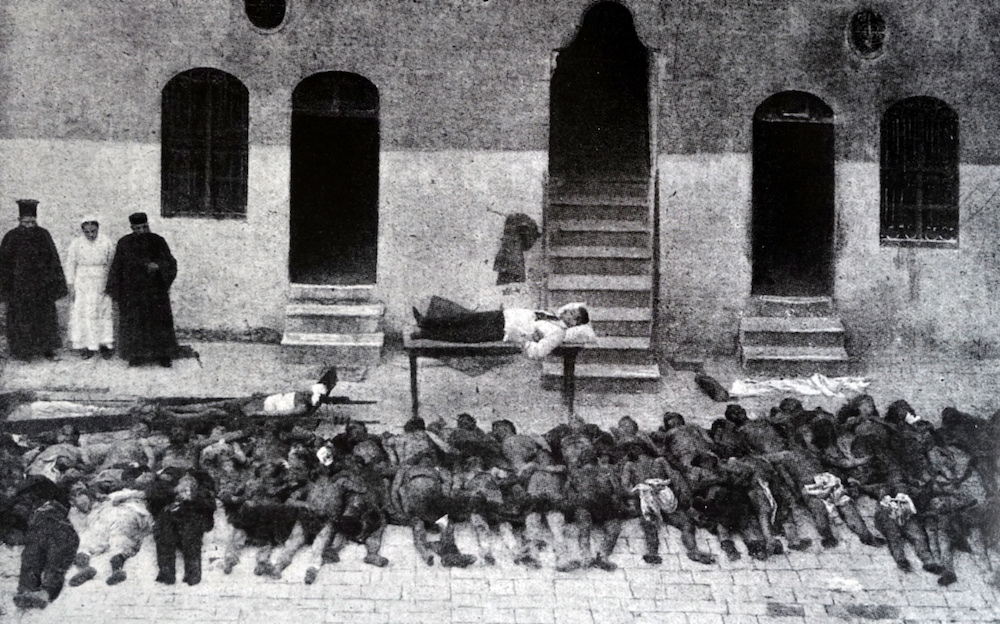
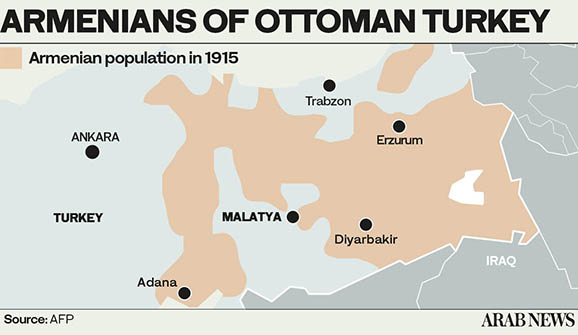
DUBAI: Armenians mark April 24 each year as a day of sorrow. It was on this date in 1915 when the Ottoman Empire launched the first in a brutal succession of atrocities against the ethnic group living under its dominion, going on to kill more than 1 million and driving many more into exile.
To this day, modern Turkey refuses to acknowledge the crimes committed during the twilight of the ancient regime.
Whether living in the Middle East, North America, Russia or modern-day Armenia, it is likely every Armenian has a parent, grandparent, or great-grandparent who witnessed the genocide firsthand.
This year, many of them will be watching closely for signs of formal recognition from the US government.
“Virtually every Armenian alive today is a descendant of a survivor of the Armenian Genocide,” said Chris Bohjalian, the New York Times bestselling author of “The Sandcastle Girls.” His sweeping historical love story, published in 2012, draws on his own Armenian heritage and the experiences of his grandparents.
“The Ottoman Empire systematically annihilated 1.5 million of its Armenian citizens, plus 300,000 Assyrians and countless Greeks, and that was after exterminating 250,000 Armenians a generation earlier in the Hamidian massacres. Moreover, Turkey denies the blood on the hands of its Ottoman predecessor,” he told Arab News.
On that spring day in the early months of the First World War, Ottoman authorities rounded up and executed several hundred Armenian intellectuals. In the weeks that followed, thousands of ordinary Armenians were forced from their homes and sent on death marches across the Mesopotamian desert.
“The day means an enormous amount to Armenians because we are grieving our ancestors, the loss of much of our homeland, and our culture in eastern Turkey — and we are grieving it all as an open wound because Turkey has never acknowledged the crime and much of the world doesn’t even know it occurred — or its magnitude, if they know a little bit.”
In fact, Bohjalian wonders whether the Nazi Holocaust, which came a quarter of a century later, would have occurred without the precedent of the Armenian Genocide.
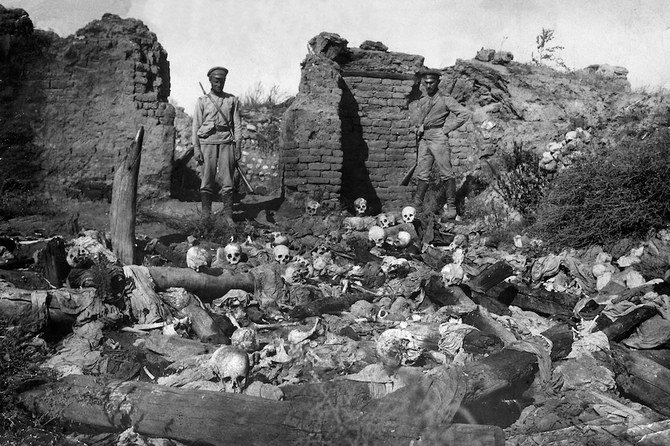

A picture released by the Armenian Genocide Museum-Institute dated 1915 purportedly shows soldiers standing over skulls of victims from the Armenian village of Sheyxalan in the Mush valley, on the Caucasus front during the First World War. (STR/AGMI/AFP)
“It might have. But in ‘Justifying Genocide,’ scholar Stefan Ihrig argues convincingly that the Armenian Genocide made the Holocaust more likely. The most quoted line from my novel ‘The Sandcastle Girls,’ is this: ‘There is a line connecting the Armenians and the Jews and the Cambodians and the Bosnians and the Rwandans. There are obviously more, but really, how much genocide can one sentence handle?’ So, I believe we still have lessons to learn,” he added.
Indeed, the parallel is often drawn between the Armenian Genocide and the many other mass displacements and wholesale slaughters that followed over the course of the 20th century.
Joseph Kechichian, senior fellow at the King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies, in Riyadh, told Arab News: “(Former German leader Adolf) Hitler is famous for having used the term, ‘who remembers the Armenian nation?’ when he embarked on his own murderous deeds.
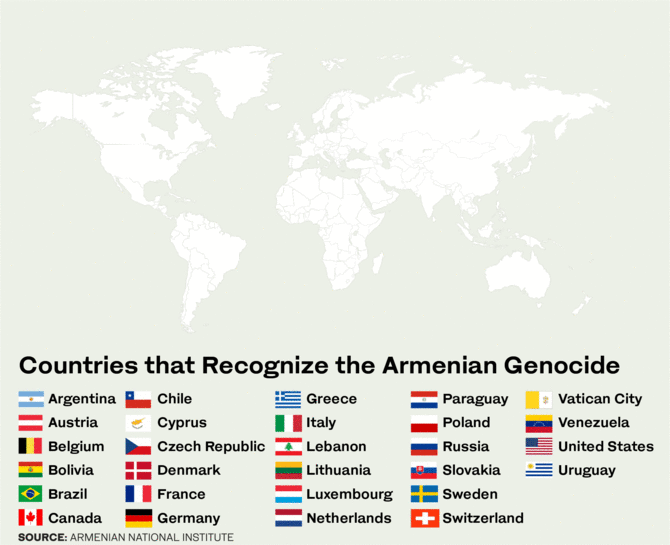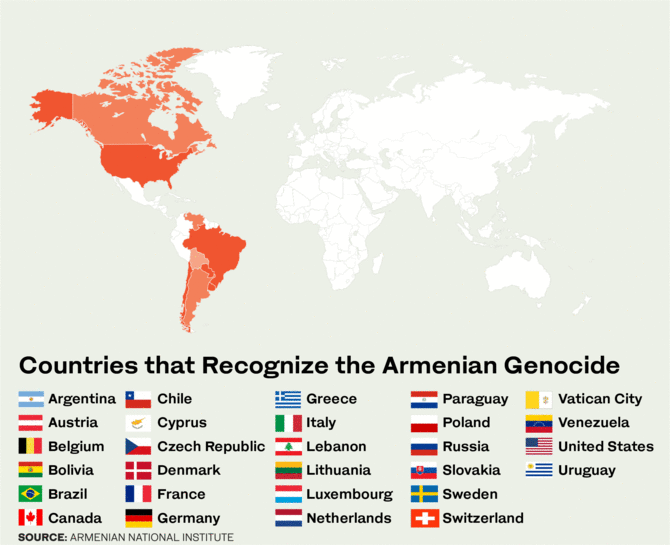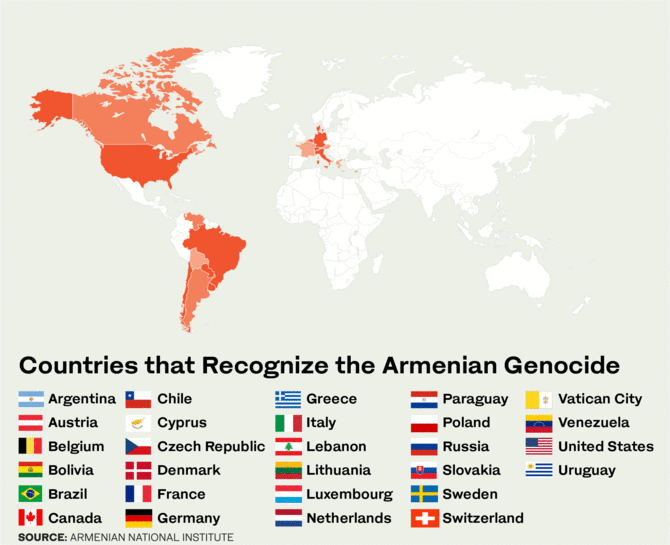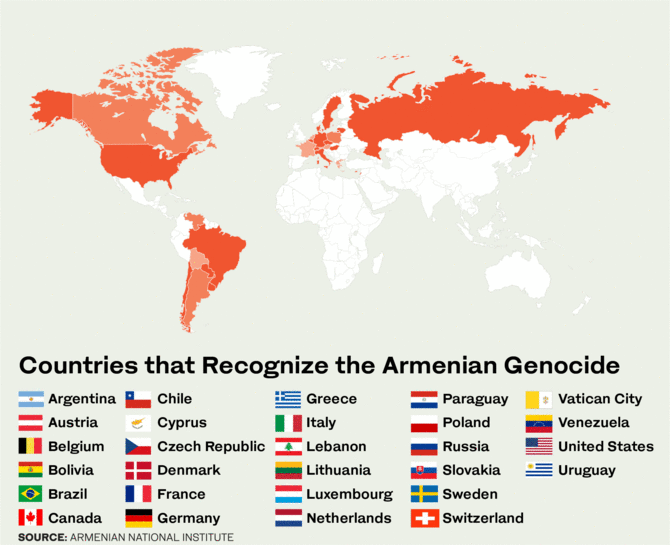
“One supposes that the other significant consequence of the Armenian Genocide is the denial that successive Turkish governments practiced, even if the last Ottoman rulers acknowledged it and actually tried a number of officials who were found guilty.
“Contentious does not even begin to explain the hurt that Armenians feel, for denial translates into a second genocide — albeit a psychological one. Eventually, righteous Turks — and there are a lot of them — will own up to the dark chapters of their history and come to terms with it. But it seems that we are not there yet,” he said.
Turkey acknowledges that many Armenians were killed in clashes with Ottoman forces during the First World War but disputes the figures and denies that the killings were orchestrated or constitute a genocide.
THENUMBER
* 1.5m - Highest estimate of Armenian deaths by massacre, starvation or exhaustion.
Kechichian’s own paternal grandmother was among the victims. “Imagine how growing up without a grandmother — and in my orphaned father’s case, a mother — affects you,” he added.
“We never kissed her hand, not even once, and she was always missed. We spoke about her all the time and my late father had teary eyes each and every time he thought of his mother.”
Almost every Armenian family has a similar story to tell.
“But we are believers and pray for the souls of those lost. We also ask the Lord to forgive those who committed the atrocities and enlighten their successors so that they too can find peace. Denial is ugly and unbecoming and it hurts survivors and their offspring, no matter the elapsed time,” Kechichian said.
For Armen Sahakyan, executive director of the Armenian National Committee of America — Western Region, the genocide never really ended.
“It continues to this very day in Turkey and Azerbaijan’s ongoing attempts to attack, empty, and ultimately erase the presence of Armenians in their ancient homeland,” he told Arab News, referring to last year’s Nagorno-Karabakh war.
“The Armenian Genocide is Turkey’s ‘original sin,’ setting the stage for over a century of human rights violations and repression against all dissidents of the Turkish state and undermining its own democratic future.”
READ MORE
US President Joe Biden would become the first US president to recognize the systematic killing of an estimated 1.5 million Armenians from 1915 onwards in modern-day Turkey as a “genocide,” a step already taken by the Senate and the House of Representatives in 2019. More here.
According to Sahakyan, without a truthful, just, and comprehensive resolution of the Armenian Genocide, Turkey stands no chance of becoming a reliable ally of the West and “will continue its destructive domestic as well as foreign policy throughout the wider Mediterranean.”
US President Joe Biden has indicated he will officially recognize the displacement and slaughter of the Armenian people in 1915 as a genocide — a move that would mark a significant break with past administrations, ever cautious not to offend their nominal NATO ally, Turkey.

US President Joe Biden has indicated he will officially recognize the displacement and slaughter of the Armenian people in 1915 as a genocide. (AFP/File Photo)
Always quick on the draw, the Turkish government has given warning that the US “needs to respect international law.”
Speaking recently to broadcaster Haberturk, Turkey’s foreign minister, Mevlut Cavusoglu, said: “Statements that have no legal binding will have no benefit, but they will harm ties. If the United States wants to worsen ties, the decision is theirs.”
Bohjalian said recognition from Washington would mean a great deal. “It would thrill me. But will we ever see justice? We may see the word ‘genocide’ used by a US president on April 24 this year, but will we ever get back Van? Ararat? Shusha? Not in my lifetime. Nevertheless, I hope with all my heart that Biden uses the word ‘genocide.’”
Sahakyan noted that such a recognition from the White House — following on the heels of 2019’s Congressional resolutions — would be the culmination of a century of tireless work by the Armenian-American community and friends of Armenia.
“It must inform US policy, at every level, including in supporting Armenia — a blockaded, landlocked, partitioned, genocide-survivor state — against continued attempts by Ankara and Baku to complete this crime.
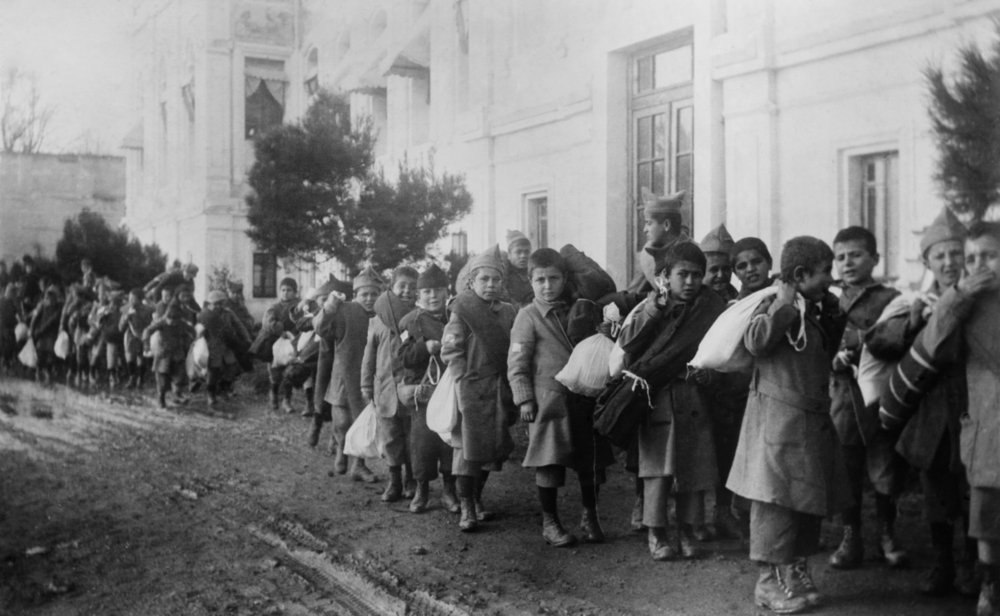

Armenian orphans being deported from Turkey in around 1920. (Shutterstock/File Photo)
“The US recognition of the Armenian Genocide would also be a tribute to America’s own heroic role in saving hundreds of thousands of survivors of the genocide through the Near East Relief,” he said.
A century on, the genocide remains a landmark event in modern history and one that besmirches the character of Turkey even today, said Peter Balakian, author of “The Burning Tigris: The Armenian Genocide and America’s Response” — another New York Times bestseller.
He told Arab News: “Turkey has shown no apology, let alone restitution and reparation. Other nations have demanded that Turkey deal with the Armenian Genocide aftermath, but it seems that this will only happen when Turkey can develop a true democracy in which its government can foster a culture of self-criticism and minority and human rights.”
For Balakian, recognition is the first step, no matter how long it takes. “We have waited for some semblance of justice for over a century,” he added.
--------------
Twitter: @CalineMalek




























