DUBAI: Countries in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region with low rates of vaccination against COVID-19 have been experiencing an explosion of new cases and fatalities linked to the spread of the highly transmissible delta variant.
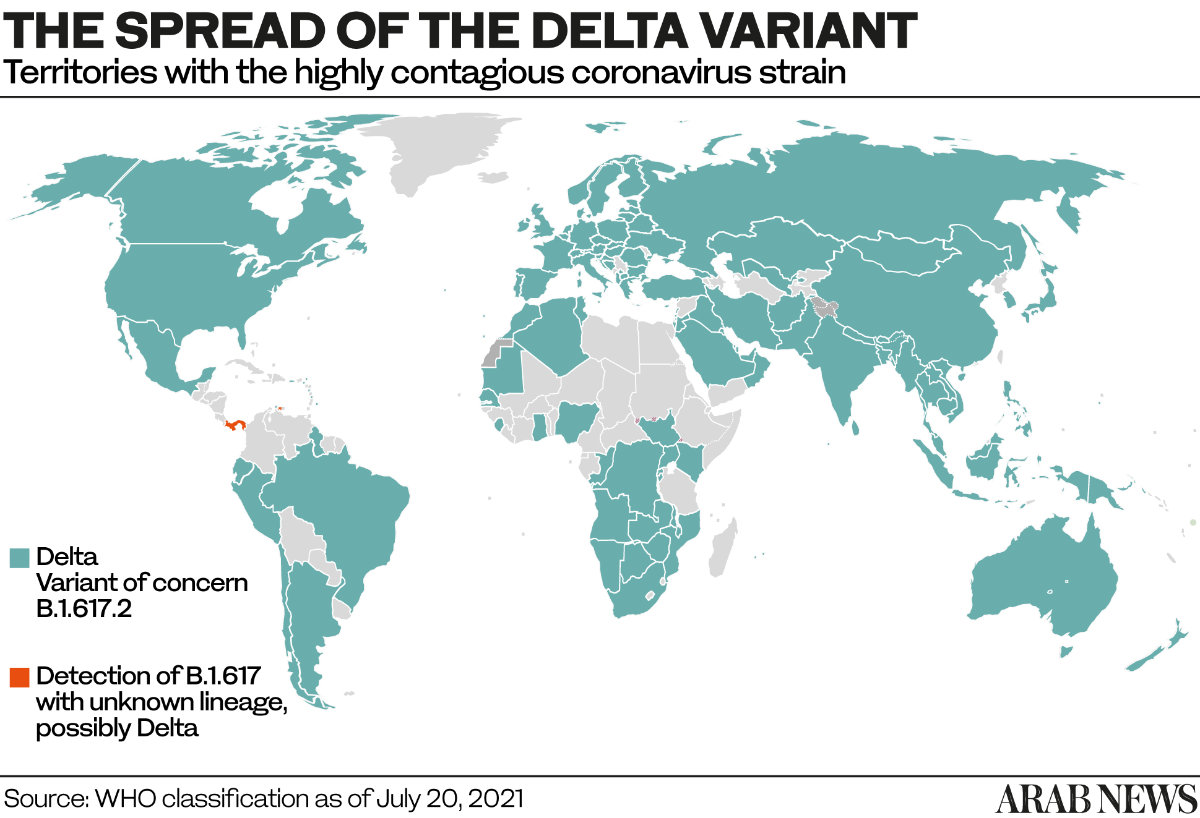
Worldwide, the variant has been detected in at least 132 countries, prompting new waves of infection, the resumption of travel restrictions, and mounting concern over the availability and effectiveness of vaccines.
In the Gulf and eastern Mediterranean region, the variant has been found in more than a dozen countries including Kuwait, the UAE, Bahrain, and Qatar. Although Saudi Arabia has not yet reported any cases, it has reimposed a raft of travel curbs in additions to bans and penalties for violators.
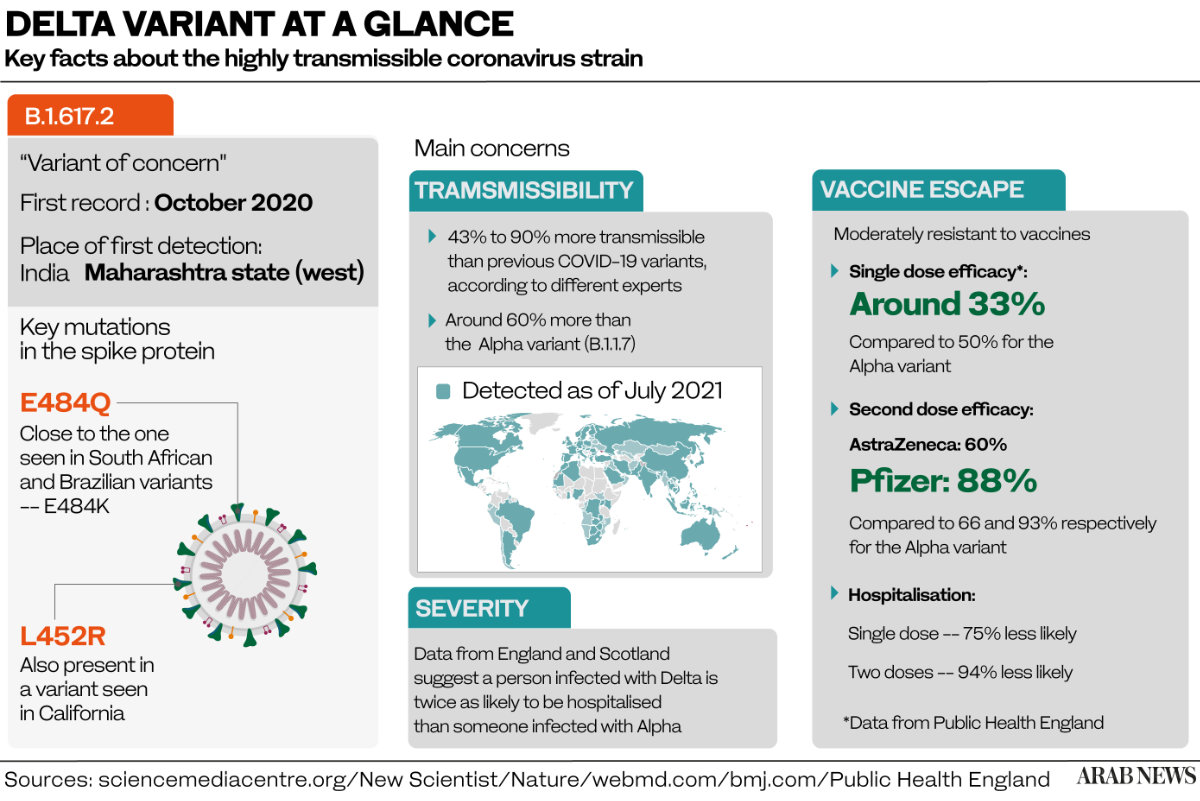
Also known by its scientific name B.1.617.2, the delta variant of the coronavirus was first detected in the Indian state of Maharashtra in October but was only labeled a variant of concern by the WHO on May 11.
Dr. Abdinasir Abubakar, head of the infectious hazards management unit at the WHO’s Middle East and eastern Mediterranean regional office in Cairo, told Arab News: “It was very easy for delta to spread throughout the region due to the many migrant workers from South Asia living in the Gulf and North Africa.”
The strain, itself the product of multiple mutations, is thought to be 60 percent more infectious than the alpha (or Kent) variant, an earlier mutation that emerged in southern England in November, and as contagious as chickenpox.
According to a confidential CDC document, picked up by US media in late July, delta is more transmissible than the common cold, the 1918 Spanish flu, smallpox, Ebola, MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) and SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome), has a longer transmission window than the original strain, and may make older people more ill — even those fully vaccinated.
US health officials said people infected with the delta variant could carry up to 1,000 times more virus in their nasal passages than other strains, resulting in higher transmissibility. The WHO predicted there could be at least 200 million new cases worldwide in a matter of weeks.
In many countries, including the UK, the delta variant has now become the dominant strain. In Israel, which has a very high rate of vaccination, delta makes up 90 percent of new infections.
What is perhaps most alarming for health professionals is the number of young people, many of them unvaccinated, who are becoming seriously ill with the variant.
Earlier iterations of the virus were considered more harmful to older demographics and people with underlying health conditions, groups that governments have tended to prioritize in vaccination drives.
Although it appears to cause more severe symptoms than its forerunners, there was currently not enough data to suggest delta was any more deadly.
More encouraging was the data on the effectiveness of vaccines. A study by Public Health England found that the Pfizer vaccine was 94 percent effective against hospitalization after one dose and 96 percent effective after two doses, while AstraZeneca was 71 percent effective after one dose and 92 percent effective after two.
On Sunday, the UK’s Guardian newspaper reported that New York-based Pfizer and Germany’s BioNTech “have tweaked their mRNA vaccine to target the delta variant and will begin testing it on humans” this month.
The global market for COVID-19 vaccines, valued at $70 billion this year, could grow bigger as scientists debate whether people will need booster shots for the delta variant.
Owing to the slow rollout of vaccines in large parts of the developing world, there is limited protection for their populations against COVID-19.
In MENA countries, outbreaks of the delta variant of the coronavirus are adding to the pressure on hospitals, life-saving equipment, and even mortuaries.
Tunisia has been gripped by social unrest, attributable to a mix of political dysfunction, stretched healthcare systems, and mounting economic hardship.
In Iran, a country which has vaccinated just 3 percent of its population, around 35,000 new infections and 357 deaths were recorded on July 27 alone.
In conflict-ridden areas of the Middle East, namely Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, and Yemen, where immunization rates remain low, the surge in delta cases poses a serious challenge to already ailing health systems and fragile government structures.
Abubakar said: “We are extremely concerned about what will happen when the delta variant spreads to emergency countries like Syria and Yemen. Delta will reach all countries in the region. The WHO is trying to work with nations to prepare for the worst, like having more ICU (intensive care unit) beds, oxygen, vaccines, and amplifying our social messaging.
“No country is immune from delta. We cannot afford for other countries in the region to go through what Tunisia is going through right now,” he added.
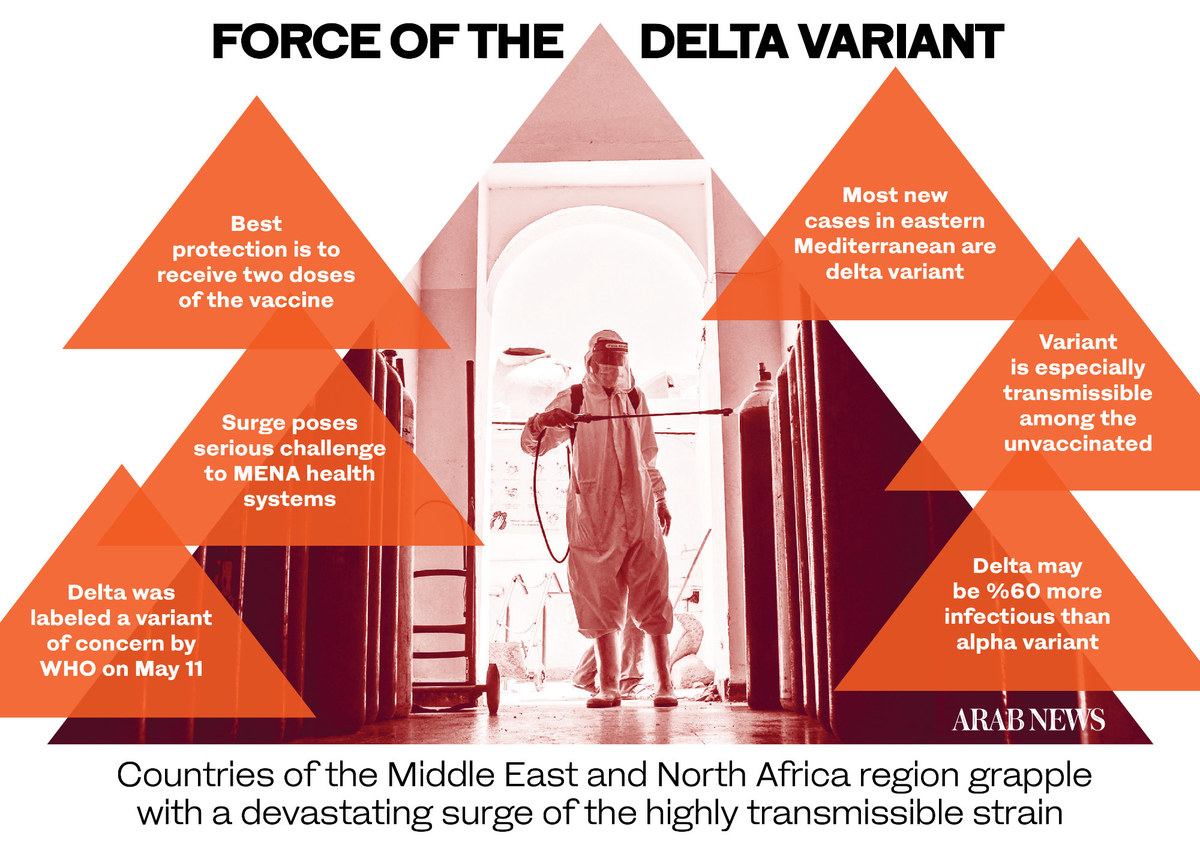
FASTFACTS
Delta was labeled a variant of concern by WHO on May 11.
Most new cases in eastern Mediterranean are delta variant.
Variant is especially transmissible among the unvaccinated.
Delta may be 60% more infectious than alpha variant.
Surge poses serious challenge to MENA health systems.
Best protection is to receive two doses of the vaccine.
In Lebanon, for instance, a rise in COVID-19 cases would place an even greater burden on a cash-strapped country already blighted by electricity and fuel shortages.
Pierre Abi Hanna, head of the infectious disease division at Rafik Hariri University Hospital, told Arab News: “The numbers in Lebanon are increasing exponentially, and the majority of coronavirus cases circulating in Lebanon, from the samples taken, are from the delta strain.
“Over the last few weeks, we have also seen an increase in the number of hospitalized patients, all of whom are unvaccinated, as well as a small increase in the number of patients in ICU as well as those requiring mechanical ventilation.”
Patients were being hospitalized because they could not take oxygen at home due to Lebanon’s electricity shortages. Those hospitalized had tended to be younger than before and mostly unvaccinated.
“Some of them have received one shot, but the majority have received none. We are now seeing a higher number of cases in the younger population, aged 20 to 49. In the last three days, we have had an increase in the number of people needing ICU beds,” Abi Hanna said.
On a brighter side of the battle, GCC countries have coped well with the delta wave thanks to high rates of vaccination, high levels of compliance with public health measures, and timely travel restrictions.
At the end of June, the UAE announced it was suspending flights from India after recording its first cases of the delta variant. Emirati authorities said the strain now accounted for around one-third of all new infections in the country.
Although it has not recorded any cases of its own, Saudi Arabia unveiled a raft of new measures on July 3 — including a ban on travel to and from the UAE, the world’s top international-transport hub.
Saudi citizens who visit countries on its red list – the UAE, Afghanistan, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Lebanon, and Turkey – now face a three-year travel ban either directly or indirectly through states on the green list.
GCC countries have coped well with the delta wave largely because of high rates of vaccination and high levels of compliance with public health measures. (AFP)
In addition to urging its citizens to continue wearing face masks and maintaining a safe social distance in public places, the Kingdom stressed that the best protection against the delta variant was to receive a second dose of vaccine.
Dr. Wail Bajhmoum, an infectious disease consultant and head of the internal medicine department at King Fahd Hospital in Jeddah, told Arab News: “Citizens should have the vaccines which have been provided by the government and the Ministry of Health free of charge and have been available for everyone in more than 587 centers all over the Kingdom.
“Researchers have shown that two doses of the vaccine will provide very good immunity against all variants of coronavirus, including delta.”
The UAE, which has implemented one of the world’s fastest vaccination campaigns, has issued a delta-detecting PCR test to help isolate the new outbreak. Cases rose at the end of June to more than 2,000 per day, contributing to a daily average of 10 deaths – the country’s highest toll in a single day since March, according to Reuter’s COVID-19 tracker.
The UAE’s National Emergency Crisis and Disaster Management Authority said the increase in deaths was due to the spread of the alpha, beta, and delta variants. Since then, cases have fallen, with 1,536 recorded infections and two deaths on July 27.
“Some countries are better prepared than others. Delta was confirmed earlier in the Gulf countries, but they have a better system in place to handle the variant. This helped limit the spread of the variant, supplemented by the high vaccination rate in Gulf countries.
“We have found that the impact of delta on Gulf countries is low compared with countries with low vaccination rates, notably Tunisia, Afghanistan, Iran, and Iraq,” Abubakar added.
The delta variant is only one of several mutations since the coronavirus first emerged in the Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019 — and it will not be the final iteration.
“It is not the last variant that we will see. We have to be prepared for new variants as well,” Abubakar said.
_____________
• Twitter: @rebeccaaproctor






























