DUBAI: When the tanker Al-Barrah cast off from the Saudi Arabian port of Al-Jubail in the summer, it looked like just another shipment of crude from the resource-rich Kingdom. In fact, it could prove to be the launch of a revolution in global energy consumption.
The ship was carrying “blue” ammonia, a chemical that can be used to generate clean power for industrial and domestic consumption, and was destined for environmentally-conscious Japan for use in the country’s power stations.
It was the first ever such shipment in the world, demonstrating that the chemical could be loaded and transported safely and cost-effectively, but it also showed the enormous potential power of what some energy experts are calling “the H Factor” - the huge possibilities presented by hydrogen — the essential ingredient of ammonia — in the global energy mix.
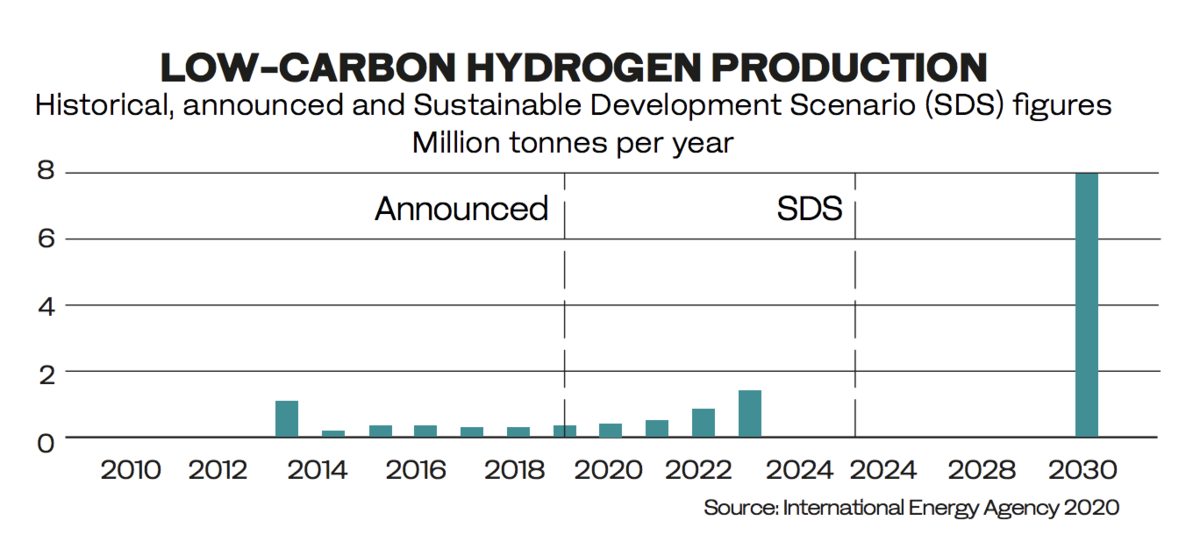
At about the same time as the Al-Barrah sailed, on the other side of the Kingdom, hydrogen was also moving to the center of the energy mix with a $5 billion plan by NEOM, the mega-city planned as part of the Vision 2030 strategy, to develop “green” hydrogen as its main power source. Developed in conjunction with Saudi and international energy companies, NEOM also aims to export green hydrogen. It is the biggest hydrogen project anywhere in the world.
Using hydrogen as a fuel is not a new technology. The space industry has been using it in liquid form for decades for rocket propulsion. But it does not occur in nature as a stand-alone chemical, so has to be extracted from various compounds.
Most industrial use involves separating it from methane gas — a common by-product of fossil fuels — but it can also be produced via the electrolysis of water. If the electricity used in this process is generated from a renewable source, like solar or wind power - then the end product is “green hydrogen.” “Blue ammonia” is a practical halfway house to completely “green” hydrogen.
THENUMBER
$5 billion
Size of NEOM’s plan to develop hydrogen as its main power source.
The beauty of the chemical is that it combines enormous power generation with zero emissions. Several countries have used it in fuel cells to power electric vehicles, but it has not been adopted widely for two very good reasons. “It is explosive and expensive,” Christof Ruehl, senior research scholar Columbia University’s Centre on Global Energy Policy, told Arab News.
Its explosive properties make production and transportation a challenge, while the cost of generating it makes it less efficient as a fuel compared to traditional hydrocarbons. “People have been trying to crack that nut forever and so far it has not worked, at a reasonable price,” Ruehl said.

Peter Terium, NEOM’s managing director of energy, water and fuel at the mega-city under construction in Saudi Arabia’s northwest, explained to Arab News how the city plans to make hydrogen cleanly. (Supplied)
This is where NEOM comes in, as Peter Terium, managing director of energy, water and fuel at the mega-city under construction in Saudi Arabia’s northwest, explained to Arab News. “Much of the hydrogen currently produced is from natural gas, leading to significant carbon dioxide emissions. However, instead of producing hydrogen from natural gas, at NEOM we plan to make it cleanly by applying renewable and carbon free electricity to water to produce green hydrogen.
“This would bring significant benefits to the climate, but the potential extends much further. It is a fuel in its own right, demonstrated by the increasing number of cars, trucks and buses running on this clean fuel. In addition to industrial sectors, it can also replace natural gas in the heat and power markets,” Terium said.
Saudi Arabia has some big natural advantages in the race to make hydrogen a real alternative to hydrocarbon. “While the opportunity is immense, the advancement of the hydrogen sector is not without its challenges. The availability of high levels of cost-effective renewable electricity is integral to its viability. This can only be found in a few countries of the world. The Kingdom, with abundant potential for low cost solar and wind energy, is one of them,” Terium said.
The attractions of hydrogen give it a potentially crucial role in the transition away from hydrocarbons — oil, gas and coal — as the world’s main energy source. Most energy experts believe that while fossil fuels will continue to be exploited extensively over many decades to come, their use will have to be reduced, and the industrial processes that produce them and use them made cleaner, if the world is to reach its climate change targets by 2050, as the Paris Agreement on climate change requires.
*****
READ MORE: Saudi Arabia could enjoy revenue ‘feast’ from changing oil demand: energy expert
*****
“Nations across the globe are alert to its tremendous potential as a viable alternative to fossil fuel. The European Union is aiming for a net-zero economy by 2050 and recently set ambitious 2024 and 2030 targets for green hydrogen.
“Japan is also firmly focused on the sector and has a strategy for a national hydrogen economy, while a number of other leading countries have plans in the pipeline. The World Energy Council estimates that by 2025 nations with a dedicated hydrogen strategy will cover more than 80 percent of the global GDP,” Terium said.
Hydrogen has also caught the attention of the big financial institutions which have recently been downsizing their investments in traditional energy sources.
“Hydrogen, the first, lightest and most abundant element in the universe, could supply our energy needs, fuel our cars, heat our homes, and help to fight climate change. All while generating $2.5 trillion of direct revenues and $11 trillion of indirect infrastructure potential by 2050, while jumping 6x in volumes. We believe we are reaching the point of harnessing the element that comprises 90 percent of the universe, effectively and economically,” Haim Israel, an investment strategist at Bank of America, said in a recent report.

When the tanker Al-Barrah cast off from the Saudi Arabian port of Al-Jubail in the summer, it looked like just another shipment of crude from the resource-rich Kingdom. In fact, it could prove to be the launch of a revolution in global energy consumption. (Supplied)
“Renewable electricity cannot provide the entire solution for decarbonization: 80 per cent of energy today comes from fossil fuels rather than renewable sources. Green hydrogen could be key in the fight against global warming, providing up to 24 per cent of our energy needs by 2050, helping to cut emissions by up to 30 percent, he wrote in a report entitled “The H Factor: Planet of the greens needs a new molecule.”
Israel compared the underexploited attractions of hydrogen to the internet in the 1990s, or smartphones before the Apple iPhone.
Saudi Aramco already appreciates the advantages of hydrogen, as the Al-Barrah voyage showed. Amin Nasser, president and chief executive of the company, said recently: “We think hydrogen will play a major role in the long term, and maybe it has a major advantage over solar and wind because you can utilize it not only in light vehicles you can also utilize it in trucks, shipping and aviation, and also in power generation, so it is exciting.”

A view of ammonia tanks at an industrial plant at the Jubail Industrial City, about 95 kilometres north of Dammam in Saudi Arabia's eastern province overlooking the Gulf. (AFP/Getty Images/File Photo)
The Al-Barrah cargo was an example of the synergies that come from Aramco’s link-up with SABIC, the Kingdom’s petrochemicals giant which produced some of the chemical, as well as international alliances with Japanese corporations which pioneered the use of hydrogen as a fuel 20 years ago.
It is also a key element of the Kingdom’s plan for tackling climate change via the “circular carbon economy,” the strategy adopted by Prince Abdul Aziz bin Salman, the Saudi energy minister, and endorsed at a recent meeting of G20 energy ministers.
Is there any contradiction between the Kingdom’s position as the world’s biggest oil exporter and its enthusiastic advocacy of a fuel that will ultimately compete with hydrocarbon resources?
At NEOM, Terium does not see it that way. “Carbon-intensive hydrogen can be replaced entirely by green hydrogen over time, though a mixed model can be used to enable a gradual implementation. Green hydrogen then becomes complementary to hydrocarbons, supporting the reuse and recycle pillars of the circular carbon economy,” he said.
--------------------
Twitter: @frankkanedubai





























