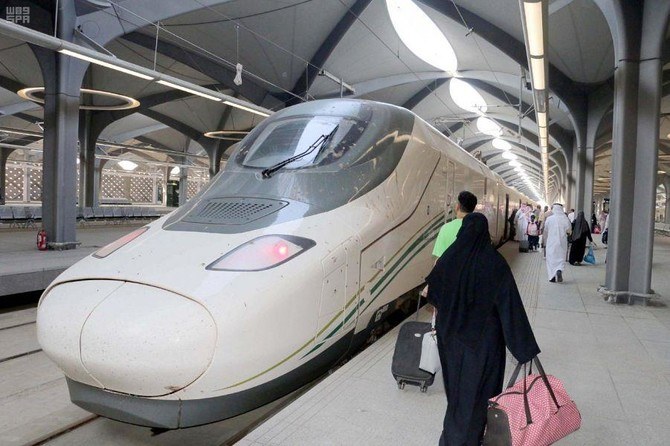
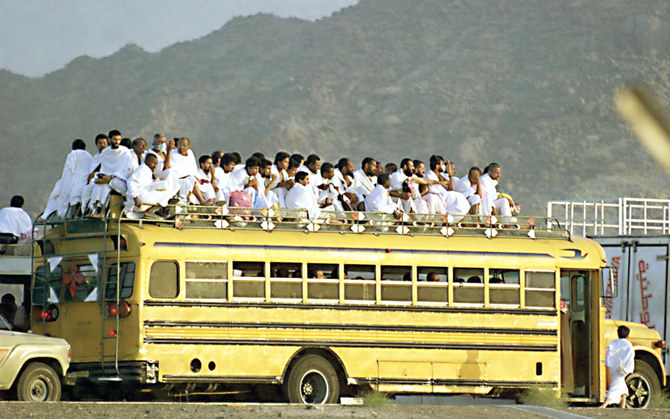
JEDDAH/MAKKAH: Before the invention of cars, buses and other modern modes of mass transit, pilgrims performing Hajj and Umrah relied exclusively on convoys of camels, horses and donkeys to reach the holy cities of Makkah and Madinah on demanding journeys that could take months to complete.
Even as the means of transport evolved from pack animal to four-wheeled vehicle, from horseback to horsepower, the older generation still recalls pilgrimages that were grueling, yet had a much stronger spiritual resonance than today’s journeys of relative comfort.
“My late parents performed Hajj on a caravan of carriages, camels and mules all the way from Gaza to Makkah,” Fadhel Mahmoud, a 76-year-old Jeddah resident, told Arab News. “After they went back home, they sacrificed the camel, and distributed its meat to the needy and poor.”
FASTFACT
3,161,573
Hajj pilgrims in 2012, the largest number in 10 years.
Mahmoud recalls his own first Hajj experience in 1968, arriving at the so-called City of Tents in the Mina valley, southeast of Makkah.
“Fifty-four years ago, my brothers and I went to perform Hajj on a pickup truck, and we camped in our tent and prayed with Shaykh Mahmoud Khalil Al-Hussary — an Egyptian Qari (Qu’ran reciter) widely acclaimed for his accurate recitation — in Mina and Arafat,” he said. “It was a very simple Hajj, with a smaller number of pilgrims than these days.”
Historically, there were seven major pilgrimage routes that would approach Makkah and Madinah from the four points of the compass, the five most popular being the Iraqi, Syrian, Egyptian, Yemeni and Omani circuits.
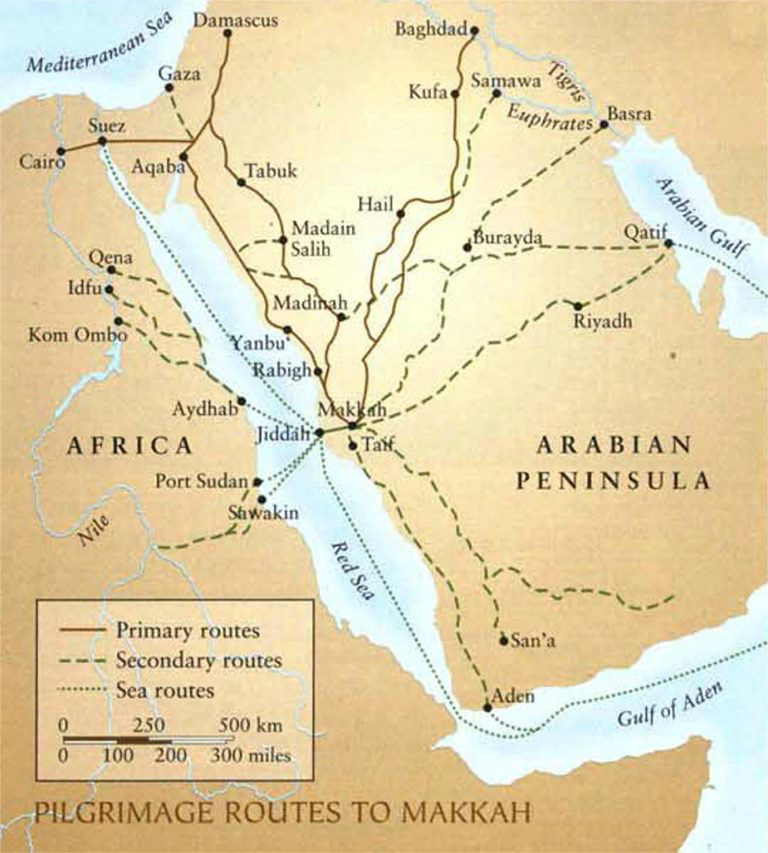
Map showing land and sea routes of the Hajj in the early 20th century. (Courtesy of AramcoWorld)
The Kufi-Makkah route, also known as the Zubaydah trail, which originated in present-day Iraq, was considered among the most important pilgrimage and trade routes of the Islamic period.
The Basra-Makkah route was seen as the second-most important, starting in the bustling Iraqi port city before passing south across the Arabian Peninsula’s northeast, through Wadi Al-Batin, then onward through the rugged Al-Dahna desert, where it would merge with the Kufa-Makkah route.
The Egyptian route to Makkah was the most popular during the first three Hijri centuries, and was used by pilgrims from as far west as Morocco and Andalusia in present-day Spain.
The Syrian route, meanwhile, tied the Levant to the two holy mosques of Makkah and Madinah, its path beginning in Damascus before wending its way through Daraa and onward to AlUla in today’s Saudi Arabia.
Along the Tabuk to AlUla route, which flourished during the Abbasid era (750-1258), archaeologists have found evidence of pools, canals and Kufic inscriptions left by travelers along this historic road.
Since ancient times, Yemeni routes have linked the cities of Aden, Taiz, Sanaa, Zabid and Saada to the Hijaz of western Saudi Arabia, including one along the coast, another through the interior and one over the highlands.
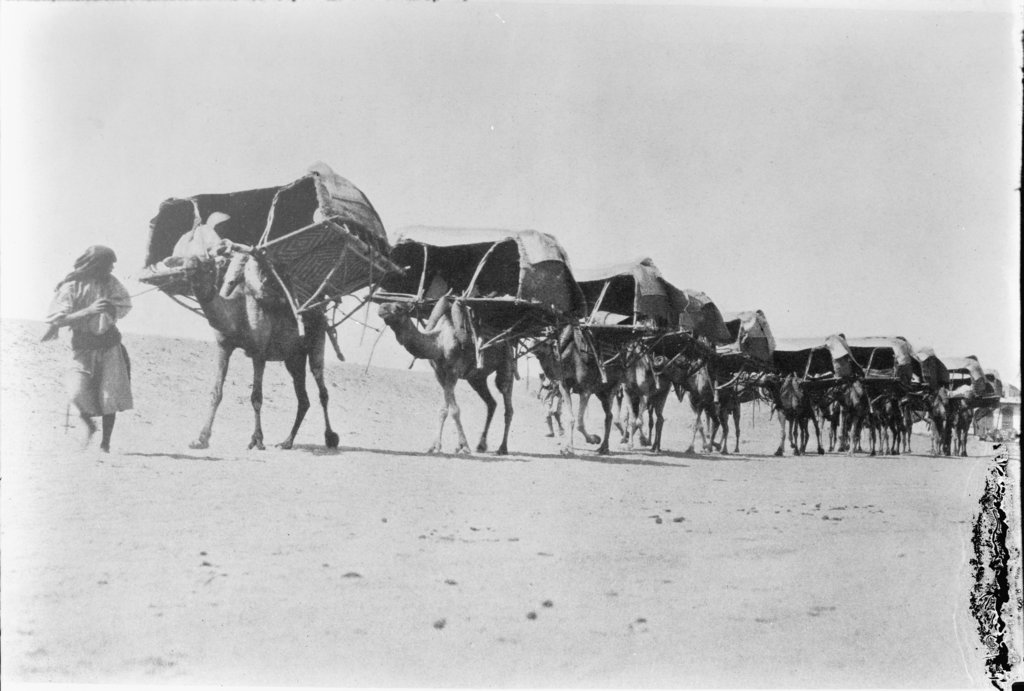

A camel caravan traveling to Makkah for the annual pilgrimage circa 1910. (Wikimedia commons)
The Omani route, meanwhile, passed through Yabrin, where it met the route from Bahrain on its way to Makkah.
Islamic caliphs and sultans down the ages have taken care of these pilgrimage routes, establishing rest stations and wells along the way to cater for weary travelers and their thirsty pack animals.
But, in 1924, pilgrims were ordered to cease using camels and instead rely on motor vehicles to complete the journey. However, due to the lack of proper roads, camels remained the preferred means of transport for several years after the ban.
Then, in 1948, the Saudi General Syndicate of Cars was born, marking the foundation of the first-ever regulated transport service for pilgrims.
Four years later, in 1952, Saudi Arabia’s founder, King Abdul Aziz, ordered the creation of the second General Syndicate of Cars, based in Makkah. What began as a collection of just five logistics firms has today grown to 69 dedicated outfits.
“The General Syndicate of Cars has actively contributed to the development of the types of vehicles that are used to transport pilgrims since its establishment, starting with the very first version of red lorries of various German and American brands used for cargo and other purposes,” Abdulrahman bin Mayouf Alharbi, chairman of the General Syndicate of Cars, told Arab News. “Then we moved to use the famous yellow school buses.”
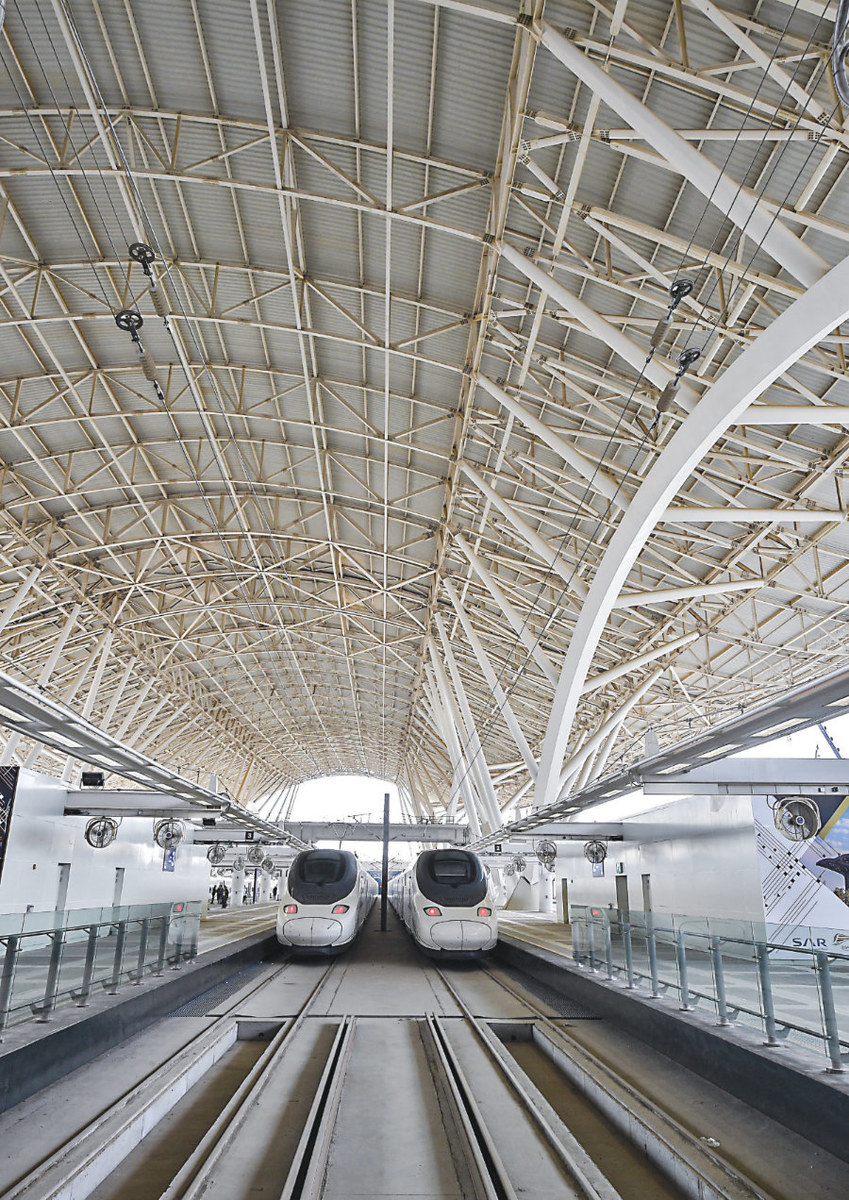

Inaugurated in 2018, the Haramain High-Speed Railway has helped increase the number of pilgrims and visitors to Makkah and Madinah with ease. (AFP)
Even today, the pilgrimage continues to shape the evolution of Makkah’s transport infrastructure and its growing urban layout. As the Hajj 2021 season approached, new roads and tunnels featuring the latest traffic-control technology were under construction to cater for the expected influx of visitors.
Dr. Othman Qazzaz, head of research at the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques Institute for Hajj and Umrah Research at Makkah’s Umm Al-Qura University, said that his researchers have explored a wide range of intuitive traffic reduction measures, including pedestrian walkways, and independent roads reserved solely for pilgrims and emergency vehicles.
“The institute has sought to help pilgrims perform Hajj and Umrah in ease and peace, most notably by introducing the shuttle bus program and expanding the transportation means provided for pilgrims between Makkah, the central area and their accommodation,” Qazzaz told Arab News.
Since it was established 10 years ago, the shuttle bus program, in particular, has boosted capacity while also reducing congestion. And, because of the city’s mountainous topography, a network of 59 bridges and 66 tunnels has been established over the past four decades to offer additional avenues for vehicles and pedestrians entering the center and to help avoid bottlenecks.
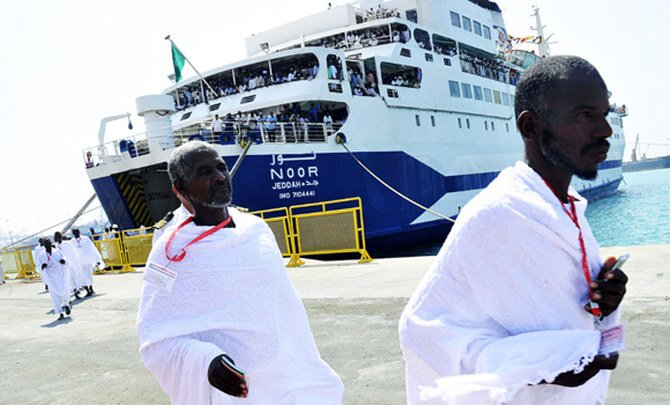

Sudanese pilgrims disembark from a ship arriving at the Saudi Red Sea port of Jeddah to attend the annual Hajj pilgrimage circa 2007. (AFP file)
Raad bin Mohammed Al-Sharif, spokesperson for Makkah municipality, told Arab News the city’s tunnels and holy sites have been equipped with command-and-control systems and a centralized CCTV surveillance network to allow officials to monitor and relieve areas of congestion.
In order to prevent congregations becoming too large, particularly given the threat of stampedes and the need to maintain coronavirus social-distancing, officials are directing pilgrims to gather at four main entrances: Al-Taneem, Al-Sharai, the Kor checkpoint and the Al-Shumaisi security zone.
Years of careful site testing and topographical surveys have gone into this vast urban reimagining, along with extensive data gathering and public questionnaires to help determine areas of high demand, possible pressure points and where there is space for improvement.

Travel time for pilgrims during the modern age has been cut from weeks or months to just hours. (AFP file photo)
In particular, researchers have examined current and future demand for services between Mahbas Al-Jinn, Kudai and the Grand Mosque, the economic and environmental viability of various modes of transport, and the likely impact of greater traffic on the quality of services on offer. Similar surveys have also been conducted in Madinah to improve transport infrastructure.
The hardships of the road to Makkah and Madinah, as well as the facilities on offer when pilgrims arrive from the distant corners of the Islamic world, have eased over the centuries, and the means of getting there have changed beyond recognition.
Nevertheless the same spiritual yearning that brought those early pilgrims across oceans, deserts and continents remains to this day — and grows with each passing year.





































