IRBIL, IRAQ: The drone threat posed to US and coalition personnel by Iran-backed militias is growing, and defenses against such threats remain limited — particularly in the face of Tehran’s growing capabilities. That was the clear message delivered by the US military commander in the Middle East during his most recent visit to Iraq.
Marine Gen. Frank McKenzie’s warning came in the wake of a rash of drone attacks launched by Iran’s proxies and allied groups in the region against coalition positions and regional partners of the US, a development viewed by many as a sign of a shift in the strategic balance of power.
“We’re working very hard to find technical fixes that would allow us to be more effective against drones,” the US Central Command (CENTCOM) commander said. “We’re open to all kinds of things. The army is working it very hard. Still, I don’t think we’re where we want to be.”
Take the drone attack launched from Iraq in January that targeted Saudi Arabia. Or the explosives-laden drone strike in April that targeted the US troop base at Irbil International Airport inside the normally secure autonomous Kurdistan region, causing a large fire and damage to a building.
While the attacks did not cause major casualties, they nevertheless underscored the evolving nature of the threat, and Iran’s rapidly advancing drone capabilities.
The Iran-backed Houthi militia in Yemen has frequently used loitering munitions, also known as suicide drones, against Saudi Arabia’s civilian and military infrastructure, which appear to feature components based heavily on an Iranian design.
In the conflict in the Gaza Strip, the Palestinian group Hamas used kamikaze-type drones against Israel, which exhibited many similarities to the same Iranian design.
In what appears to be more than just a coincidence, a complex that houses a factory that makes Iranian drones suffered a major explosion just days after Israel claimed that Iran was providing drones to Hamas.
Sunday’s blast injured at least nine workers at the petrochemical factory in Isfahan. The Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Company, which makes a variety of aircraft and drones for Iranian and pro-Iranian forces, is located in the complex, owned by Sepahan Nargostar Chemical Industries.
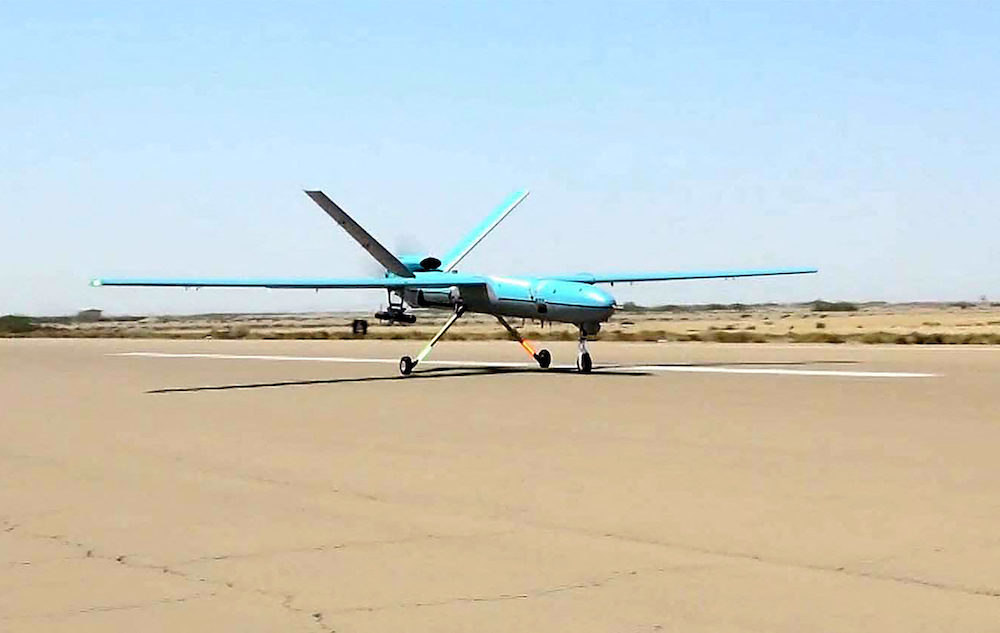

A handout picture provided by the Iranian Army's official website on September 11, 2020, shows an Iranian Simorgh drone during the second day of a military exercise in the Gulf, near the strategic strait of Hormuz. (AFP/Iranian Army website/File Photo)
There was no independent confirmation of the cause of the explosion or the precise factory affected. Analysts pointed out that Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu had displayed on Thursday parts of a drone that he said were made by Iran and had flown over from Iraq or Syria.
A recent Reuters report suggests that Iran has changed its strategy in Iraq with regard to use of projectiles. Instead of relying on larger established Shiite militia groups to carry out proxy attacks against US and coalition forces, it is now relying on much smaller militia groups completely loyal to Tehran.
The regime reportedly took 250 of these fighters to Lebanon last year, where they were trained by Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) advisers to fly drones and carry out rocket attacks. The result has been a spate of drone attacks, both within and originating from Iraq.
Weaponry of this kind can be difficult to defend against, even for US forces operating advanced air defense systems, according to experts.
“The use of weaponized drone systems in Yemen, or during the latest conflict in Gaza, is a blueprint for how drones will be used in conflict from this point forward,” Dr. James Rogers, of the Center for War Studies at the University of Southern Denmark, told Arab News.
“The ability to send multiple drones and missiles all at once means that even the most sophisticated defense systems can be saturated and overrun.”
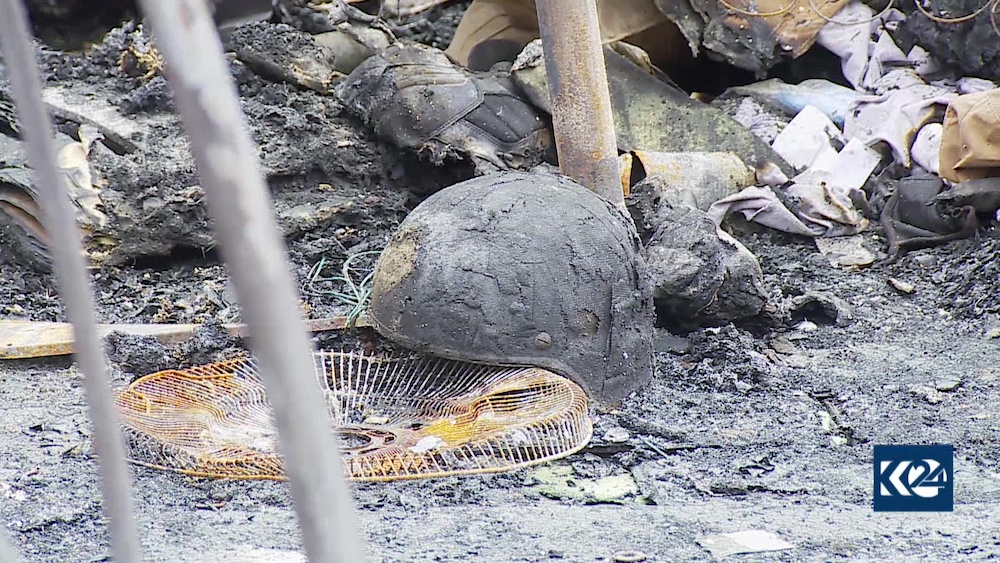

An image grab taken from Kurdistan 24 TV channel on February 19, 2021 shows damage following a rocket attack two days ago targeting a military complex inside the Irbil airport that hosts foreign troops deployed as part of a US-led coalition. (AFP/Kurdistan 24/File Photo)
Iran’s fingerprints are all over the recent proliferation of armed drones among non-state actors and militias throughout the Middle East. As Rogers notes, the distance and deniability afforded by the drone has made it “a valued tool” in Iran’s arsenal.
“The Iranian drone program has innovated with sophisticated, indigenously produced drones, which it supplies to regional allies,” he said.
“This broad diffusion of Iranian drone technologies makes it almost impossible to tell who conducted a lethal drone strike in the region, and thus who should be held responsible and accountable. This is only going to get more difficult.”
The designs Iran supplies are very similar to Tehran’s own models, notably the Ababil series. Variants of these drones have appeared in the Houthi and Hamas arsenals, and in that of Iran’s main regional proxy, the Lebanese Hezbollah.
The technology has the added benefit of being easily disassembled for covert transport and reassembly at its destination.
For example, an anonymous Iraqi official told the Associated Press news agency that the drone that targeted Riyadh in January was delivered to Iraqi militiamen “in parts from Iran … assembled in Iraq, and launched from Iraq.”
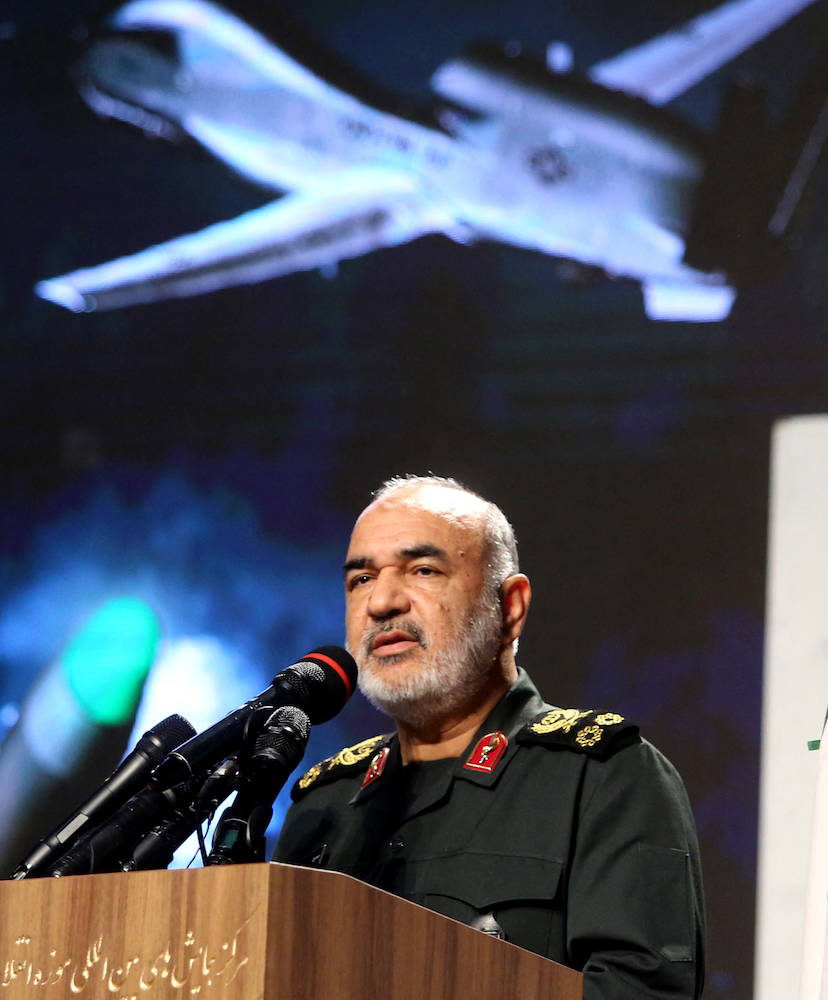

Iranian Revolutionary Guards commander Major General Hossein Salami at Tehran's Islamic Revolution and Holy Defence museum during the unveiling of an exhibition of what Iran says are US and other drones captured in its territory, in the capital Tehran on September 21, 2019. (AFP/File Photo)
The efficacy of the weapons in question has been augmented by recent advancements in commercial drone technology.
“Now a number of non-state actors have Iranian designs. They are able to produce their own systems, fitted with commercially available technologies, which they can then supply to their allies,” Rogers said. “In essence, the drone is out of the bag, and the threat is spreading.”
Iran is well aware it has found a chink in its opponents’ armor — and is actively exploiting this vulnerability.
“Using suicide drones is a way for Iran to score a serious hit on the US presence (in Iraq) by potentially taking out a high-value asset, which is very hard to do with a spray of unguided long-range rockets, while also being more discriminate and avoiding the risk of a serious kinetic US response,” Alex Almeida, an Iraq security analyst at the energy consultancy Horizon Client Access, told Arab News.
“I think it’s very likely the militias will use these larger fixed-wing drones in the future — if they haven’t already — including potentially for longer-ranged strikes outside Iraq.”
Almeida believes that the US has the “tools” to adequately defend its bases and forces from this drone threat, “even if they don’t seem to have performed effectively in recent attacks” at Irbil or Al-Asad.
“The issue is that if these attacks become more frequent, all US points of presence in Iraq, Syria, and eventually other locales in the region are going to require their own layered counter-drone defenses,” he said.
“Iran is deliberately presenting a multi-layered threat, from conventional ‘dumb’ mortar and rocket fire to small quadcopter and larger fixed-wing drones. These defensive requirements impose their own additional costs on the US presence, which the Iranians are no doubt aware of.”
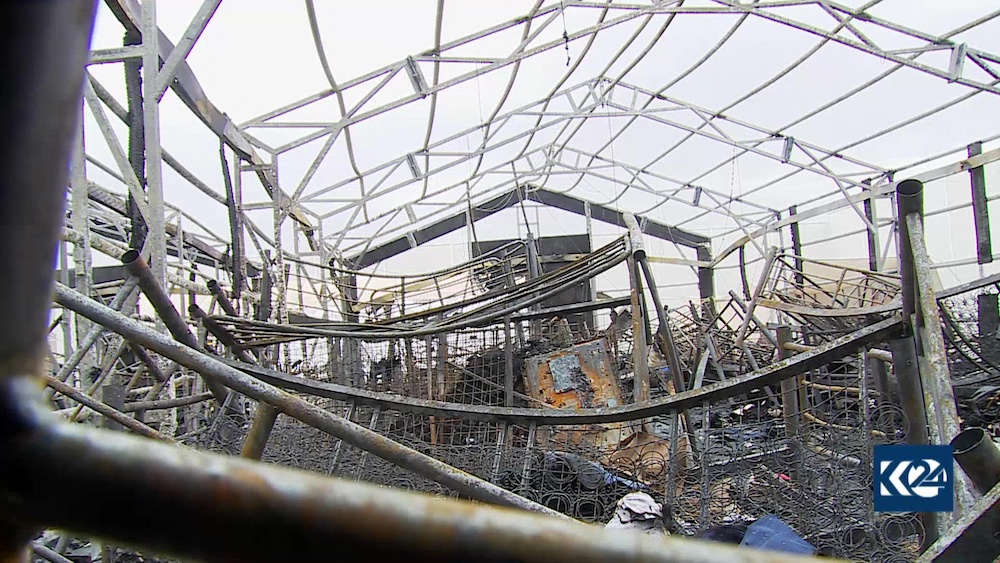

An image grab taken from Kurdistan 24 TV channel on February 19, 2021 shows damage following a rocket attack two days ago targeting a military complex inside the Arbil airport that hosts foreign troops deployed as part of a US-led coalition. (AFP/Kurdistan 24/File Photo)
For her part, Kirsten Fontenrose, Middle East security director at the Atlantic Council, believes drone training, technologically complex drone components and the blueprints for locally manufacturing drones are all provided by the IRGC to the militias it directs or arms across the Middle East.
“For the US and its partners in the region, the proliferation of more sophisticated Iranian drone designs made with commercially available Chinese parts requires a reassessment of what the US force presence should look like, what kinds of systems we prioritize developing, and how we train together,” she told Arab News.
Fontenrose said there are three key factors in countering such drone attacks. First is the direction of attack. “Drone detection systems do not always have a 360-degree range of detection,” she said. “If you incorrectly predict the direction from which a drone attack will come, your defenses may be facing away and never see it coming.”
Second, there are the flight guidance enablers on the drone. “You must know whether a drone is guided by GPS, or using cellular signals, or know the frequency it operates on, for example,” she said. “If you target the wrong enabler, you will not defeat the drone.”
Finally, there is the drone’s payload.
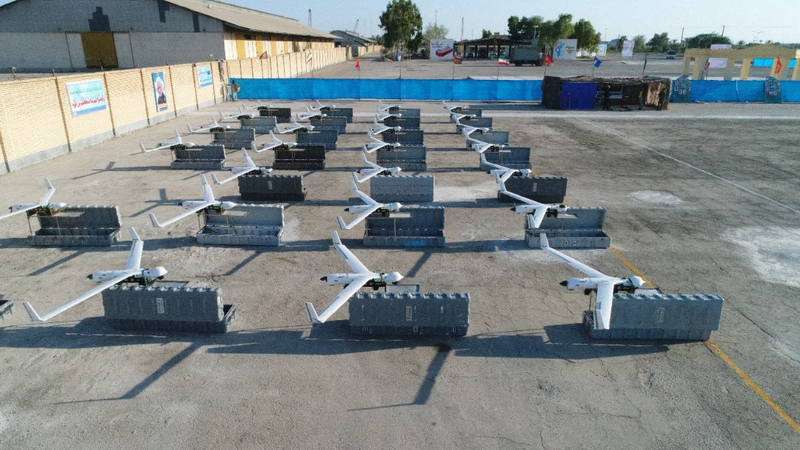

Drones during a ceremony in Iran's southern port city of Bandar Abbas. (AFP/Iran’s Revolutionary Guard via Sepah/File Photo)
“If you successfully counter and take over control of a drone that is flying at you, you must know whether it is carrying an explosive, a chemical agent, or a camera before you decide whether to bring it to you to investigate, land it in a populated area to prevent it reaching the target, or return it home possibly carrying sensitive information,” Fontenrose told Arab News.
The Biden team had signaled loudly even before it took office of its determination to find a pathway back into the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action with Iran. This stated objective has since translated into indirect talks in Vienna.
Strategic and defense experts believe Iran has been testing the US administration with calculated provocations in multiple theaters, partly in an effort to take the measure of President Joe Biden, and partly as a way to gain leverage in the nuclear negotiations.
Nicholas Heras, senior analyst and program head for State Resilience and Fragility at the Newlines Institute, says Iran’s defense establishment is “leaning into a strategy of utilizing drone forces to present asymmetric challenges to more technologically advanced state actor competitors.
“Iran is building best-in-class capabilities with the concept of drone swarms in the air and at sea, which is a skill set that worries US defense and intelligence officials who are required to protect US forces deployed to the Middle East,” Heras told Arab News.
“The IRGC is the global leader in disseminating the tactics, techniques and procedures for drone warfare to non-state actors, who can then execute highly sensitive attacks against Iran’s opponents while giving Iran the ability to deny that it ordered the attacks.”
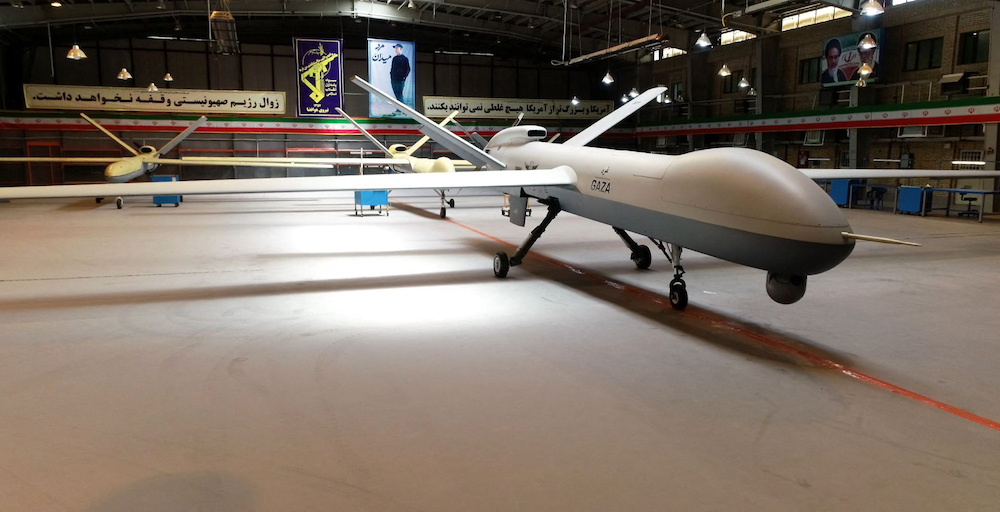

This handout photo provided by Iran's Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) official website via SEPAH News on May 22, 2021 shows new combat drones dubbed "Gaza" in tribute to Palestinians, unvailed in the capital Tehran, hours after a ceasefire between Israel and Palestinian armed factions took effect. (AFP/Iran's Revolutionary Guard via Sepah News)
The IRGC’s preferred models of choice are kamikaze drones, which crash into their respective targets and explode on impact, since they are easy to assemble, easy to operate, easy to use for overwhelming swarm attacks, and very challenging to counter. Such drones are most likely what McKenzie has in mind.
“There is no one anti-air system that will work best against the drone warfare methods that the IRGC is teaching Iran’s partners and proxies,” Heras said.
“Countering Iran’s networked drone warfare requires active signals intelligence to identify operatives and drone manufacturing sites, and rapid reaction strikes to hit them before they get off the ground.”
The threat posed by drones to the US — and, by extension, to its regional partners — has become impossible to ignore even by an administration whose stated goal is to end America’s “forever wars” and focus on the threats from Russia and China.
“These small- and medium-sized (drones) present a new and complex threat to our forces and those of our partners and allies,” McKenzie told Congress in April.
“For the first time since the Korean War, we are operating without complete air superiority.”
---------------
Twitter: @pauliddon



































