WASHINGTON: Jeff Bezos, the richest person in the world, is set to join the astronaut club Tuesday on the first crewed launch by Blue Origin, another key moment in a big month for the fledgling space tourism industry.
The mission comes days after Virgin Galactic founder Richard Branson crossed the final frontier, narrowly besting the Amazon magnate in their battle of the billionaires.
Blue Origin’s sights are, however, set higher: both literally in terms of the altitude to which its reusable New Shepard craft will ascend compared to Virgin’s spaceplane, but also in its future ambitions.
Bezos founded Blue Origin back in 2000, with the goal of one day building floating space colonies with artificial gravity where millions of people will work and live.
Today, the company is developing a heavy-lift orbital rocket called New Glenn and also a Moon lander it is hoping to contract to NASA under the Artemis program.
“They’ve had 15 successful New Shepard uncrewed flights and we’ve been waiting years to see when they’re going to start flying people,” Laura Forczyk, founder of space consulting firm Astralytical, told AFP, calling it an “exciting time” for enthusiasts.
New Shepard will blast off at 8:00 am Central Time (1300 GMT) on July 20 from a remote facility in the west Texas desert called Launch Site One, some 25 miles (40 kilometers) north of the nearest town, Van Horn.
The event will be live streamed on BlueOrigin.com beginning an hour and a half before.
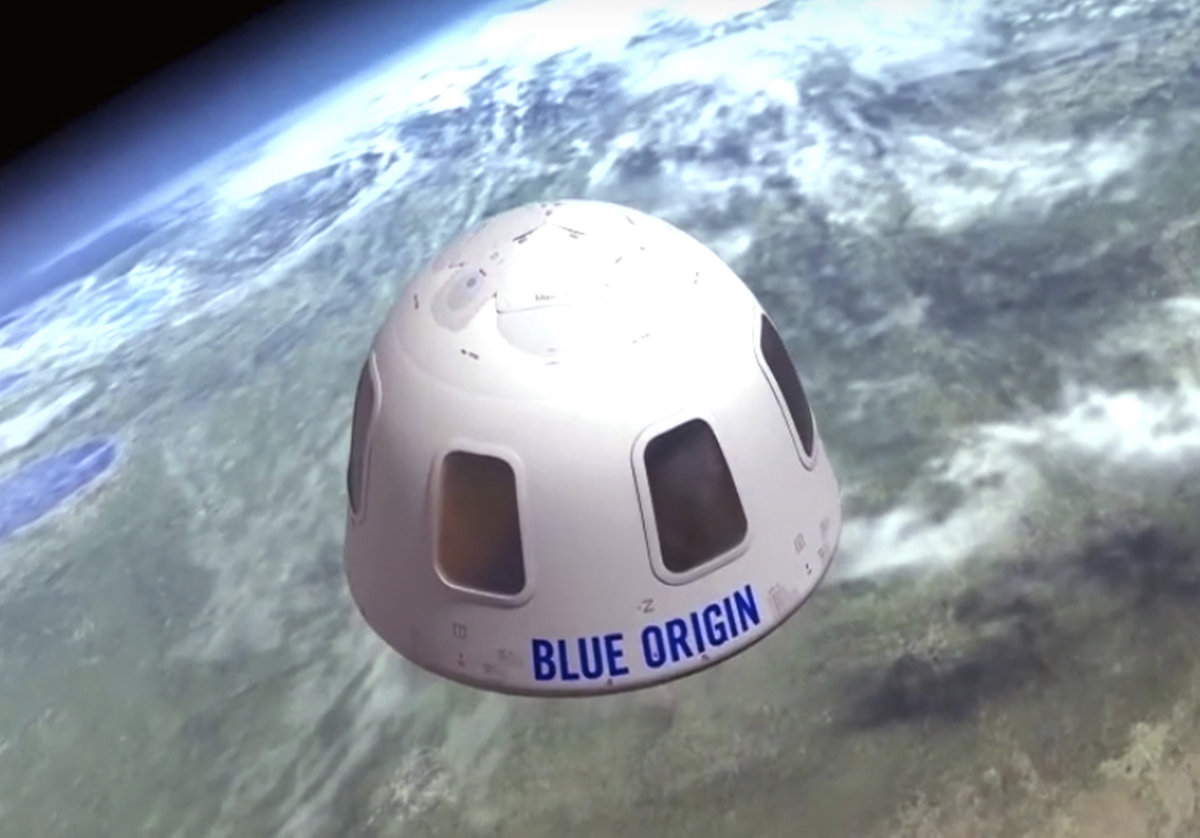

This undated image shows an illustration of the capsule that will be used to take tourists into space. (Blue Origin via AP)
Joining Bezos on the fully autonomous flight will be barrier-breaking female aviator Wally Funk, who at 82 is set to be the oldest ever astronaut, Dutch teenager Oliver Daemen, the company’s first paying customer, who will become the youngest astronaut.
Rounding out the four-member crew is Jeff Bezos’ brother Mark, a financier who directs the Bezos Family Foundation and works as a volunteer firefighter.
The pair are best friends, and Jeff shared the moment he asked his younger sibling to join him in a viral video on Instagram last month.
Notably absent is the mysterious winner of a $28 million auction for a seat, who had “scheduling conflicts” and will take part in a future flight, and has asked to remain anonymous, the company said.
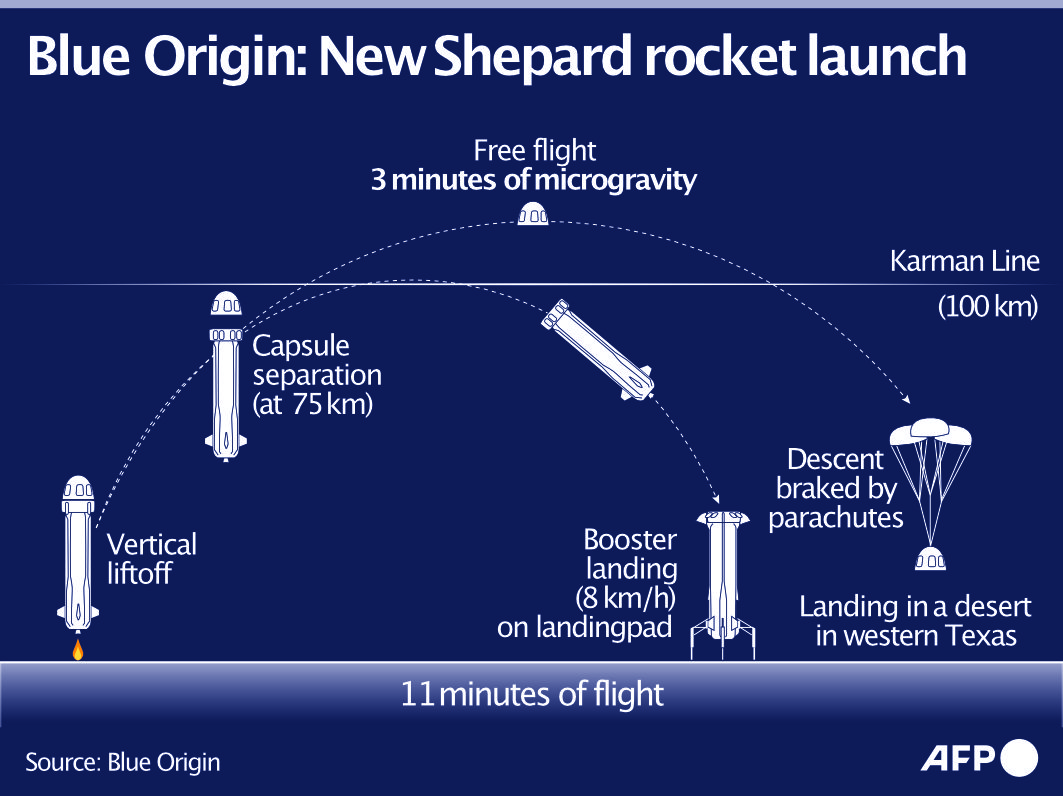
After lift-off, New Shepard will accelerate toward space at speeds exceeding Mach 3 using a liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine with no carbon emissions.
The capsule soon separates from its booster, and the astronauts unbuckle and begin to experience weightlessness.
The crew will spend a few minutes beyond the Karman line — the internationally recognized boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and space, at 62 miles altitude (100 kilometers), as the spacecraft peaks at 65 miles high (106 kilometers).
They will be able to admire the curvature of the planet — and the inky black of the rest of the universe — from large windows that comprise a third of the cabin’s surface area.
The booster returns autonomously to a landing pad just north of its launch site, while the capsule freefalls back to Earth before deploying three giant parachutes, and finally a thruster, to land gently in the west Texas desert.
Beyond the first flight, relatively little is known about Blue Origin’s future tourism plans.
The company has a history of secrecy, its existence only becoming public knowledge three years after its creation. It then pursued a policy of “self-imposed silence” until 2015.
Unlike Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin hasn’t officially started selling tickets — Daemen won his spot through the auction process. The company wants two more flights this year, then “many more” in 2022, it told AFP.
Forczyk, the analyst, said it will all depend on the level of demand that is generated by these early flights, and how well the industry recovers from accidents “which there inevitably will be, because spaceflight is inherently risky.”
Elon Musk’s SpaceX will enter the fray in September with an all-civilian orbital expedition on its Crew Dragon, and is tying up with another company, Axiom, for visits to the International Space Station.
Beyond tourism, Blue Origin would like to supplant SpaceX as NASA’s leading private sector partner, and sees New Shepard as “sort of the stepping stone and also the way to make money along the way for the greater ambition,” said Forczyk.
Who’s who on Blue Origin’s first crewed flight
Jeff Bezos, 57: The spaceship Blue Origin was built by the company he founded in 2000, when he was still merely a single-digit billionaire. Six years before that, he started a small online bookstore called Amazon.com out of his garage. Bezos’ net worth is today estimated at more than $200 billion.
Mark Bezos: The brother of Jeff is a financier who directs the Bezos Family Foundation and works as a volunteer firefighter. The pair are best friends, and Jeff shared the moment he surprised his sibling, six years his junior, by asking him to join the mission in a video that went viral on Instagram last month.
Wally Funk: At 82, barrier-breaking woman aviator is about to become the oldest ever astronaut, fulfilling a lifelong dream that was thwarted by the sexism of the early space era. Funk, who took her first flying lesson aged nine, excelled in the Mercury 13 project which was intended to train women for space using the same standards as male astronauts, but the program was eventually nixed. She nevertheless had an accomplished career in aviation, becoming the first female air safety investigator for the National Transportation Safety Board, and serving as chief pilot in several flight schools.
Oliver Daemen: At 18, she is set to become the youngest astronaut. He holds a private pilot’s license and is a space enthusiast who will study physics in university this fall. The Dutch teen is flying in place of the still anonymous winner of a $28 million public auction, who asked to pass this time because of “scheduling conflicts,” and will go on a later trip. Daemen’s ticket was paid for by his father, the CEO of a private equity firm, CNBC reported.
How can you become a space tourist?
Thrill-seekers might soon be able to get their adrenaline kicks — and envy-inducing Instagram snaps — from the final frontier, as space tourism finally lifts off.
All you’ll need is a bit of patience. And a lot of money.
Here’s a rundown of where things stand.
Two companies are offering short “suborbital” hops of a few minutes: Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, founded by Richard Branson.
Blue Origin’s New Shepard rocket takes off vertically and the crew capsule detaches and crosses the Karman line (62 miles, or 100 kilometers, in altitude), before falling back to Earth with three parachutes.
Virgin Galactic uses a massive carrier plane, which takes off from a horizontal runway then drops a rocket-powered spaceplane. This in turn soars to over 50 miles altitude before gliding back.
In both cases, up to six passengers are able to unbuckle from their seats to experience a few minutes of weightlessness and take in the view of Earth from space.
Virgin Galactic has said regular commercial flights will begin from 2022, following two more test flights. Their waiting list is already long, with 600 tickets so far sold.
But the company predicts it will eventually run up to 400 flights per year. Two seats on one of the first flights are up for grabs in a prize draw: registrations are open until September 1.
As for Blue Origin, no detailed calendar has been announced.
“We’re planning for two more flights this year, then targeting many more in 2022,” a spokesperson told AFP.
Another way to get to space is via reality television. Space Hero, an upcoming show, says it plans to send the winner of a competition to the International Space Station (ISS) in 2023.
The first tickets sold by Virgin Galactic went for between $200,000 and $250,000 each, but the company has warned that the cost for future sales will go up.
Blue Origin hasn’t announced prices. The anonymous winner of a public auction for a seat on the first crewed flight paid $28 million, but decided to defer their trip.
It’s not known what amount was bid for the seat secured by Dutch teen Oliver Daemen, who will fly in the auction winner’s place.
The more “budget conscious” might consider spending $125,000 for a seat on Space Neptune: a capsule that offers 360 degree windows and is lifted to the upper atmosphere by a balloon the size of a football stadium.
Despite the promise of spectacular views, the balloon ascends only 19 miles — far from the boundary of space, and weightlessness.
The 300 seats for 2024 have all been sold, but reservations are open for 2025.
No — you’re only expected to be in reasonable shape. Virgin Galactic’s training lasts just five days.
Blue Origin promises to teach you everything you need to know “the day before you launch,” and its first crewed flight includes pioneering aviator Wally Funk, who at 82 will become the oldest astronaut.
The company’s requirements include being able to climb seven flights of stairs in under 90 seconds (the height of the launch tower) and being between 5’0” and 110 pounds (152 centimeters and 50 kilograms) and 6’4” and 223 pounds (193 cm and 100 kg).
Elon Musk’s company is also getting into the space tourism game, but its plans involve journeys that are far longer. The costs are also predicted to be astronomical — tens of millions of dollars.
In September, American billionaire Jared Isaacman has chartered a mission called Inspiration4 to take him and three other passengers into orbit around the Earth on a SpaceX Crew Dragon, launched into space by a Falcon 9 rocket.
Then in January 2022, three businessmen will travel to the ISS with an experienced astronaut. The mission, named Ax-1, is being organized by the company Axiom Space, which has signed up for three other future flights with SpaceX.
Elon Musk’s company is also planning a trip to orbit for four people, organized by intermediary Space Adventures — the same company in charge of the flight of the Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa to the ISS in December, aboard a Russian Soyuz rocket.
Maezawa is also supposed to take a trip around the Moon in 2023, this time aboard a rocket that is still under development by SpaceX, called Starship.
He invited eight members of the public to join him — but applications are now closed.




























