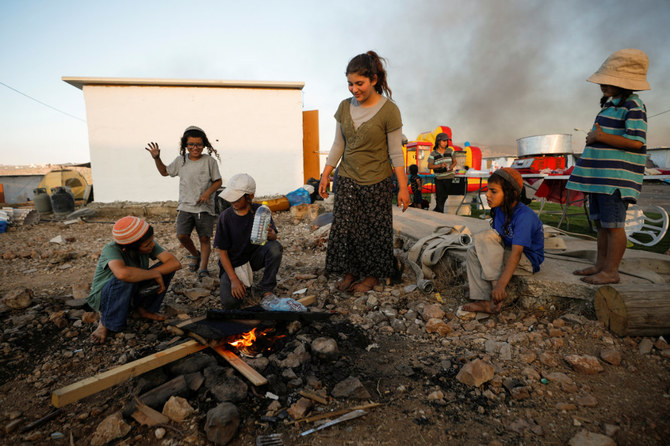
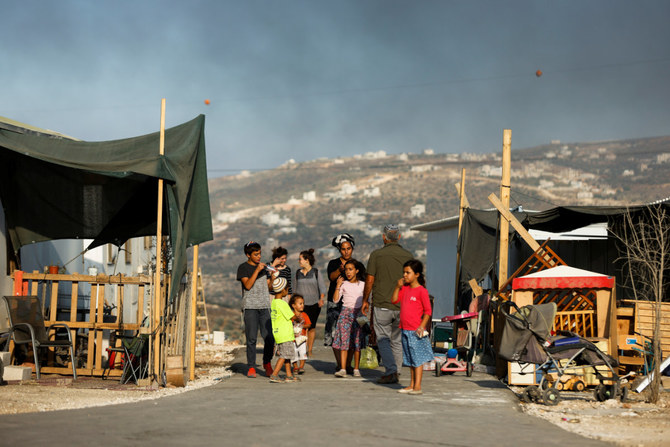
UNITED NATIONS: The United Nations on Thursday accused Israel of flagrantly violating international law by expanding settlements in the West Bank and east Jerusalem, saying settlements are illegal and urging the country’s new government to halt their enlargement immediately.
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres and UN Mideast envoy Tor Wennesland reported on implementation of a 2016 Security Council resolution that declared settlements have “no legal validity.” It demanded a halt to their expansion in the West Bank and east Jerusalem, lands the Palestinians want to include in a future state.
Wennesland said in a briefing to the council on Guterres’ 12-page report that he was “deeply troubled” by Israel’s approval of a plan to add 540 housing units to the Har Homa settlement in east Jerusalem as well as the establishment of settlement outposts. He said that is “illegal also under Israeli law.”
“I again underscore, in no uncertain terms, that Israeli settlements constitute a flagrant violation of United Nations resolutions and international law,” the UN envoy said. “They are a major obstacle to the achievement of a two-state solution and a just, lasting and comprehensive peace.”
“The advancement of all settlement activity must cease immediately,” Wennesland said.
Israel disputes its settlements are illegal.
Both Guterres and Wennesland also called on Israeli authorities to end the demolition of Palestinian homes and other property and the displacement of Palestinians — another flashpoint — “and to approve plans that would enable these communities to build legally and address their development needs.”
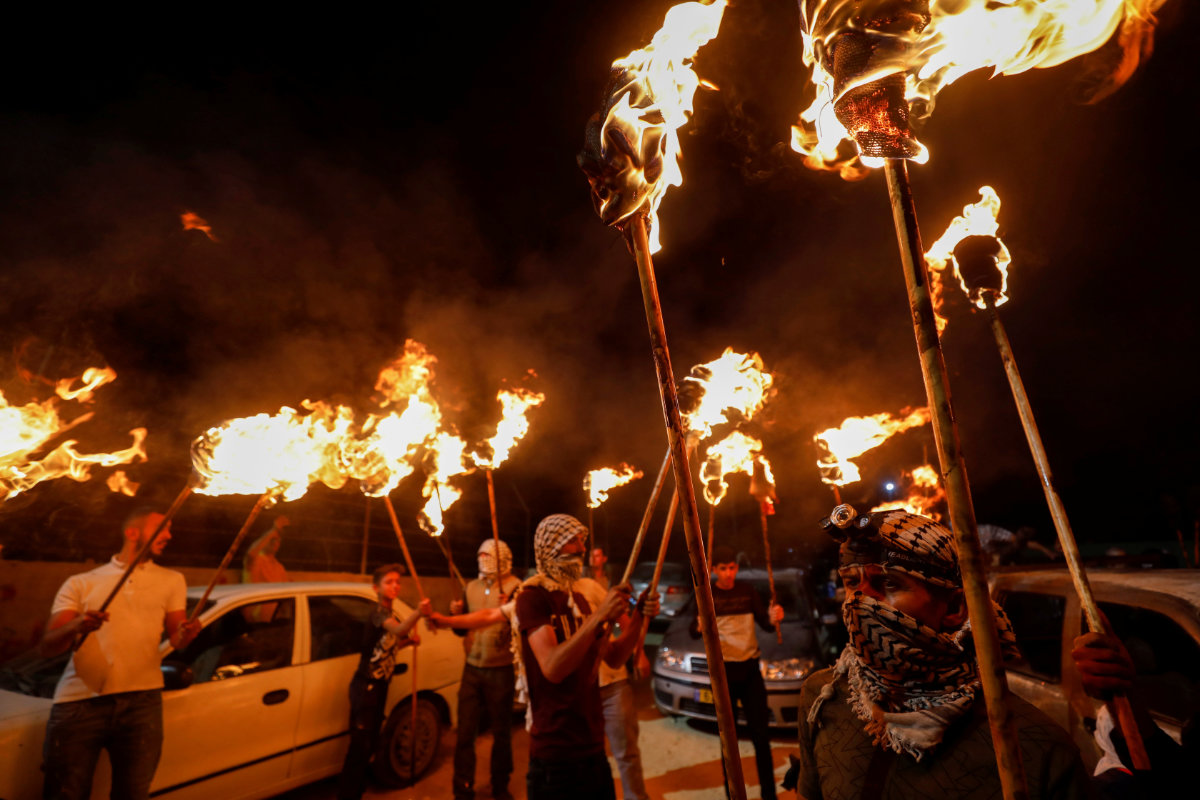
Palestinian demonstrators hold a night protest against Israeli settlements in Beita in the West Bank on June 22, 2021. (REUTERS/Mohamad Torokman)
The December 2016 resolution, which the United States abstained on in the final weeks of the Obama administration, also called for immediate steps to prevent all acts of violence against civilians and urged Israel and the Palestinians to exercise restraint and refrain from provocative actions, incitement and inflammatory rhetoric.
It also called on all parties to launch negotiations on final status issues and urged intensified international and regional diplomatic efforts to help end the decades-old Israeli-Palestinian conflict and achieve a two-state solution where Israelis and Palestinians can live side-by-side in peace.
Guterres and Wennesland made clear that 4½ years after the resolution’s adoption, none of these appeals have been met.
Wennesland said the period between March and June covered in the report “witnessed an alarming increase in the level of violence between Israelis and Palestinians, including hostilities between Israel and factions in Gaza at a scale and intensity not seen in years.”
He said the cessation of hostilities after last month’s 11-day Gaza war “remains very fragile,” adding that the United Nations is working closely with Israel, the Palestinians and partners including Egypt “to solidify a cease-fire, allow the entry of urgent humanitarian assistance and stabilize the situation in Gaza.”
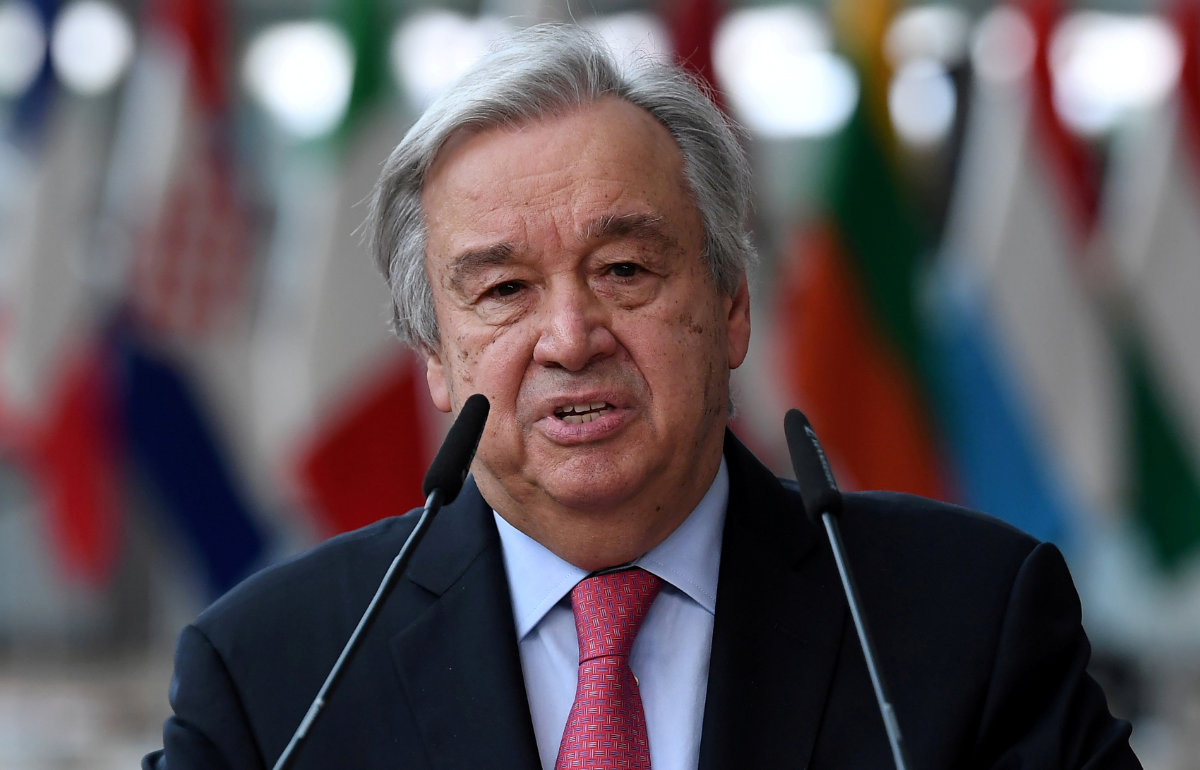

UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres says that more than four years have passed since the Security Council approved its resolution, but none of the appeals have been met. (Reuters photo)
Hamas, which controls the Gaza Strip, has demanded significant easing of the Israeli blockade. Israel has said it won’t tolerate even relatively minor attacks from Gaza, including the launch of incendiary balloons, which triggered Israeli airstrikes last week.
“I urge all sides to refrain from unilateral steps and provocations, take steps to reduce tensions, and allow these efforts to succeed,” Wennesland told the council. “Everyone must do their part to facilitate ongoing discussions to stabilize the situation on the ground and avoid another devastating escalation in Gaza.”
He called on all Palestinian factions “to make serious efforts to ensure the reunification of Gaza and the West Bank under a single, legitimate, democratic, national government,” saying that Gaza must remain part of a Palestinian state and a two-state solution.
During the March to June reporting period, Guterres said 295 Palestinians, including 42 women and 73 children, were killed by Israeli security forces and 10,149 were injured during demonstrations, clashes, search-and-arrest operations, air strikes, shelling and other incidents in Gaza, the West Bank and east Jerusalem.
The UN chief said 90 members of the Israeli security forces and 857 Israeli civilians were injured by Palestinians during the same period in clashes, incidents in which stones and firebombs were thrown, the indiscriminate firing of rockets and mortars and other incidents.
The Gaza war was the worst escalation of hostilities since 2014, with Palestinian armed groups firing over 4,000 rockets and projectiles toward Israel and Israeli forces carrying out over 1,500 strikes from air, land and sea across the Gaza Strip, Guterres said, quoting Israeli sources. During the conflict, 259 Palestinians were killed, including 66 children and 41 women, while nine Israelis, including two children, were killed along with three foreigners. Hundreds of Israelis were wounded.





























