ABU DHABI: When it comes to smoking, all the facts are known yet they have proved to be no cure. Smoking is the leading cause of preventable deaths and tobacco use causes more than 8 million deaths per year worldwide, says the World Health Organization (WHO).
To put that into perspective, the COVID-19 pandemic, which has necessitated national lockdowns, has seen the significantly smaller 3.56 million deaths so far.
Low- and middle-income countries pay a disproportionately heavy price as they have more than 80 percent of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users.
The Eastern Mediterranean region has a comparatively high number of tobacco consumers and that number is rising fast.

A youth smokes a waterpipe (Shisha) at a cafe in Dubai on May 31, 2008. Nicotine contained in tobacco is highly addictive and tobacco use is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, over 20 different types or subtypes of cancer, and many other debilitating health conditions. (File/AFP)
The good news is that Gulf states are using the whole gamut of measures to reduce tobacco consumption.
The largest of the GCC countries, Saudi Arabia, with a population of more than 34 million, has been taking a number of steps to curb the menace. These include increasing sales taxes and fines, conducting anti-smoking campaigns, establishing smoking cessation clinics and introducing dedicated mobile applications.
“Saudi Arabia has an ambitious strategic tobacco control plan to reduce smoking rates from 12.7 percent to 5 percent by 2030,” Dr. Tawfiq Al-Rabiah, Saudi Arabia’s Minister of Health, was quoted as saying in 2019.
In 2017, the Saudi National Committee for Tobacco Control imposed a 100 percent tax on all tobacco products and banned smoking in public areas including malls, parks and workplaces.

A performer walks past an Emirati man as he lights a cigarette at the Meydan race track before the start of the Dubai World Cup, on March 27, 2010. Nicotine contained in tobacco is highly addictive and tobacco use is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, over 20 different types or subtypes of cancer, and many other debilitating health conditions. (File/AFP)
Additionally, the Saudi health ministry expanded its specialized clinics to 900 locations across the country.
Consequently, data from 2019 showed an increase in visits to clinics by 213 percent, a drop in tobacco imports by 54 percent, and a 307 percent spike in the number of people quitting smoking.
Neighboring UAE faces a no less daunting challenge. Authorities have set a target of reducing tobacco consumption from 21.6 percent to 15.7 percent among men and from 1.9 percent to 1.66 percent in women by the end of the year.
FASTFACT
World No Tobacco Day is observed on May 31 to raise awareness of the harmful and deadly effects of tobacco use.
By far the most common form of tobacco consumption in the UAE is cigarette smoking (77.4 percent), followed by midwakh use (a small pipe used for smoking tobacco) at 15 percent, waterpipes at 6.8 percent and cigars at 0.66 percent.
The government has launched awareness campaigns on the harms of smoking via regular means as well as social media, said Dr. Buthaina Abdulla bin Belaila, head of non-communicable disease in the UAE’s Ministry of Health and Prevention.

A man smokes waterpipe (Shisha) at a cafe in Dubai on May 31, 2008. Nicotine contained in tobacco is highly addictive and tobacco use is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, over 20 different types or subtypes of cancer, and many other debilitating health conditions. (File/AFP)
“The country has started imposing excise tax on tobacco products that has led to a doubling of the price that consumers pay, which will be reflected in a reduction in consumption, according to studies,” she said.
“The UAE has also expanded provision for smoking cessation services by increasing the number of clinics and training more doctors to offer such services, which has resulted in an increase in the number of those wishing to quit smoking.”
INNUMBERS
UAE excise tax rates
* 100% Tobacco products
* 100% Electronic smoking devices
* 100% Liquids used in such devices and tools
The Oman Medical Journal study found that in the UAE prevalence rates of smoking were highest among Arab expatriates (31.9 percent), followed by non-Arab expatriates (22.6 percent) and Emiratis (21.6 percent).
According to Dr. Muhammed Anas Ayoob, a specialist in pulmonary disease at NMC Specialty Hospital in Abu Dhabi,, this could be because smoking is widespread in countries such as Jordan and Egypt, the home countries of many of the UAE’s Arab expats.
Living far away from loved ones and job-related stress may be among the reasons for high tobacco consumption by expats.
Of the GCC countries, Oman has the lowest rate of tobacco consumption, but future projections suggest it can ill afford complacency.
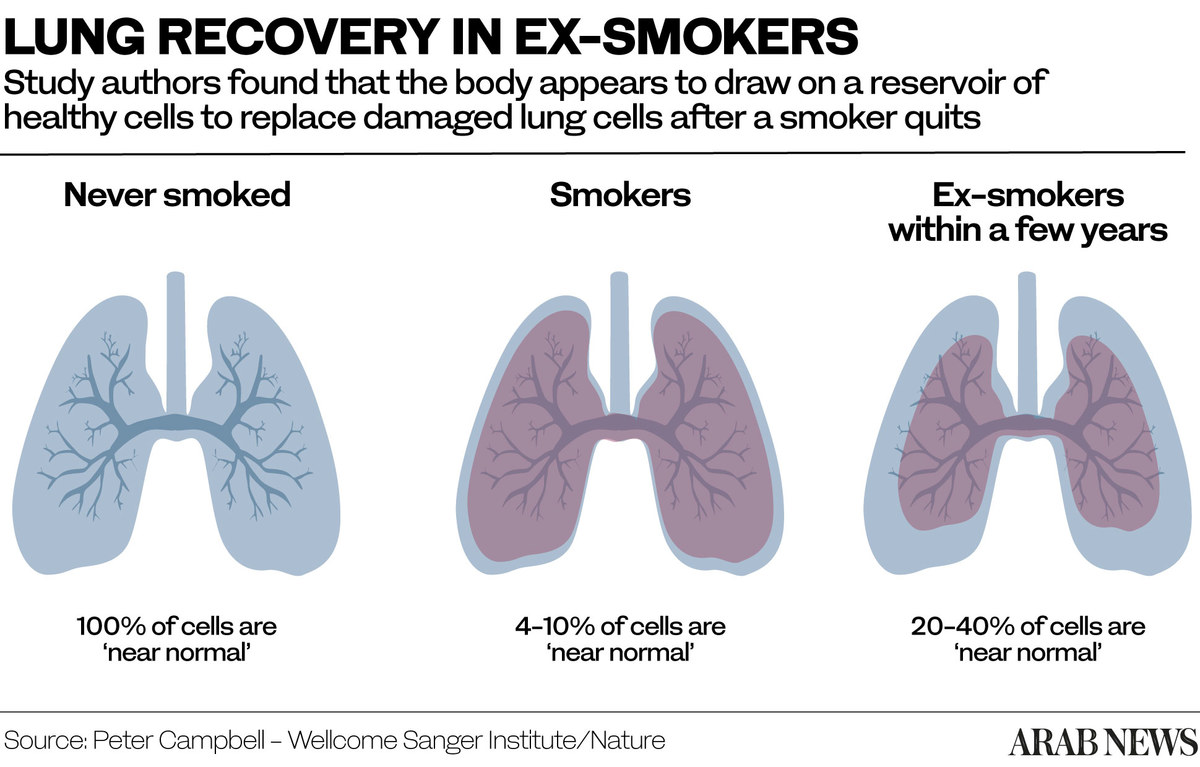
The prevalence of tobacco use among men in Oman (which stood at 17.9 percent in 2010) is predicted to rise to 33.3 percent by 2025, according to a 2017 study in the Oman Medical Journal.
This figure is still low compared with the predicted figures for 2025 for other Arab countries: Lebanon (45.4 percent), Bahrain (48.8 percent) and Egypt (49.9 percent).
The study claimed that before 1970, the ban on smoking in all indoor and outdoor public areas in Oman was enforced by public flogging and jail sentences.
These days, the government has a very different approach: it has set up cessation clinics for smokers and imposed a comprehensive ban on the advertising, promotion and sponsorship of tobacco products.
The study also noted that Oman has no tobacco product manufacturing facilities, so more than 80 percent of the domestic demand is met through imports from the UAE, followed by Germany, Switzerland, Poland and Turkey.
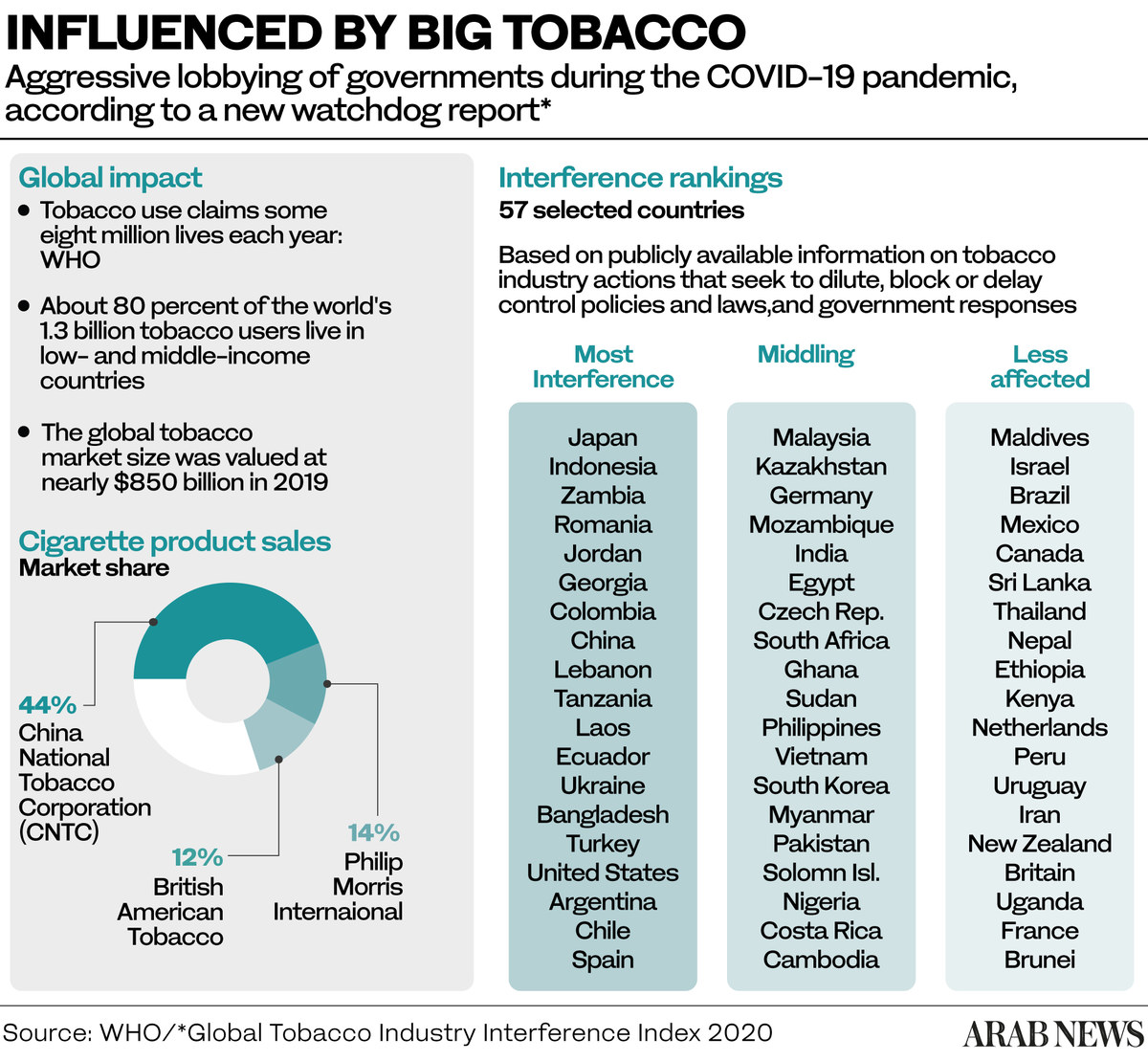
In Qatar, a 2021 report on the epidemiology of tobacco use said the government’s National Vision 2030 and the Ministry of Public Health Strategy 2018–2022 aim to reduce the prevalence of smoking by 5 percent.
Qatar’s health ministry has pledged to establish a system for monitoring tobacco consumption and to conduct regular smoking surveys in accordance with the recommendations of the Global Tobacco Monitoring System.
It also intends to offer services to smokers who want to kick the habit, including a helpline and a local website.

A woman smokes waterpipe (Shisha) at a cafe in Dubai on May 31, 2008. Nicotine contained in tobacco is highly addictive and tobacco use is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, over 20 different types or subtypes of cancer, and many other debilitating health conditions. (File/AFP)
The ministry says it will establish a practical and comprehensive tax model on tobacco products, including customs duties and taxes on tobacco production and sale.
“Evidence from countries of all income levels shows that price increases on cigarettes are highly effective in reducing demand,” Dr. Ayoob, of NMC Specialty Hospital, said.
“Higher prices encourage cessation and prevent initiation of tobacco use. They also reduce relapse among those who have quit and reduce consumption among continuing users.
“Several reviews have demonstrated that a price increase of 10 percent results in a decrease of 2.5 percent to 5 percent in cigarette consumption.”

A picture taken on September 28, 2017 shows a man organising cigarette packs at a shop in in Ras al-Khaimah. Nicotine contained in tobacco is highly addictive and tobacco use is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, over 20 different types or subtypes of cancer, and many other debilitating health conditions. (File/AFP)
On the question of whether e-cigarettes are a healthier alternative, Dr. Ayoob says that smoking does appear to be more harmful than vaping.
“This does not mean that vaping is safe. E-cigarettes produce an aerosol by heating a liquid that usually contains nicotine, flavorings and other chemicals that help to make the aerosol. Users inhale this aerosol into their lungs. Bystanders are also at risk of inhaling this aerosol when the user exhales into the air,” he said.
Dr. Ayoob pointed out that the US Food and Drug Administration has not confirmed that vaping helps people quit smoking. On the contrary, many e-cigarette users fail to kick their addiction, he said.
“According to a report, 58.8 percent of the people who recently used e-cigarettes also continued to smoke cigarettes,” he said.
Twitter: @farahheiba94




























