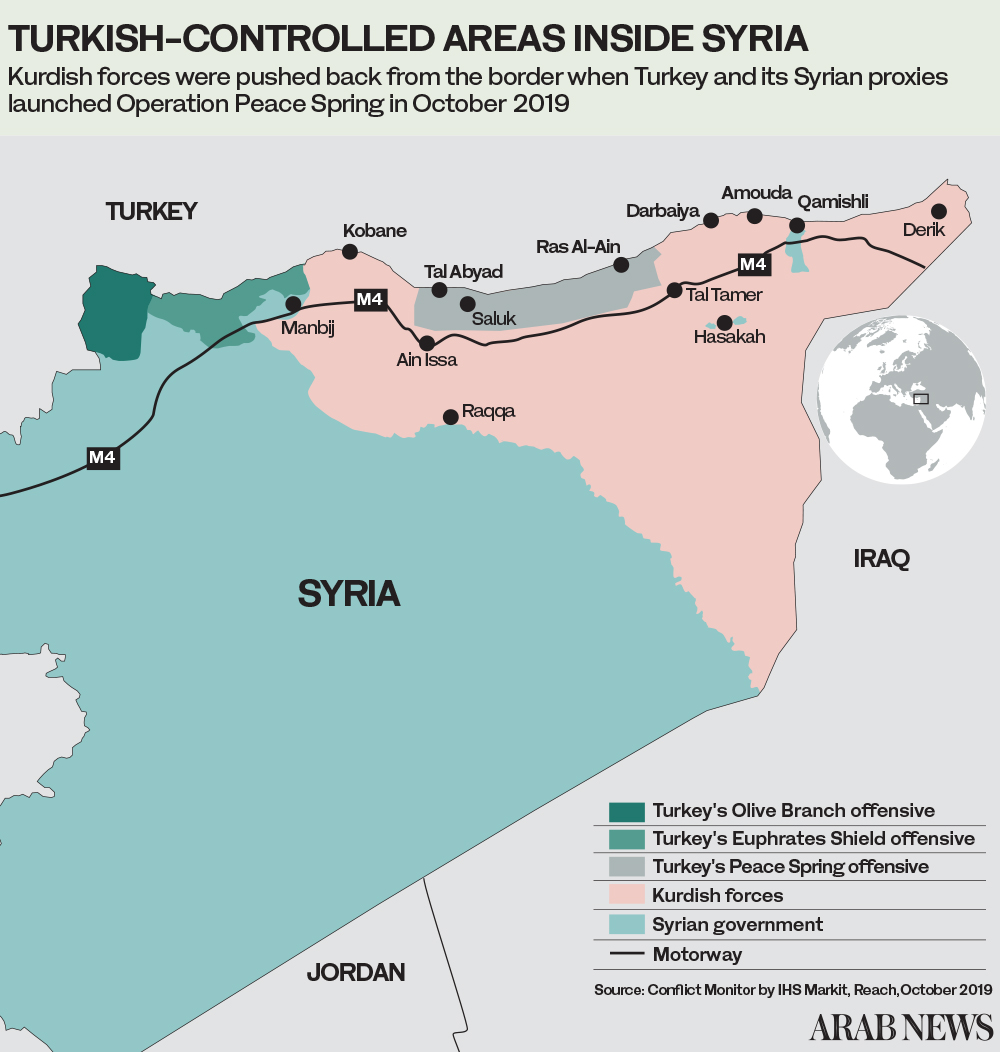
Just a few hours into Turkey’s cross-border offensive, artillery shells hit the Alouk pumping station, immediately putting it out of service. Although the facility has since been repaired with international oversight, it remains under Turkish control.
Under the circumstances, the area’s limited water reserves can be exploited at will, regardless of what international humanitarian laws guarding civilian infrastructure say. This puts additional pressure on the Kurdish-led Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (NES), which currently administers the area also known as Rojava.

A Kurdish boy takes his turn to get his share of water delivered by trucks near the town of Ras Al-Ain in Hasakah, northeastern Syria. (Photo courtesy of Jamal Photography)
“The NES has dug a few water wells as an alternative, but this does not provide enough water,” Wladimir van Wilgenburg, a political analyst and journalist who covers Kurdish affairs, told Arab News. “The only solution is for the international community to put pressure on the Turkish government to stop cutting off water to parts of northern Syria.”
When the taps ran dry in August, the international community began applying pressure on Ankara, but with little success. James Jeffrey, the US special envoy for Syria, reportedly urged the Turkish leadership to resume water supplies, while Russian military engineers in the area set to work on a pipeline to help quench Ras Al-Ain’s thirst.
Russia backs Syrian President Bashar Al-Assad, whose regime is locked in a low-intensity war with Turkish forces in the northwestern province of Idlib and in a three-way contest with the Turks and the SDF over control of northeast Syria.
Russia is keen to win favor with the Kurds to help promote a diplomatic solution to the civil conflict in Syria. Moscow believes the Kurds must be included in constitutional talks with the regime, otherwise a mutually accepted government and a unified country will not be possible.
The stated aim of Ankara’s Operation Peace Spring was to force the SDF back from the Turkish border by creating a self-declared safe zone reaching some 30 kilometers into Syrian territory.
Almost a year on, and with the US now bolstering its Syria deployments with Sentinel radars, additional fighter patrols, and Bradley Fighting Vehicles in its escalating rivalry with Russia, the area remains anything but safe.
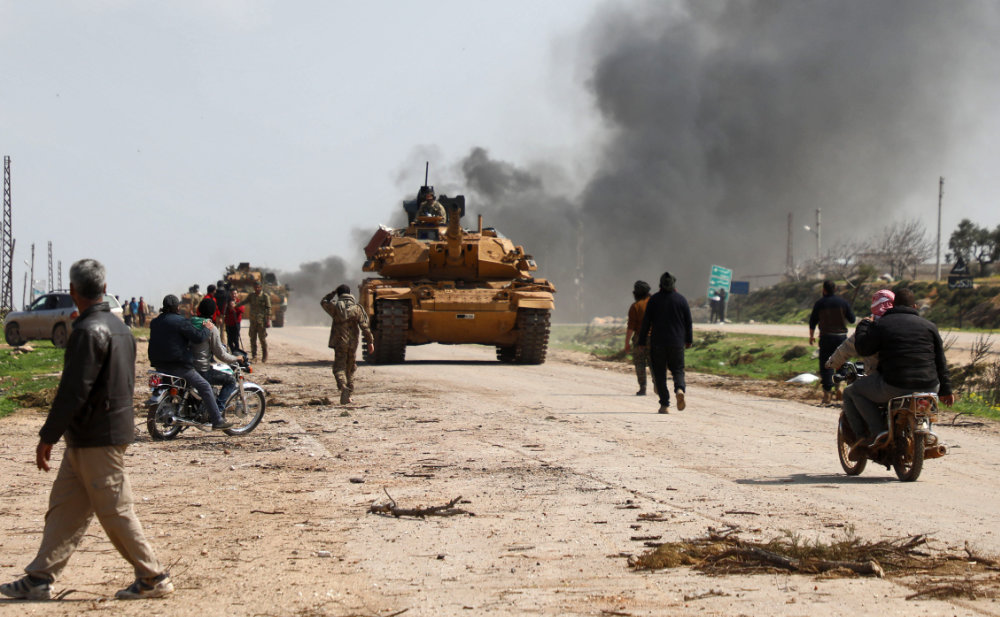

A Turkish military battle tank is seen along the M4 highway, which links the northern Syrian provinces of Aleppo and Latakia, in this March 15, 2020 file photo. (AFP)
“I am from Ras Al-Ain. After Turkey occupied my town and cut off the water from the Alouk pumping station, people in Hasakah, who have already been living in difficult conditions, did not have any water for drinking or washing, and this was all in the middle of the COVID-19 crisis,” Muhammed Baqi, of the Hevy Organization for Relief and Development, told Arab News.
“The Kurdish administration tried to drill a water well called Al-Himme Water Station, but it did not work because the water they drilled was not drinkable — it was only good for washing,” he said. “The amount of water from this well was also not enough. Alouk continues to be the main source for water in Hasakah.”
Disputes over the supply of electricity to the Alouk pumping station appear to have inflamed an already tense situation.
According to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a Britain-based watchdog, the Turkish side cut off Hasakah’s water supply to pressure the NES to supply more electricity from its Mabrouka power plant to areas controlled by Turkey’s Syrian proxies. But Turkey’s Ministry of National Defense insisted in early August that Alouka was under maintenance and that Hasakah was continuing to receive water.
“Though the Alouk pumping station has been fixed under international mediation, Turkey regularly cuts the water flow to NES areas and prevents repairs from taking place,” said Thomas McClure, a researcher at the Rojava Information Center.
“Turkey has cut off the water supply from Hasakah 13 times this year, according to the UN, in order to exert political pressure on the NES.
“Most recently, the whole Hasakah region spent two weeks in the sweltering August heat totally without water, and some neighborhoods spent over two months without a drop of water being delivered.”
As COVID-19 cases rise and temperatures remain high, all efforts to reopen the Alouk pumping station have failed. Meanwhile, the Kurdish Red Crescent and other aid agencies have struggled to find alternative water sources for the region.
The Al-Himme Water Station offers a partial solution for now. “However, it doesn’t cover more than 25 percent of the people’s needs,” said Bassam Al-Ahmad, director of Syrians for Truth and Justice, a nongovernmental organization working on documenting human rights violations in Syria.
“The long-term solution is for Turkey to withdraw from northern Syria. It is Syrian land. At the moment we need a strong international position against Turkish assaults.”
Pressing for justice, local aid agencies say Turkey has not only broken international humanitarian law by denying Hasakah access to running water but has actually committed a war crime. They say that since the water-pumping stations and dams of northeastern Syria are located near the front lines, their protection is vital for the well-being of the local population.
“According to international humanitarian law and the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, to cut the water supply to a civilian population is a crime against humanity and a war crime,” Sara Montinaro, a lawyer and project manager for the Kurdish Red Crescent, told Arab News.
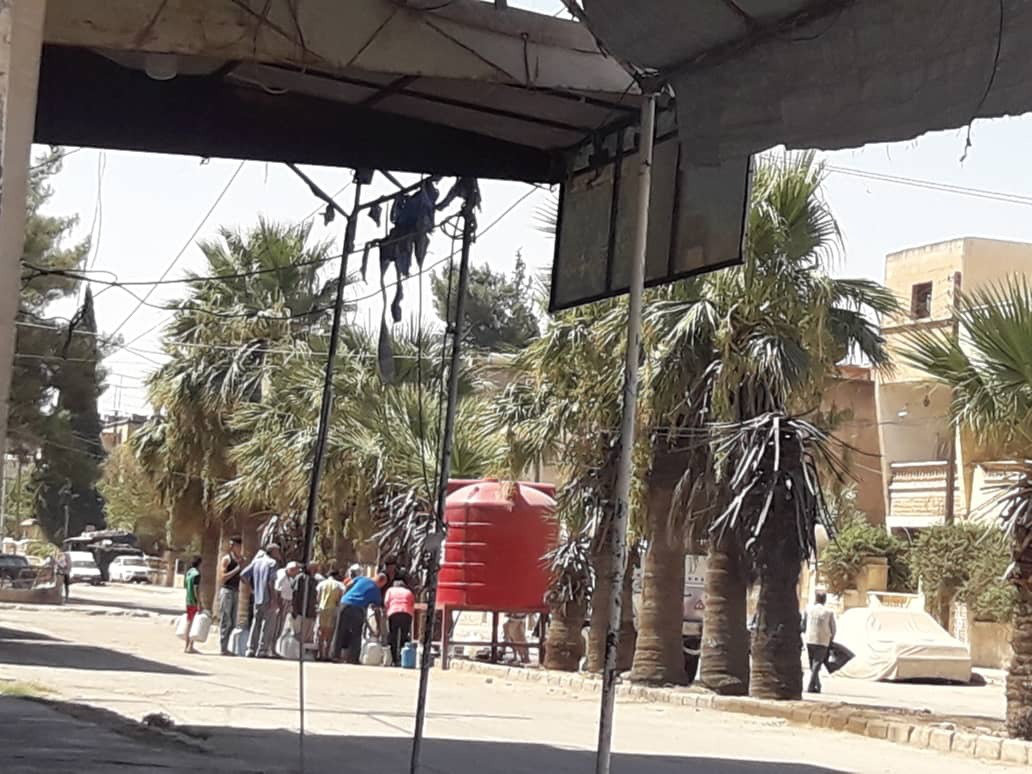

Residents queue for water near the town of Ras Al-Ain in Hasakah, northeastern Syria, after Turkish occupation forces cut off the water supply for their community. (Photo courtesy of Jamal Photography)
According to the Geneva Conventions and their Additional Protocols, military operations must be conducted in accordance with international humanitarian law and avoid the destruction of objects indispensable to the survival of the civilian population, including water and sanitation.
“With the current COVID-19 situation, the situation on the ground is even worse than before, yet Turkey does not seem to be changing its behavior towards the Syrian Kurds,” Montinaro said.
“There are now several statements from the UN asking Turkey to stop cutting off water from the people, but until now they haven’t done anything. What is happening is a violation of international humanitarian law.”
For now, the women on the roadside near Ras Al-Ain must continue intermittently to rely on water trucked in by road until a more sustainable source can be found and secured — or Turkey lifts its boot off the hose.
-----------------
Twitter: @rebeccaaproctor









































