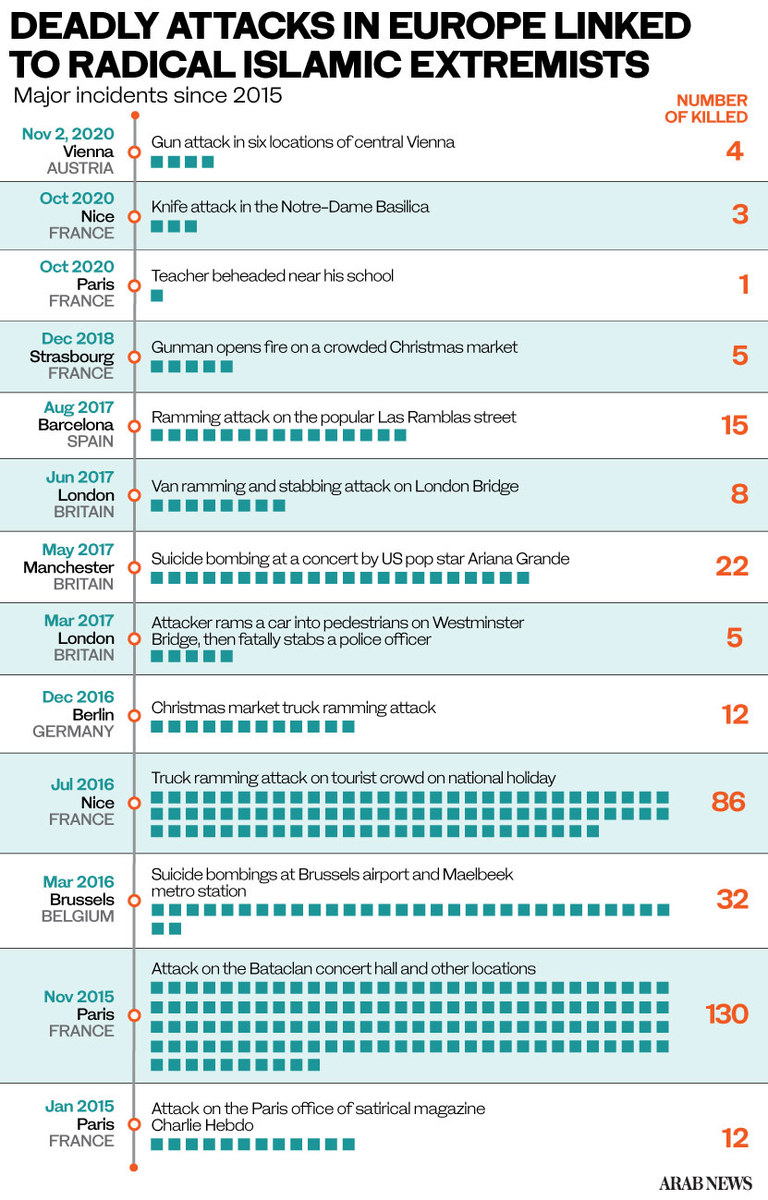
LONDON: Terrorism has once again reared its proverbial ugly head in Europe. While all eyes were fixed on the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, a string of incidents in late October shook the continent to its core.
Three deadly attacks by Islamist extremists in France and Austria served as a visceral reminder that Europe’s pre-pandemic problems are anything but resolved.
In fact, according to experts, the pandemic and its subsequent lockdowns may have actually fueled radicalization and pushed the threat of terrorism to new heights, and that fiery rhetoric from non-Western political opportunists is not helping either.
In response to the developments, the UK raised its terrorism threat level to “severe” — indicating an attack is “considered highly likely.” But observers are now asking whether more can be done to prevent further incidents in Britain or elsewhere.
Hedda Halvorsen, Europe analyst at the London-based political risk consultancy Sibylline, says it is notoriously difficult to prevent attacks such as those carried out in France and Austria — particularly at a time of such high tensions.
According to her, the focus should instead be on preventing radicalization from happening in the first place — a significant challenge in the middle of a pandemic that has created an environment highly conducive to extremist recruitment.
“The pandemic has created conditions in which radicalization efforts are a lot easier,” she told Arab News. “People from minority backgrounds have been shown to be the most impacted by the pandemic financially, and have also been affected in terms of rising xenophobia.
“People that were already feeling disenfranchised and disconnected from mainstream society may have felt like they were being pushed even further to the side.”
Furthermore, Halvorsen said, “people are spending much more time alone, in isolation and online, creating optimal conditions for radicalization efforts to take place.”
Groups like Daesh and Al-Qaeda, as well as various rightwing extremist groups, were already trying to exploit these conditions to push their ideologies, she says. But when controversy erupted over French President Emmanuel Macron’s remarks in the wake of the beheading of a school teacher by a radicalized Muslim refugee of Chechen origin, these groups saw another opportunity to sow chaos.
Macron’s comments and the ensuing diplomatic firestorm “contributed to an overall rising of tension,” Halvorsen said, which was then seized upon by radical groups.
“Al-Qaeda and Daesh have been encouraging Muslims in every country to avenge the insult to their religion because of these cartoons, so there is certainly a heightened threat level at the moment,” she said.

Sure enough, two attacks by Daesh affiliates followed the beheading of Samuel Paty, a French history teacher who was targeted by an online campaign in the lead up to his murder for showing caricatures of Prophet Muhammad in a free-speech class.
Halvorsen made clear, however, that it is not just clandestine terrorist groups that added fuel to the fire in the wake of the Macron controversy. Various current and former leaders of the Islamic world were outspoken in their condemnation of the French president, but Halvorsen singles out Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s reaction as being particularly inflammatory.
Erdogan questioned whether Macron needed “some sort of mental treatment” over his attitude toward Muslims in France, and asked: “What is Macron’s problem with Islam? What is his problem with Muslims?”
His words sparked a diplomatic furore, with France recalling its ambassador from Turkey and an Elysee spokesperson branding the comments “unacceptable,” before demanding “Erdogan change the course of his policy because it is dangerous in every way.” The damage, however, may have already been done.
Rakib Ehsan, a research fellow at the UK’s Henry Jackson Society, echoed Halvorsen’s analysis of the role of both extremist groups and “unhelpful” foreign governments in encouraging terrorism.
These attacks “have taken place after the likes of Islamic State (Daesh) have encouraged jihadists to step up their activities, sensing that a number of European countries may be more vulnerable due to their preoccupation with the COVID-19 pandemic,” he told Arab News
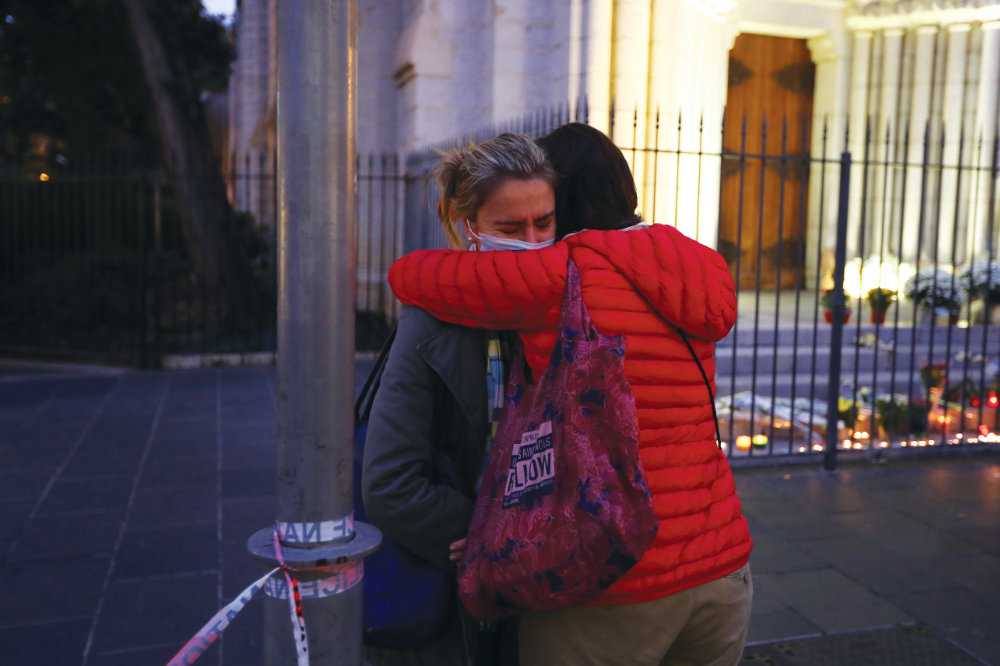

Two women react to the attack at the Notre-Dame de l’Assomption Basilica in Nice by a knife-wielding murderer. (AFP)
Halvorsen said: “This use of language, for example saying that Macron needs mental checks, but also making comparisons to Nazi Germany, and accusing leaders of being anti-Muslim, might be picked up by someone who might already be on the edge or might just be tipped over.”
She stopped short of saying his words directly caused the attacks, but argued that “this stark rhetoric from leaders such as Erdogan did come before the attack. I’m not saying that that was a direct result of it, but I do think that we have to look at the potential of leaders who come out with these statements having an impact on vulnerable individuals.”
Halvorsen added: “The reactions of French President Emmanuel Macron and Austrian Chancellor Sebastian Kurz have been robust and mature — pointing out the threat posed by Islamist separatism to liberal-minded secular Muslims in their respective countries.
“However, unhelpful interventions by President Erdogan … have the potential to feed Islamist separatism in Europe.”
Ehsan said the threat of terrorism remains serious across the continent and that European unity may serve as something of an antidote to Erdogan’s poison.
“Recent terrorist attacks in France and Austria have collectively served as a brutal reminder of the prevailing terror threat of Islamist extremism,” he said. “It is vitally important that European leaders present a united front in the face of divisive non-Western political figures who threaten to create further instability in European societies.”
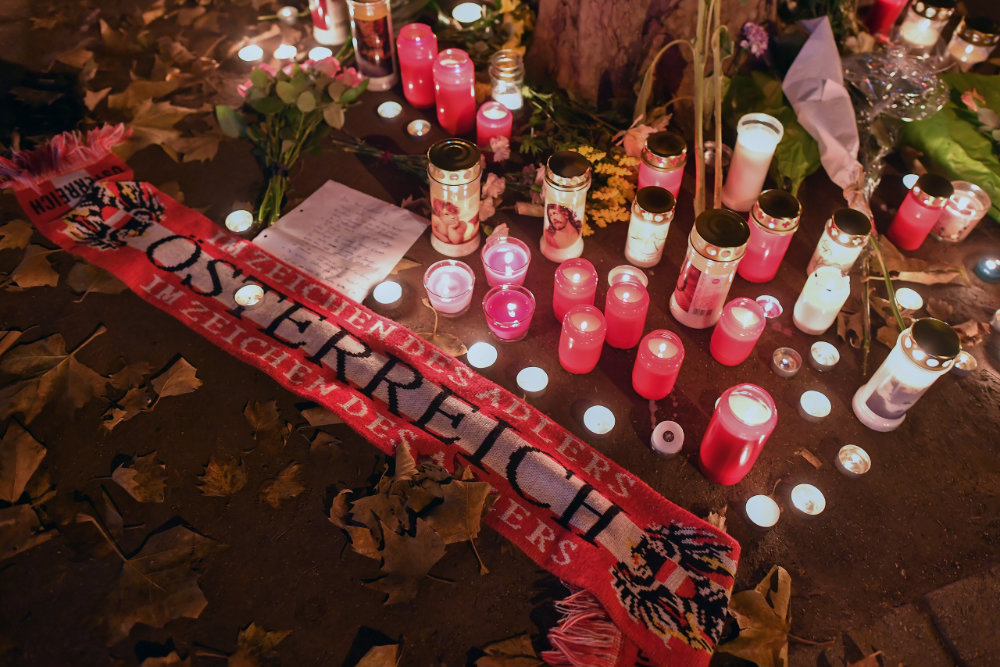

Flowers, candles and an Austria scarf are left at a memorial site at the scene of an attack in Vienna, Austria on Nov. 3, 2020, one day after a shooting at multiple locations across central Vienna. (Photo by JOE KLAMAR / AFP)
Macron and other European leaders are now looking at drastic measures to help prevent future attacks. Immigration is high on Macron’s list, since one of the attackers in France was a Tunisian man who had only recently arrived on the continent. Border security is also likely to occupy officials in Austria, as the Vienna attacker had reportedly tried to purchase ammunition in neighbouring Slovakia.
“I am in favor of a deep overhaul of Schengen to rethink its organisation and to strengthen our common border security with a proper border force," Macron said recently during a visit to the Franco-Spanish border, calling the recent attacks a warning to Europe that "the terrorist risk is everywhere.”
European migration policies, Halvorsen said, have undoubtedly played a role in increasing the threat of terrorism on the continent. Not least because “there are clandestine migrant smuggling networks by organized crime gangs that link in with terrorism.”
This will not be an easy process, however. “It is a very difficult and sensitive issue in many ways, especially when you talk about making changes to free movement across Europe, which is such an essential part of the European project,” she said.
More likely than reform of internal migration policies is the strengthening of Europe’s external borders. “This string of attacks in France and Austria could potentially make some countries more likely to increase security, especially around the external borders of the bloc,” she added.
However, any changes to European movement policies could take months or even years to process. Meanwhile the threat of more attacks is immediate.
_______________________
• Twitter: @CHamillStewart





























