MISSOURI, US: Iran’s woes during 2020 proved worse than most. The year began with shockwaves from the fuel price hike protests (which broke out in late November 2019) still reverberating all across the country.
Then on Jan. 3, the US assassinated Qassem Soleimani, Iran’s regional “shadow commander.” On edge due to fear of another American or Israeli attack, Iranian air defense forces then mistakenly shot down a Ukraine-bound civilian airliner minutes shortly after it took off in Tehran, killing all 176 people on board.
Almost one year later, authorities in Tehran have still not managed to rectify the problems or vulnerabilities that emerged so starkly in January 2020.
Key Iranian figures still look like easy targets for American or Israeli covert operations, as evidenced by the November 27 assassination of top nuclear scientist Mohsen Fakhrizadeh.
Fakhrizadeh was in Tehran when an AI-controlled machine gun from another vehicle targeted his car.
Three months earlier the Israelis also killed a top Al-Qaeda commander, Abu Muhammad al-Masri, who had found refuge in Iran.
Like Fakhrizadeh, Al-Masri was gunned down in broad daylight in the streets of Tehran. In this case, the assassins escaped on motorcycle.
Most observers believe the Israelis conducted the assassination at America’s behest.
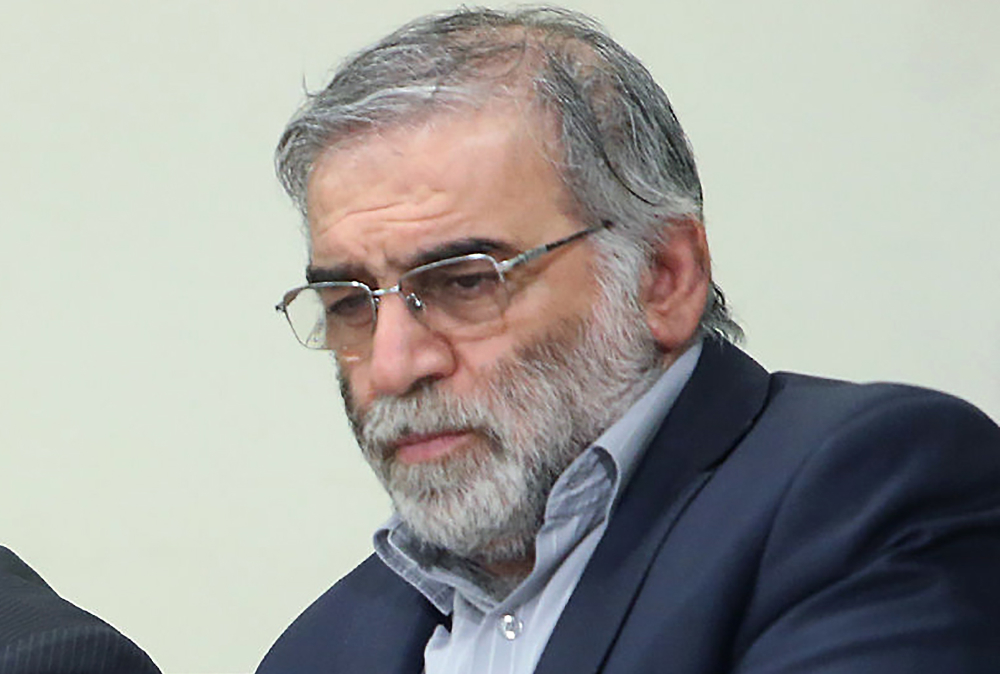

Top nuclear scientist Mohsen Fakhrizadeh was assassinated in November. (AFP)
Al-Masri masterminded the 1998 attacks on US embassies in Africa, and his killing occurred on Aug. 7, which was the anniversary of the embassy attacks.
As the Iranian economy remains belly-up from American-led sanctions, the same popular discontents that caused the late 2019 protests continue to simmer.
Iranian authorities’ rush to intimidate and silence protestors led them in September to hang popular Iranian wrestler Navid Afkari.
Afkari was only one of many executed by the regime in 2020 for what most viewed as political crimes.
Worldwide condemnations of Iran increased accordingly. At the UN, Canada brought forward a successful resolution in November condemning the human-rights record of the regime.
Referring back to the protests at the end of 2019, Amnesty International completed research concluding that the Iranian state killed 304 people, including children, during the protests and arrested thousands more.

Iran either lacks the ability or fears the consequences of direct attacks on its more serious enemies. (AFP)
Iran responded to the UN resolution and other criticisms by claiming they have “no legal validity” and otherwise ignoring them.
In response to the assassination of some of the regime’s most key figures, Tehran vowed serious retaliation — but shows little capacity for following through on such threats against America or Israel.
Iranian cat-and-mouse games with the US fleet in the Gulf in 2020 did nothing but raise tensions a bit, at the same time that the Americans seized a number of Iranian vessels transporting fuel to Venezuela in August.
Last week, as Israel sent one of its submarines through the Suez Canal towards the Gulf, Iran again replied with only threats.
Throughout 2020 Israel continued to hit Iranian personnel in Syria with air strikes and missiles.
All the while, Tehran seemed impotent to stop them. Under such circumstances Iran’s 2020 launch of its first military satellite, the unveiling of new missiles, and holding annual war games only looked like so much bravado.
The September-November Nagorno-Karabakh war between Armenia and Azerbaijan added to Tehran’s headaches during this period.
Iran used to play an important role in the Caucasus region and even mediated past disputes between Armenia and Azerbaijan. They have since been eclipsed by Turkey and Russia, with no say in the latest war or its resolution.
Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan even visited his victorious allies in Baku in December and read a nationalist Azeri poem there which seemingly makes claims upon the Azeri region of northwest Iran. The reaction from Tehran was loud but otherwise toothless.

Since then COVID-19 has killed over 50,000 Iranians and infected some 1.1 million. (AFP)
On top of the economic and political problems, COVID-19 appears to have hit Iran harder than most. In Feb. 2020 — before anywhere else in the Middle East — Iran experienced its first wave of the virus. Since then COVID-19 has killed over 50,000 Iranians and infected some 1.1 million.
The virus led to economic shutdowns and closures that competed with US-led sanctions to see which could damage the country more.
With a vaccine now coming out, Iranian authorities are accusing the US of blocking their access to vaccinations as well as to international loans to help combat it.
All these difficulties highlight a central, inescapable reality for 2020: The Iranian state saw itself significantly weakened and incapable of protecting, much less securing, its principal interests.
Although the regime in Tehran remains quite capable of kidnapping or killing Iranian dissidents abroad (such as a Paris-based dissident leader recently kidnapped from Iraq and a Balochi activist murdered in Canada last week), the same does not hold true for American and Israeli targets.
Iran either lacks the ability or fears the consequences of direct attacks on its more serious enemies.
Even indirect responses have serious limitations. Iran’s foes assassinated Soleimani after his supposed role in spurring on Iraqi Shiite militias to launch rockets on American bases in that country.
Any dramatic Iranian move to avenge attacks on its people — even if carried out by an Iranian proxy rather than Tehran itself — thus appears too risky for a regime so outclassed by the Americans and the Israelis.
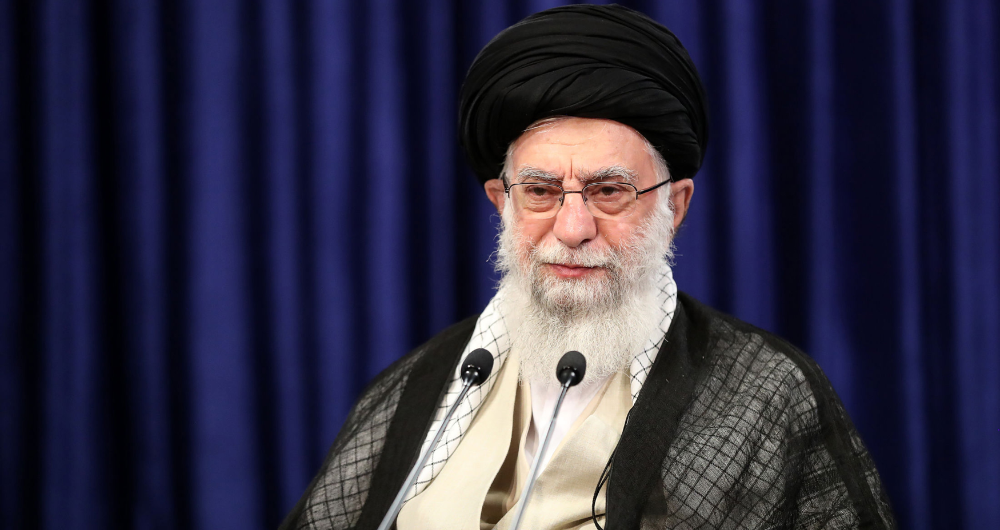

Iran's Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. (AFP)
Less dramatic Iranian stratagems, such as pressuring the Shiite-led government in Baghdad to evict American forces from Iraq, likewise seem limited in terms of what they can accomplish.
Iraqis, including Shiite ones, have their own interests and problems, leading to them to continue working with Americans in Iraq.
If the incoming Biden administration in the US proves savvier than Obama and his advisers were regarding Iran, they will take this Iranian weakness into account.
Although President-elect Biden has clearly expressed his desire to return to the nuclear accord’s framework agreement with Iran, he may do so more carefully than his predecessors.
The Obama administration’s mistake with Iran involved treating the regime there as if it were a deer that might get “spooked” away from negotiations.
As a result, the Obama administration halted all kinds of US anti-Iran efforts unrelated to the negotiations.
This included, for example, shutting down a major multi-year Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) investigation into Lebanese Hezbollah’s international money laundering.
The net effect of Obama and Secretary of State John Kerry’s efforts to “encourage negotiations” was to empower Iran and give it carte blanche to do whatever it liked.
A more sophisticated Biden administration policy would be to consider negotiating to resume the nuclear deal with Iran while truly keeping other unrelated matters separate.
This would mean maintaining a good deal of US pressure as well as non-nuclear related sanctions on Iran. In effect, the Iranians would receive at the most a partial lifting of sanctions for abiding by the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (a.k.a. the “nuclear deal”).
If the Iranians wanted relief from other sanctions, such as the ones applied for supporting terrorism, they would have to adjust their behavior accordingly.
In the final analysis, if the incoming Biden administration proves sufficiently savvy to take advantage of Iran’s annus horribilis, they could thus conceivably contain both Iran’s nuclear weapon ambitions and its more destabilizing policies in the region.
Such a more nuanced approach would in turn reassure other Middle Eastern allies that Iran is not simply getting its Obama-issued carte blanche back.
• David Romano is Thomas G. Strong Professor of Middle East Politics at Missouri State University

































