BERN, Switzerland: Afghanistan is no stranger to foreign interference. In the 19th century, Britain and Russia sparred for control over the ancient terrain in a shadow match popularly known as the Great Game.
Today, the game continues, only now it has many more players, and the stakes are arguably far higher.
After 20 years in Afghanistan, America’s longest war is finally drawing to a close. But for the Afghan people, whose war began decades before US boots even touched the ground, the prospect of peace seems a very long way off as their sense of certainty and security once again unravels.
As US and NATO forces pull out, people within and outside Afghanistan alike have voiced concern about the cohesion of the country in the wake of soaring ethnic and tribal tensions, waves of troop surrenders and a weakened central government.
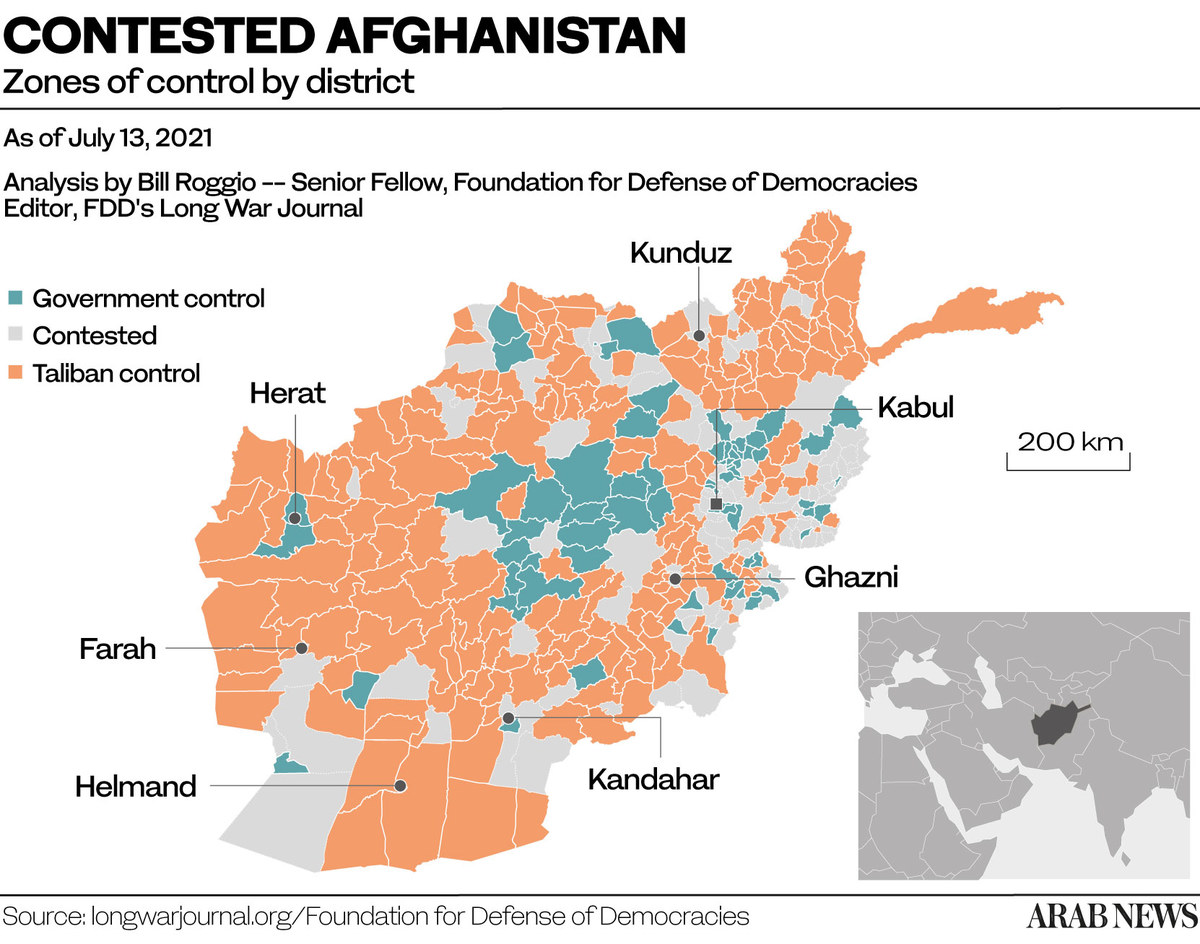
Nick Carter, Britain’s chief of the defense staff, has been quoted as saying it is “plausible” that the Afghan state would collapse without international forces there.
Unlike the Iraq invasion of 2003, Afghanistan was often viewed as “the good war” — emancipating the Afghan people, particularly women, from the cruelties of Taliban misrule. And yet, with every passing day, a resurgent Taliban is seizing control over ever more territory.
Furthermore, the economic gains of the past 20 years have been modest at best. The World Bank put the country’s nominal gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 at $19.8 billion — just slightly ahead of Mali, Gabon, and Burkina Faso. Per capita GDP was $507, near the bottom of global rankings.
The Afghan economy remains largely dependent on overseas aid. Some 44 percent of the population works in agriculture, while 60 percent derive at least part of their income from farming. Private-sector development has been hampered by Afghanistan’s chronic security deficiencies.

US Army soldiers from 2-506 Infantry 101st Airborne Division and Afghan National Army soldiers race to get out of the way of a CH-47 Chinook helicopter landing in hostile territory during the launch of Operation Radu Bark VI in the Spira mountains in Khost province, five kms from the Afghan-Pakistan Border. (AFP/File Photo)
To trace the genesis of the current conflict, it is necessary to rewind to the events of 1979, when Soviet tanks rumbled across the Oxus River to help shore up a fractious communist regime in Kabul. When a decade-long mujahideen rebellion, backed by the US and its allies, finally sent the Russians packing in 1989, a bloody civil war ensued, culminating in the rise of the Taliban.
The Taliban regime lasted five brutal years, sending the country back to the dark ages. It was from his hideout in Afghanistan that Osama bin Laden masterminded the Sept. 11, 2001, terror attacks. When the regime in Kabul refused to hand him over, the US quickly invaded and removed the Taliban from power.
Fast forward to 2021, and NATO forces are themselves withdrawing in a manner similar to their erstwhile Soviet opponents before them. US President Joe Biden has assured the American people their troops will be home by Aug. 31.
The political upheavals since 1979 have led to flights of Afghans to neighboring countries in search of safety and economic security. According to estimates from the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), there are 3.5 million Afghan refugees — 90 percent of them hosted by Pakistan and Iran and 65 percent of them children, creating what many are calling a lost generation.

Farzana, who fled her village in Helmand province when it was taken over by the Taliban earlier this year, waits to see a doctor at a mobile clinic for women and children set up at the residence of a local elder in Yarmuhamad village, near Lashkar Gah in Helmand province. (AFP/File Photo)
The UNHCR has given warning of a fresh wave of displacement if the security situation deteriorates any further in the wake of the NATO withdrawal. The agency counted 1.44 million Afghan refugees in Pakistan as of July this year. Since January alone, 224,000 more have crossed the Pakistani frontier. Islamabad has said it simply cannot take any more.
Refugees place a significant strain on host countries — and few more than Pakistan, where per capita GDP in 2020 stood at around $1,170 and fiscal deficit was 8.1 percent. This has no doubt grown worse under the pressures of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
Pakistan’s porous border with Afghanistan has been exploited by Taliban fighters, Al-Qaeda operatives, and all manner of smugglers and bandits. The resulting violence and lawlessness have taken their toll on the economy and local people. In Balochistan and Sindh, a flood of drugs and arms has had a disintegrating effect on vulnerable sections of society.
As a strategic ally in America’s war on terror, Pakistan has often been lavished with Western aid, but has also been penalized for hosting Islamic militants of every stripe within its borders.

An Afghan National Army (ANA) helicopter takes off inside the Bagram US air base after all US and NATO troops left, some 70 Kms north of Kabul on July 5, 2021. (AFP)
From a Pakistani perspective, which way this pendulum swings appears to depend on Washington’s relations with India, which took a keen interest in the reconstruction of war-torn Afghanistan to counter Pakistani influence.
Iran, for its part, hosts roughly 980,000 documented Afghan refugees. When the undocumented are included, the number swells to 1.5 million. For sanctions-crippled Tehran, this is a huge economic burden.
Per capita GDP in Iran fell from $6,950 to $5,940 between 2017 and 2020, according to Trading Economics. But unlike Pakistan, the government at the very least has the means to regulate its borders.
The regime is also known to have used young Shiite Afghans to fight its battles in Syria under the banner of the Fatemiyoun division. It also holds a significant stake in the local economy of Afghanistan’s western province of Herat.
Given its interest in Afghanistan’s fortunes, Iran is now reportedly in negotiations with both the Taliban and the government in Kabul.
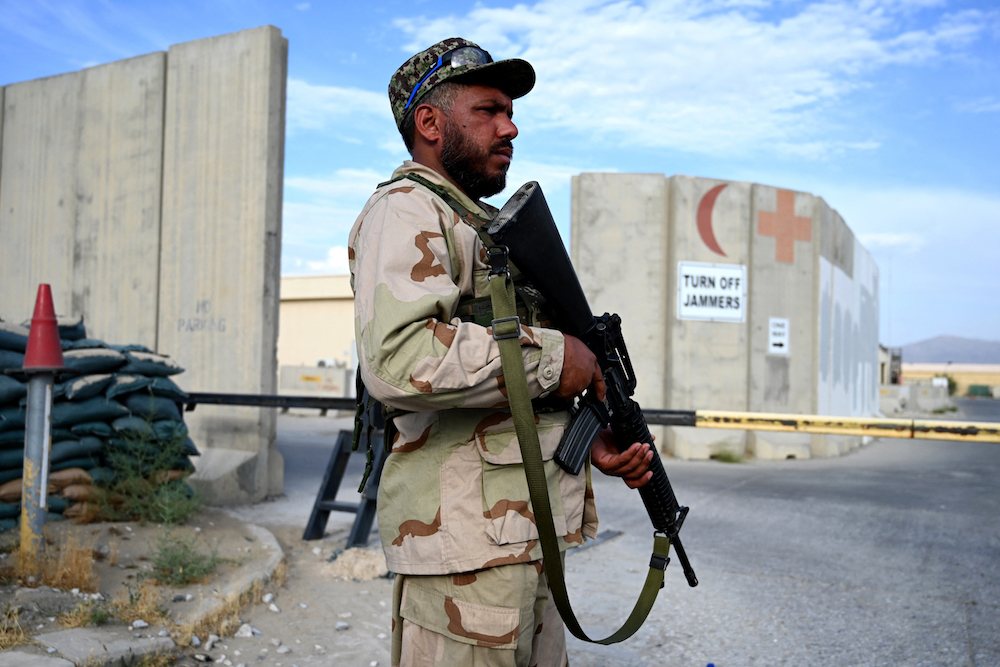

An Afghan National Army (ANA) soldier stands guard at a gate of a hospital inside the Bagram US air base after all US and NATO troops left, some 70 Km north of Kabul on July 5, 2021. (AFP)
Afghanistan’s northern neighbors Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan, meanwhile, are also concerned about a potential wave of refugees. Their economies would have a hard time absorbing such an influx given their structural difficulties and relatively low median per capita GDP in 2019 of $2,465, $3,580, and $8,005, respectively.
All three countries have held consultations with the local power broker, Russia, on the economic and security ramifications of the deteriorating situation in Afghanistan.
Zamir Kabulov, the Russian deputy foreign minister and special envoy for Afghanistan, last week met with Taliban leaders, who assured him they would respect the territorial integrity of the former Soviet republics should they retake power.
Then there is China — a nation with major investments, and ambitions, in the region.
Beijing believes the NATO withdrawal from Afghanistan is premature — unsurprising, given it is overseeing investments worth more than $60 billion in the China Pakistan Economic Corridor, which links the Middle Kingdom to the Baloch deep-sea port of Gwadar.
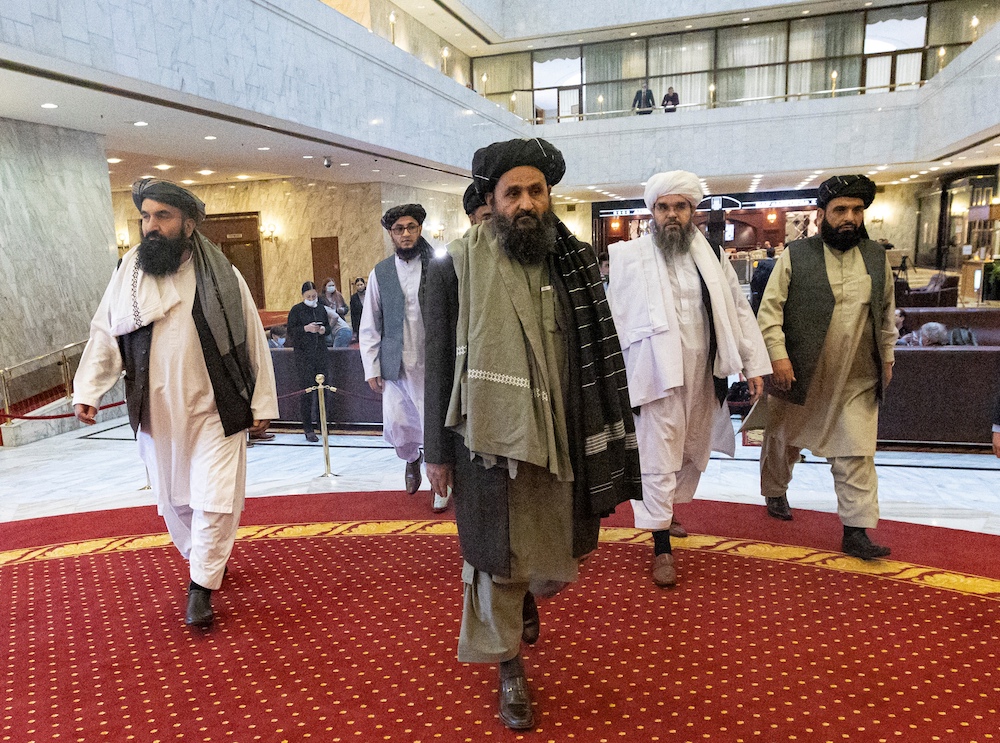

Taliban co-founder Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar (C) and other members of the Taliban delegation arrive to attend an international conference on Afghanistan over the peaceful solution to the conflict in Moscow on March 18, 2021. (AFP/File Photo)
China also has sizable investments in the Central Asian republics, which supply it with gas and minerals, and which are also part of its Belt and Road Initiative, as is Iran. Wang Yi, the Chinese foreign minister, is currently visiting Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan to take the regional pulse.
In Afghanistan itself, China had signed a $2.8 billion deal to exploit a copper deposit in Mes Aynak, southeast of Kabul, and in 2019 imported Afghan pine nuts worth $40 million. But, overall, China’s involvement in reconstruction projects has been modest and it has thrown little money into the Afghan economy.
The Taliban has assured China its investments in the country are more than welcome. Habitually cautious Beijing is nevertheless concerned about the rapidly changing facts on the ground.
With so many regional players having a stake in what comes next for Afghanistan, there is more than a mere whiff of the Great Game about the period ahead. Indeed, the withdrawal of NATO troops will leave a geopolitical vacuum that many players are now eager to fill.
In a commentary on Thursday, Indian strategic expert and syndicated columnist, Brahma Chellaney, drew an analogy between Afghanistan and Vietnam. He said: “Recall the last time the US left a war unfinished: In 1973, it hastily abandoned its allies in South Vietnam. The next year, 90,000 South Vietnamese soldiers and civilians were reportedly killed as a result of the conflict, making it the deadliest year of the entire Vietnam War.”
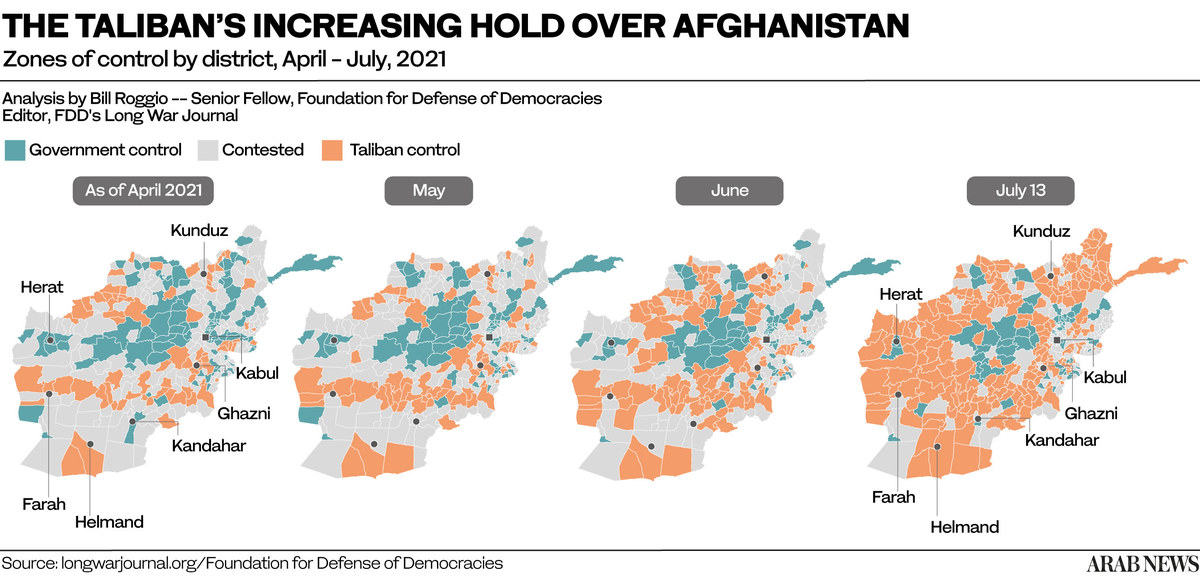
If the Taliban retakes power or engages the Afghan government in a prolonged and savage conflict, there will be serious political, economic and humanitarian ramifications for Afghanistan’s neighbors, especially those with ethnic ties to the rainbow of cultures that make up Afghan society.
But there is far more at stake for the Afghan people than the interests and investments of foreign states. The last 20 years have seen the creation of an active civil society in Afghanistan, including a vibrant free press and active women’s representation.
On the possibility of those gains evaporating soon, former US President George W. Bush, who deployed American forces to the Middle East in the wake of the 9/11 attacks, said: “I’m afraid Afghan women and girls are going to suffer unspeakable harm.”
Every kilometer the Taliban advances toward Kabul, the faster the worst-case scenario unfolds for the region.
----------------
* Cornelia Meyer is a Ph.D.-level economist with 30 years of experience in investment banking and industry. She is chairperson and CEO of business consultancy Meyer Resources. Twitter: @MeyerResources


























