WASHINGTON, D.C.: This summer marks the 100th anniversary of a journalistic triumph against hate. In 1921, The Times of London definitively demonstrated that the infamous “Protocols of the Elders of Zion” was nothing but a crudely plagiarized forgery. Yet despite that, the “Protocols” went on to fuel a century of hate, violence and even genocide against the Jewish people.
This disconnect highlights one of the greatest challenges faced by the press and international community today: Disproving something slanderous is not sufficient to prevent those who are unaware from believing it, especially if extremists have an incentive to keep promoting the slander.
In recent weeks, the Anti-Defamation League (ADL) broke the news when our CEO exposed in Newsweek that Iran’s President-Elect Ebrahim Raisi chaired a foundation while it produced a horrifying 50-episode documentary to promote the “Protocols.”
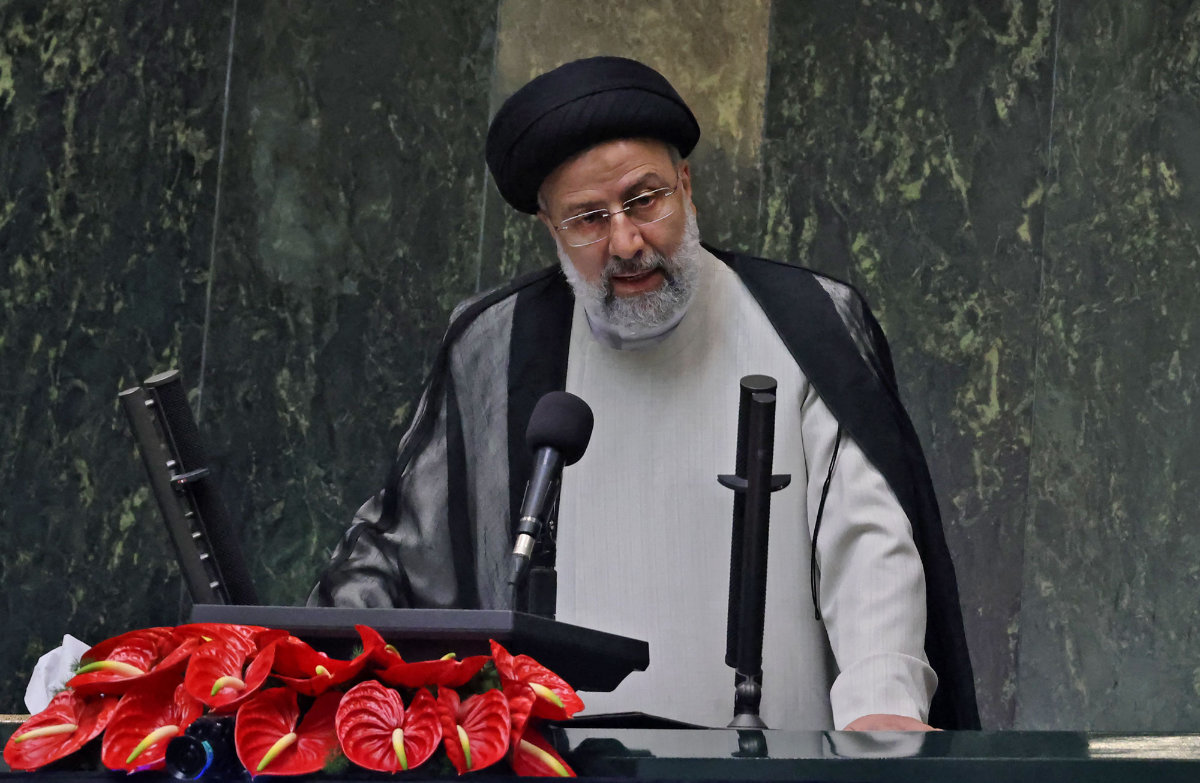

Iran's newly elected President Ebrahim Raisi speaks during his swearing in ceremony at the Iranian parliament in Tehran on August 5, 2021. (AFP)
Even worse, under Raisi’s tenure, the foundation distributed the documentary to some of the millions of pilgrims that visit the Imam Reza Shrine in Mashhad under its control. The documentary, titled “The Devil’s Plan,” aired on some public television stations in Iran, and was even the subject of a quiz about the “Protocols” that pilgrims were urged to participate in at the shrine.
Raisi’s willingness to commit horrible crimes on behalf of Iran’s regime is already well-known. It therefore makes obvious sense that he would have willingly overseen the exploitation of holy sites and modern media to amplify the “Protocols” in service to Tehran’s worldview.
What is more surprising is the widespread ongoing use of the “Protocols” themselves, a full century now after they were proven to be false. Understanding that story can help all of us today as we grapple with the challenges posed by disinformation, including from Iran.
What the ‘Protocols’ allege
The “Protocols” emerged in the Russian Empire around the turn of the 19th century. They purport to be a series of secret meeting minutes from a summit of unnamed Jewish leaders to plot the imposition of a single world government under a dictatorial Jewish king.
Each of the document’s 24 so-called “protocols” is a chapter that focuses on a different aspect of this supposed Jewish plot, such as controlling all the world’s gold, governments, media, education systems, and Freemason societies. Other themes include anti-Jewish stereotypes such as greed, disloyalty, bloodthirstiness, supremacy, and moral corruption.
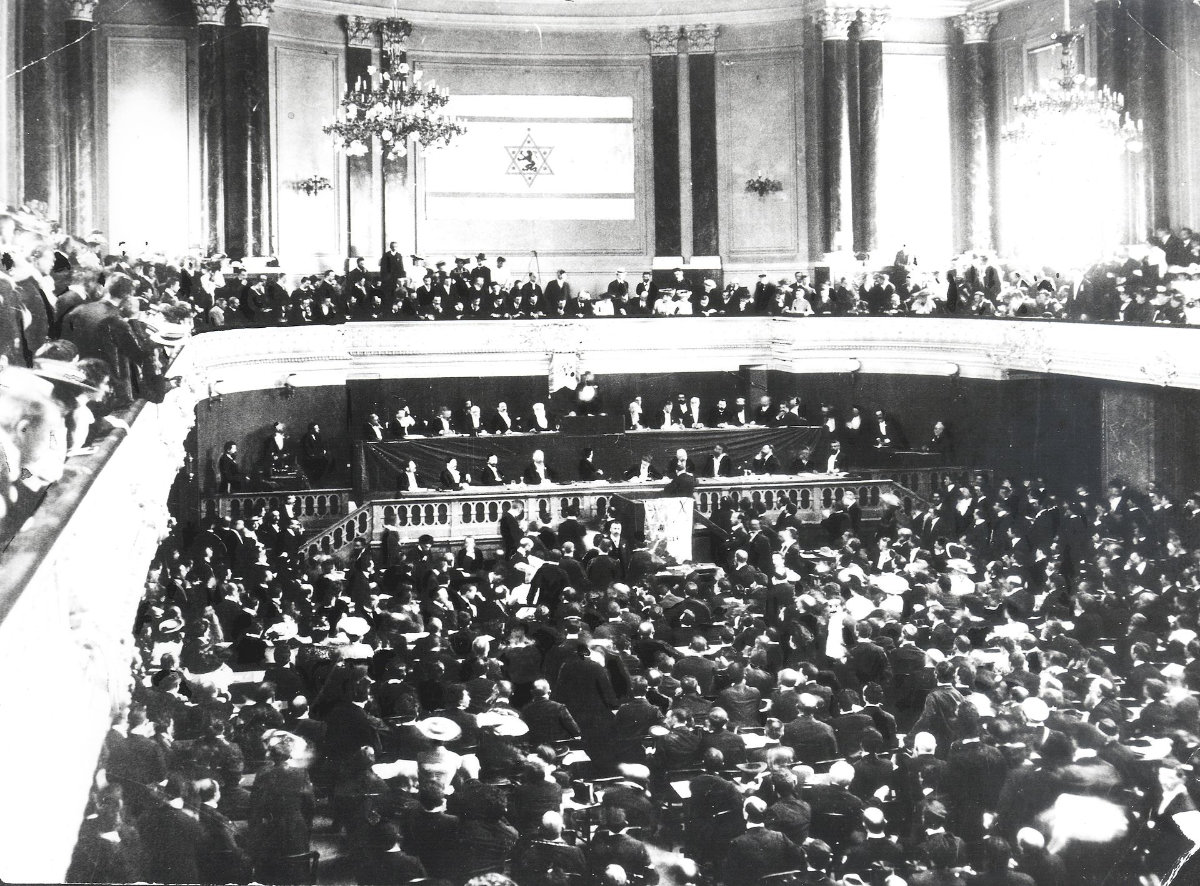
Theodor Herzl at the Second Zionist Congress in Basel in 1898. (Wikimedia Commons)
Some claim that the “Protocols” are the proceedings of the 1897 summit known as the First Zionist Congress that Theodor Herzl organized in Basel, Switzerland. Yet this ignores that the “Protocols” themselves actually pay little heed to Zionism, which was the entire focus of Herzl’s summit, held under scrutiny of the press corps and for which the minutes are publicly accessible in detail.
As the “Protocols” began to circulate outside Russia, the ADL’s forerunner organization and other Jewish-American groups issued a joint statement in 1920 rejecting them as “a base forgery.” The following year, The Times found definitive proof to that effect, in what the paper reflects could be “perhaps the greatest scoop by The Times” in its history.
What The Times found
In August 1921, The Times published a series of articles revealing how they discovered that enormous swaths of the “Protocols” were actually plagiarized from a much older work of fiction that had nothing to do with Jews.
Whereas several other passages in the “Protocols” were already known to be stolen from other works of political fiction, The Times found “the main basis of the forgery on which it was hung, or into which was incorporated, material from other sources.”

Title Page of the antisemitic work Serge Nilus, Great within the Small, The Protocols of Zion, 1905, Russia, an antisemitic hoax purporting to describe a Jewish plan for global domination. (Wikimedia Commons)
That book was Maurice Joly’s “Dialogues in Hell Between Machiavelli and Montesquieu,” a work of French political propaganda published in 1864. Joly sought to mobilize opposition at the time to Emperor Napoleon III by condemning and even demonizing powerful rulers in vague terms. The “Protocols” merely swapped in a shadowy council of unnamed Jews as its main villain.
The Times was given Joly’s book by a Russian expat in Turkey and verified a second in the British Museum. It seemed the “Protocols” were shoddily written “with the intention of furthering antisemitic propaganda in Russia, and at the same time with the idea of enhancing the autocratic power of the Tsar, as the one man who could save the world form the ‘Jewish Peril’.”
Subsequent refutations
More information about how and why the “Protocols” were forged in this manner emerged over time. In 1934-35, two Swiss Jewish groups took local Nazi agitators to court in Bern on defamation charges for publishing the “Protocols.”
The groups brought witnesses who debunked the claims about the 1897 Basel conference and a supposed Jewish-Masonic alliance, while the defense failed to bolster even its most basic claims.
Witnesses for the prosecution even included Russia experts who identified the Russian secret police agents by name involved in forging the “Protocols” in the hope of influencing Tsar Nicholas II while weakening reformists and scapegoating Jews for Russia’s hardships.
The court ruled for the prosecution, concluding “now it has been proven with the utmost clarity” that the texts “had been copied” from Joly’s work, most likely “to gain influence at the Tsar’s court.”
In the US, automaker Henry Ford published an adaptation of the “Protocols” as a series of articles in a local newspaper from 1920 to 1922 and in the form of a book called “The International Jew” that sold half a million copies.

The Ford publication The International Jew, the World's Foremost Problem. Articles from The Dearborn Independent, 1920. (Wikimedia Commons)
But facing possible legal penalties for spreading a forgery, Ford disavowed the “Protocols” in 1927 and apologized to the ADL. And in Russia itself, a Moscow court case in 1992 ruled in favor of a Jewish newspaper being sued for libel when it called an ultranationalist group antisemitic for serializing the “Protocols.”
Three Russian academics, agreed to by both the defense and the prosecution, uniformly gave testimony concluding that the “Protocols” were fake. And in 1999, a historian identified records from Russia’s archives proving what had been alleged by two expert witnesses at the 1934-35 trial in Switzerland: That the “Protocols” were crafted by an operative of Russia’s secret police named Matthieu Golovinski to demonize Jews and marginalize Russian reformers.
How a proven forgery spread
In spite of such refutations, the “Protocols” continued to spread, perhaps because they merely confirmed what many people already believed.
For example, in his 1925 manifesto “Mein Kampf,” Adolf Hitler displayed an awareness that the “Protocols” were identified by mainstream media as a forgery. Yet he was so convinced that his hatred toward Jews was warranted that he described such refutations as “the best proof that they are authentic.”
And he referred to the “Protocols” as a means to achieve his political ends, writing that once the public can be convinced to believe in them, “the Jewish menace may be considered as broken.”

Placards are held up at a counter-demonstration to an anti-Jewish rally, held by a group of far-right protesters on Whitehall in central London on July 4, 2015. (AFP)
His Nazi Party began their campaign against Germany’s Jews in 1933 with a boycott of Jewish-owned shops, calling it a defense against the “Basel Plan,” an allusion to the “Protocols.” Ultimately Nazi Germany published and distributed more than twenty editions, and the book was even used to teach children in some German schools.
By legitimating the myth of a Jewish conspiracy aimed at world domination, the “Protocols” contributed to the Nazi genocide of six million Jewish men, women and children. Yet it was after Hitler’s defeat that the “Protocols” reached their widest audience, gaining a global footprint in the second half of the 20th century.
Controversies over the “Protocols” were reported in 1968 not just in Poland but also Lebanon, where 200,000 copies were reportedly set to be published for distribution to Francophone Africa. And in 1972, they were the subject of stories not just involving the education minister in Greece, but also Libya’s former leader Muammar Qaddafi, who kept a stack on his desk and told visitors “you must read it.”
The ADL noted that by the 1970s the “Protocols” were documented in Latin American countries such as Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Panama, and also published by then in both India and Pakistan. Other editions emerged in Japan in 1987, in Mexico in 1992, and in Indonesia in 2003.
The ‘Protocols’ in the Middle East
No one region has a monopoly on the “Protocols” today. For example, a June 28 opinion poll of US adults found that, out of those respondents who believe in the far-right conspiracy theory QAnon, 49 percent of that subgroup believe the “Protocols,” too. Yet because of the Arab-Israeli conflict, the “Protocols” have also been particularly appealing to some audiences in the Middle East.
Scholars documented 102 different instances of the “Protocols” published as a book or newspaper series in Turkey between 1946 and 2008, versus only three times before that.
The ADL documented in a pamphlet called “The Protocols: Myth and History” that from 1965 to 1967 “about 50 books on political subjects published in Arabic were either based on the ‘Protocols’ or quoted from them.”
Extremists have had the greatest interest in the “Protocols” because it validates their position. Hamas’s 1988 charter declared: “Today it is Palestine, tomorrow it will be one country or another. The Zionist plan is limitless … when they have digested the region they overtook, they will aspire to further expansion, and so on. Their plan is embodied in the ‘Protocols of the Elders of Zion’.”
Likewise, Iran’s fundamentalist regime has been propagating the “Protocols” since its earliest years. The Iranian leader’s Islamic Propaganda Organization has been publishing and distributing the “Protocols” since the 1980s.
The foundation that President-Elect Raisi ran until several years ago, and that produced its 50-episode film series on the “Protocols” under his tenure has also been publishing its own hardcopy editions since the 1990s.
And in 2003, Hezbollah’s Al-Manar broadcast a 29-part series based on the “Protocols” called “Al-Shatat.” The film’s production was facilitated by the Assad regime, but diplomatic pressure led Syrian state TV to drop it, and French officials forced Al-Manar off Eutelsat over the film.
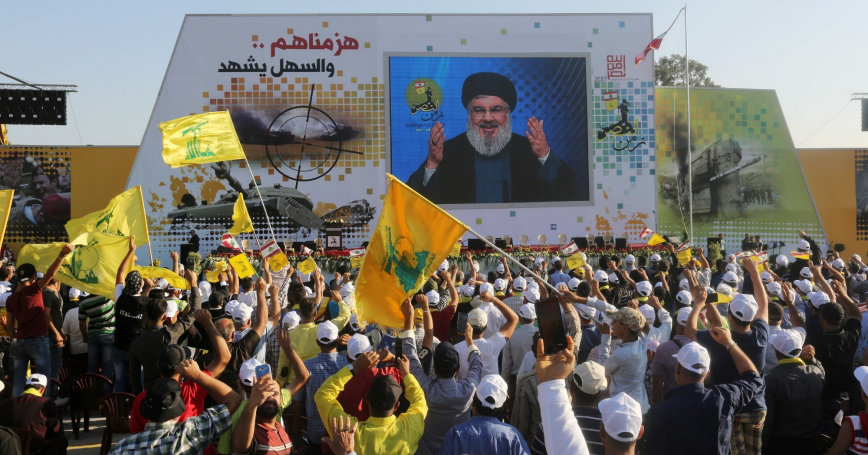

Supporters of Lebanon's Hezbollah leader Sayyed Hassan Nasrallah listen to him via a screen during a rally in Khiam, Lebanon, on August 13, 2017. (Reuters file photo)
Yet moderate forces have sometimes raised up the “Protocols” in regrettable ways as well, such as in 2002 when Egyptian state TV and a private station broadcast “Horseman Without a Horse,” another multi-episode documentary based partly on the “Protocols.”
In response to complaints, state TV cut parts of the film and added a disclaimer, but it was rebroadcast both in Egypt and abroad. The film’s star brags it inspired the sale of two million copies of the “Protocols.”
Arab News published an op-ed noting that the “Protocols” were “long since shown to be a fake” and that even if only one percent of “Horseman Without a Horse” is based on the book, “that’s 1 percent too many.”
Asharq Al-Awsat published an interview with a Palestinian academic criticizing the film and calling the text “a fictitious book” that harms Palestinian advocacy. In 2008, Egypt’s Grand Mufti called the “Protocols” a “fictitious book which has no basis in fact.”
Both in the Middle East and in other regions too, the myth of a Jewish cabal controlling the world is still quite common in some circles today, even if the “Protocols” are not explicitly mentioned.
And in my own work, I do encounter copies of the “Protocols” sold by private exhibitors at state-run book fairs in parts of the region, including one taking place in Egypt this past month. I have also found them in some state textbooks, yet thanks to education reformers this has become far less common today.
Defending against disinformation today
On June 22, the US Department of Justice seized 36 websites linked to Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) and its proxies, many of which had a record of spewing blatantly hateful and untrue propaganda targeting Saudi Arabia, America, Israel, and the Jewish people. And some of them have routinely invoked the “Protocols” for propaganda purposes.

Iranian Revolutionary Guard celebrate after launching a missile in an undisclosed location in Iran on July 3, 2012. (AP file/IRNA, Mostafa Qotbi)
Such disinformation can be dangerous. Another IRGC-run site disrupted by the Justice Department in 2020 was AWD News, once the number one web domain promoted by Iranian trolls on Twitter.
In 2016, AWD News baselessly reported Israel had threatened Pakistan with nuclear weapons if it entered Syria, and in reaction an account for Pakistan’s defense minister actually tweeted, and then deleted, a warning that “Israel forgets Pakistan is a Nuclear state too.”
Thankfully, the internet and social media also offer new tools for countering disinformation. There are good primers on how to identify fake news, for example. Social media platforms and governments are being encouraged to take an array of actions to help push hate and extremism back to the Internet’s fringes.
Where defamation is legally actionable, brave litigants may also be able to ask courts to stop the publication of treatises like the “Protocols.”
But most of all, the digital world provides vast new spaces for all people of good conscience to speak out. To debate such controversial ideas, and to spread accurately grounded messages of intercommunal and interfaith tolerance, countering hateful myths such as the “Protocols” and explaining how we have known for a full century that they are simply without basis.
_______________________
• David Andrew Weinberg is the Anti-Defamation League’s Washington Director for International Affairs.






























