RIYADH: Yemen’s Iran-backed Houthi militia has responded to its removal from Washington’s list of Foreign Terrorist Organizations (FTO) by escalating its attacks on the governments in Aden and neighboring Saudi Arabia, Brigadier General Turki Al-Malki, spokesperson for the Saudi-led Coalition, has told Arab News in an exclusive interview.
The US State Department branded the Houthis (also known as Ansar Allah) an FTO on Jan. 19 this year in one of the final acts of the Donald Trump administration in its “maximum pressure” campaign against Iran and its proxy armies in the Middle East.
Far from repaying the Joe Biden administration’s gesture of reversing the designation on Feb. 15, Al-Malki says the Houthis have actually escalated their attacks on Yemeni government forces and its cross-border missile and drone assaults on Saudi civilians and infrastructure.
“We think the Houthis have misinterpreted the decision to be delisted from the FTO,” Al-Malki said.
“That has led them to start increasing their hostile acts and to start increasing the number of attacks using ballistic missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) inside Yemen and toward its neighbors.”
Al-Malki, who has served as Coalition spokesman since 2017, believes the Houthis’ terror designation had been well deserved given its behavior, which closely resembles the activities of Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and Daesh.
“If you go back to the threat by the Houthis in 2016, the Houthi militia targeted an American vessel, a military ship, called the USS Mason, and the American administration at that time struck a couple of targets inside Yemen to counter that attack,” Al-Malki said.
“There is no difference between the Houthi militia’s activity in the southern Red Sea and also the Bab Al-Mandab compared to that of Al-Qaeda in Yemen, which also struck an American ship back in 2000, called USS Cole. So, it is the same activity they are doing. The threat is not just for the Kingdom,” he said.
“The only difference between the Houthis and other terrorist groups around the world is, first of all, they are the first group that has obtained ballistic missiles, UAVs, cruise missiles and bomb-laden USVs — and that’s never happened, that a terrorist group has obtained this kind of capability.
“Also, the Houthis want to practice their terrorist acts under the frame of a country. If we look at Daesh, AQAP and other terrorist groups around the world, they mostly work independently ... . But they (the Houthis) want to practice their ideology, they want to practice their malign activity, under the umbrella of a Yemeni government. These are the only two differences.”
Although Al-Malki believes the escalation of violence — including the Houthis’ latest assault on Marib — is part of a wider strategy to negotiate from a position of strength, he argues the militia’s backers in Tehran are in fact exploiting the conflict to bolster their own bargaining power in future talks over its nuclear program.
THENUMBER
$430m
* Saudi Arabia’s donation to Humanitarian Response Plan of UN agencies for Yemen in 2021.
“When we talk about Marib, I think the Houthis … want to come to the table with a strong hand. They want to have Marib under control so when they come to the table they can give some concessions,” Al-Malki said.
“The Iranian intervention is making things complicated in Yemen, because they are escalating the situation right now knowing that they want to sit with the P5+1 in their nuclear agreement and they want to use Yemen as a card. And I am sure the Houthis can see this.
“They are just a card in the hand of the Iranians, of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), and they (the Iranians) are going to give it away the first (thing when they) sit at the (negotiating) table.”
Fighting in Yemen escalated in 2015 when the Houthis overthrew the UN-recognized government of President Abed Rabbo Mansour Hadi. Backed by multiple global and regional actors, the Coalition launched a military campaign to restore the legitimate government to power.

Coalition spokesman Brigadier General Turki Al-Malki giving explanations during a press conference, in Riyadh, on the missile debris fired on March 28 by Yemeni Houthi militia. (AFP/File Photo)
Iran’s support for the Houthis has been an open secret since long before the Houthi takeover of Sana’a in 2015. It has allowed the brutal war to rage on unabated and one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises to fester. In fact, Al-Malki believes Tehran has no interest in peace in Yemen until conditions favor its own geopolitical agenda.
“The IRGC generals, with the support of the Iranian regime, don’t want good faith or talks between the Houthis and the Americans, the international community, the Yemeni government and the Coalition … . They want to make things complicated. They don’t want the Yemenis to reach a political solution to end the crisis in Yemen.”
For Al-Malki, it is Tehran’s supply of advanced weaponry to the Houthi militia that has allowed the war in Yemen to grind on for six long years.
“When the campaign started, we knew exactly what the capability of the Yemeni national army was. Yet we saw how the Houthis started launching ballistic missiles and UAVs towards the cities and the villages of the border,” Al-Malki said.
“Looking at the timeline, they started increasing their capability, trying to attack Taif. Then they were trying to attack Makkah, which irritated millions of Muslims around the world. And they have started going further in their range to Yanbu and to Riyadh, and also lately they have been trying to attack Saudi Aramco in Dhahran.
“The point is, the Houthis, they don’t have that capability. They have been provided with this capability by the Iranian regime. All the indications, all the physical evidence that we have shown, it shows that the Iranians are involved.”

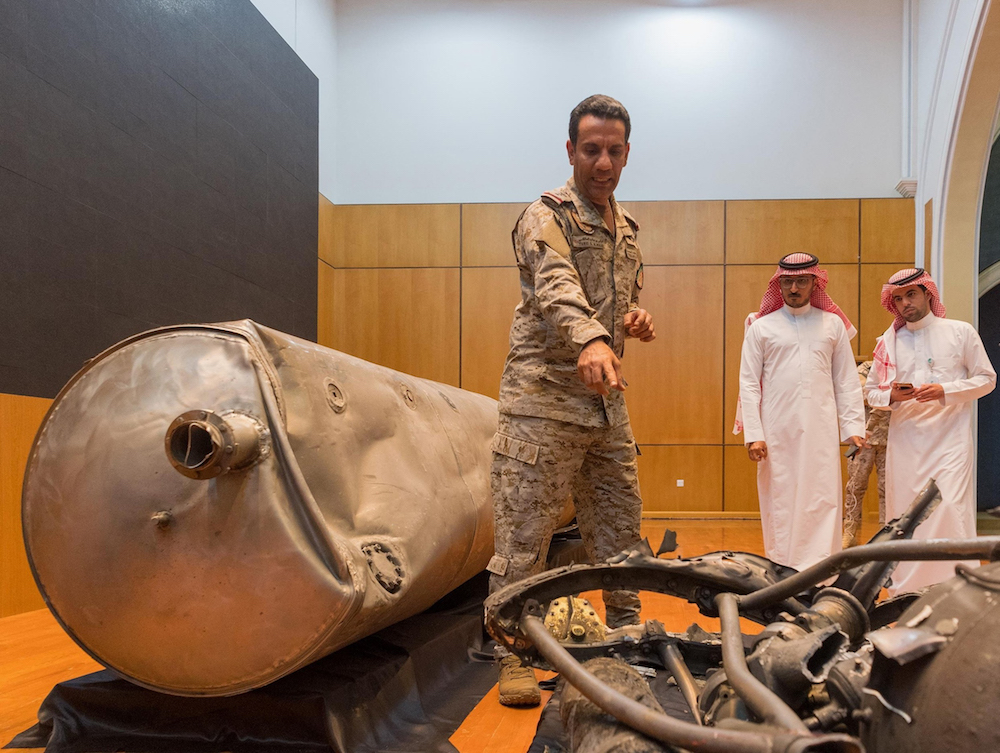
This combination of handout pictures provided by the Saudi Press Agency (SPA) on February 27, 2021 shows damage to a home and debris on the roof of a building in Saudi Arabia's capital Riyadh in the aftermath of a missile attack claimed by Yemen's Houthi militia. (AFP/File Photo)
Although Iran may view the conflict in Yemen as a proxy war, Al-Malki says Saudi Arabia and its Coalition partners see it as a war of necessity.
“The Iranian involvement in Yemen is a proxy war. They are going for a proxy war. For us, it is not a proxy war, because this war is a necessity,” he said.
“If we go back to 2015, the Houthis conducted exercises using heavy weapons on our southern border. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) called on all Yemeni parties to come to Saudi for talks and to try to reach a political solution. The Houthis refused.”
Al-Malki pointed to Iran’s long-running support for the Houthis, which predated the conflict, evidenced by the ship Jihan I, which was seized carrying weapons to Yemen in 2013. He also highlighted the air bridge between Iran and Sanaa, established just days before the capital fell, used to deliver weapons — not food and medicine as Tehran claimed.
For Al-Malki, the only solution to the conflict is a firm stance from the UN, Security Council and the international community against Iran, which would force the Houthis to the negotiating table.
“I would say more pressure from the international community to hold the Iranian regime accountable for its intervention, and also its violation of 2216 and the other UN Security Council resolutions, will stop the Iranians from supporting the Houthis,” Al-Malki said.
“Those weapons, the major component in support to the Houthis, is what has sustained the Houthis during the conflict. If that support is cut, I think the Houthis could come to the table.
“A political solution is the best for the crisis in Yemen and the Yemeni parties. They have to sit and they have to decide what they need for their country and what they need for their future.”





























