DUBAI: The news that the Biden administration is restarting US funding to aid programs in Afghanistan will be greeted with relief by international groups that have been warning of an economic collapse and a humanitarian catastrophe in the wake of the Taliban’s takeover of the country.
The Wall Street Journal reported on Saturday that the US decision will benefit organizations such as the UN’s World Food Program (WFP), World Health Organization (WHO) and International Organization for Migration (IOM) among other independent groups that work through representatives and local staff based in the war-torn country.
According to an IOM estimate, up to 1.5 million could flee Afghanistan westward in search of safety and jobs in 2021. It is not just the fear of the cruelty and anachronistic morality of the Taliban that is causing Afghans to flee their homes; they are struggling with the economic fallout of the militants’ rapid capture of the country, including the capital Kabul on Aug. 15.
“We must not turn away. A far greater humanitarian crisis is just beginning,” Filippo Grandi, the UN’s High Commissioner for Refugees, said in a statement last week as the combined impact of runaway inflation, a plummeting currency, rising food prices and cash shortages forced hundreds of Afghans in Kabul to try to sell their meager possessions.
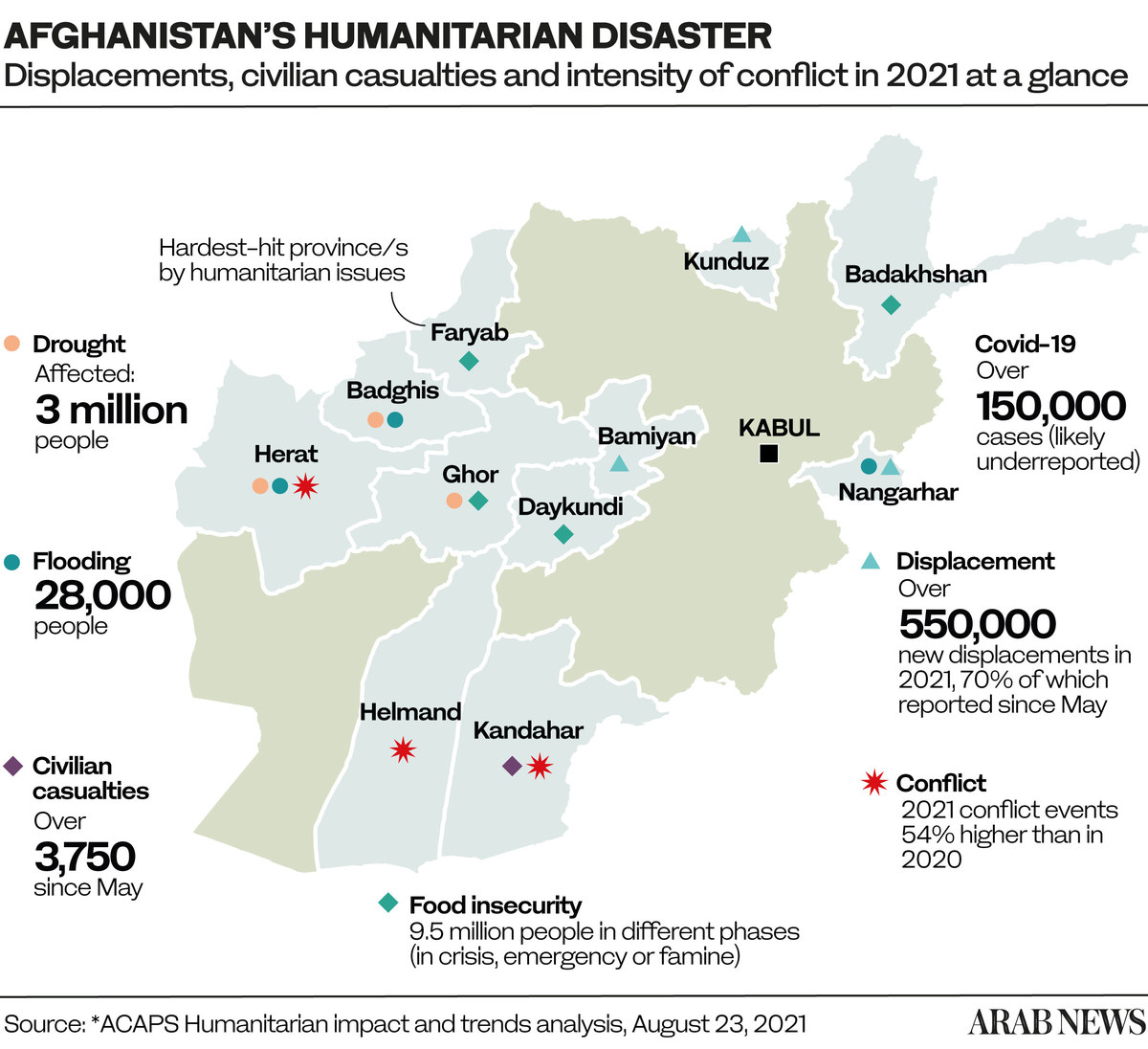
At the beginning of 2021, the UN said that a third of Afghanistan’s population was already facing food insecurity due to a second drought in three years. With very little functioning irrigation, Afghanistan relies on snow melting in its mountains to keep its rivers flowing and fields watered during the summer months. However, snowfall last winter was extremely low.
Climate scientists believe that a La Nina phenomenon and a weakening jet stream moving weather systems more slowly across the planet could be factors behind Afghanistan’s dry weather.
“It is hard to talk of a single crisis in Afghanistan at the moment,” Richard Trenchard, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) representative in Afghanistan, told Arab News. “Multiple crises are affecting the people of Afghanistan. Separate, distinct ones that often intersect and reinforce one another.
“Nowhere is this more evident than in Afghanistan’s rural areas. Millions of rural men, women and children are seeing their livelihoods collapse, and if the situation cannot be turned around in the near future, it could get so much worse, triggering spikes in hunger, economic collapse and large-scale displacement.”

A child stands at a camp for internally displaced people (IDP) where new apartment buildings are located in Kabul on June 21, 2021. (AFP/File Photo)
Food security in Afghanistan has been seriously compromised by an increase in prices over the past five years — by 10-20 percent according to some estimates — primarily because of drought, COVID-19’s impacts, steadily accelerating year-on-year inflation and seasonal changes.
To compound the situation, average incomes have fallen for 75 percent of people while personal debt has increased. According to assessments for the UN’s OCHA, about 73 percent of households reported having debt and 74 percent cited food as the main reason for borrowing.
In February, the now-deposed Afghan government predicted the country’s wheat crop would drop by nearly two million tons in 2021 and that more than three million livestock were in danger of dying due to a lack of fodder and water.
Added to this are “the continuing effects of COVID-19, in particular in terms of reduced remittances from abroad, growing market constraints, reduced purchasing power, and displacement and access issues resulting from recent conflicts, and now, we are seeing a growing cash crisis across the country,” Trenchard said.
“All of these are putting enormous pressures on millions of rural livelihoods. If these livelihoods cannot be protected and strengthened, then I fear further disaster looms in the coming months.
“We all know this, and we need to act soon. Now. The winter wheat planting season begins very soon, at the end of September. Seeds cannot wait. Farmers cannot wait. FAO aims to assist 250 000 vulnerable farming families — some 1.5 million people — for the upcoming winter wheat season.”
INNUMBERS
* 500,000 - Afghans expected to flee to neighboring countries.
* 7m - Afghans whose livelihoods are threatened by drought.
* 12m - Afghans facing food insecurity before Taliban takeover.
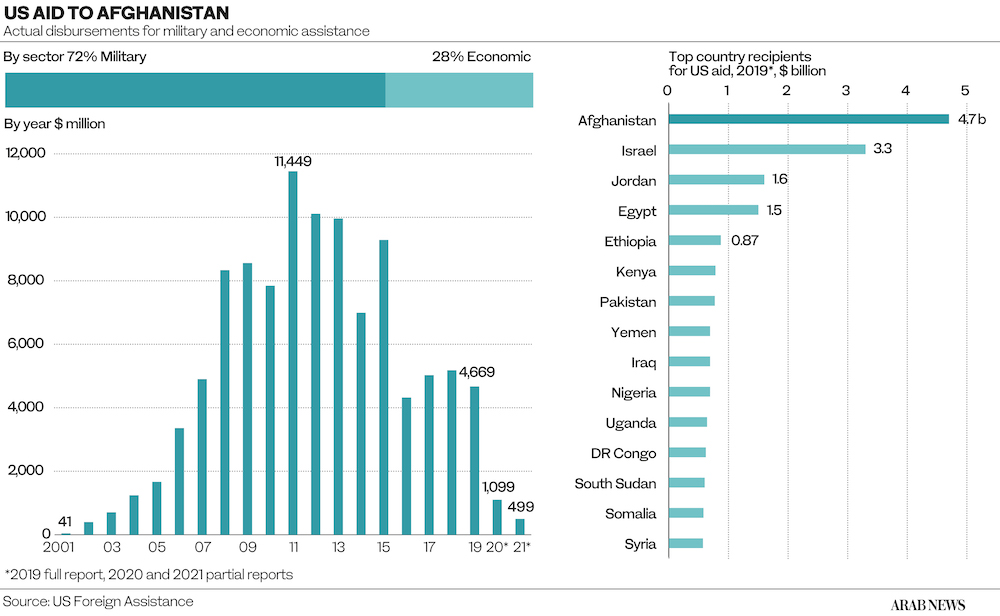
* $500m+ - US State Department annual spending until recently.
* $260m USAID money to be redirected to humanitarian programs.
Trenchard said that the FAO would continue to implement its Drought Response Plan, but funding was a major constraint.
“Planting begins in late September and runs into October in many areas. However, current funding will only enable FAO to support 110,000 families. That is almost 800,000 rural people. We are trying to urgently mobilize further resources, as this next winter wheat season is a tipping point. If we miss it, disaster looms.

Taliban fighters atop vehicles with Taliban flags parade along a road to celebrate after the US pulled all its troops out of Afghanistan, in Kandahar on September 1, 2021. (AFP)
“Needs are far greater than funding available,” he said, especially while the nation’s banks remain closed, making it extremely difficult to get money into Afghanistan. The FAO response is short by $18 million.
Part of the problem is the continuing lack of certainty in Afghanistan as the Taliban, a UN-designated terror group, struggles to form a government and $10 billion of the country’s central bank assets remains frozen in overseas accounts.
“There are no banking and money transfers,” Shakib Noori, the US-based director of sustainable solutions at AMS, told Arab News. “That’s the biggest challenge now.”
Another major challenge is the closure of Kabul airport, which has prevented aid flights from arriving in the country.
On Aug. 30, the WHO said that it had established an air bridge allowing it to bring essential medical supplies into Afghanistan for the first time since the Taliban took power.
However, Ahmed Al-Mandhari, WHO regional director for the eastern Mediterranean, said in a statement that these supplies could only “partially replenish stocks of health facilities in Afghanistan and ensure that — for now — WHO-supported health services can continue.”
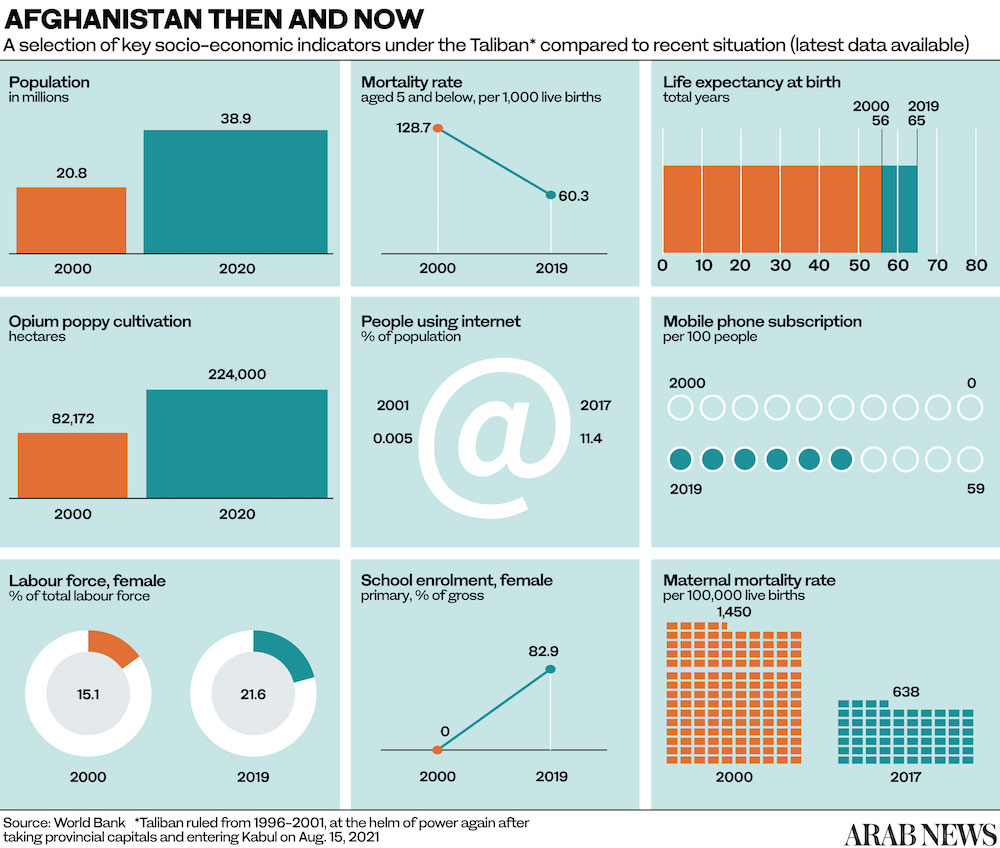
Afghanistan had enjoyed a period of rapid economic growth in the years after the arrival of Western forces in 2001 thanks to an influx of foreign aid money.
According to the World Bank, Afghanistan’s “annual growth averaged 9.4 percent between 2003 and 2012, driven by a booming aid-driven services sector, and strong agricultural growth.”

Defiant Afghan women held a rare protest on September 2 saying they were willing to accept the all-encompassing burqa if their daughters could still go to school under Taliban rule. (AFP)
However, a number of factors, including a resumption of the Taliban insurgency, reduced development aid, drought, and endemic corruption at every level of government, soon caused economic growth to slow by 2.5 percent per year.
Having failed to develop its potentially lucrative mining and mineral extraction sectors, the country has few sources of revenue to make up for the loss of international assistance.
As part of the Biden administration’s latest plan to restart humanitarian aid flows, the US Treasury Department has issued a special waiver for government aid programs, enabling USAID to redirect funding to UN food, health and migration programs.
However, Afghanistan still faces the possibility of additional international sanctions if the Taliban rulers fail to provide tolerant, inclusive governance or honor their counterterrorism and human-rights promises. The World Bank halted financial aid to the country amid concerns about “the country’s development prospects, especially for women,” a spokesperson said on Aug. 25.

A man paints over murals on a concrete wall along a street in Kabul on September 4, 2021. (AFP)
The International Monetary Fund (IMF), for its part, has said that Afghanistan will no longer be able to access lenders’ resources due to “a lack of clarity within the international community” over the new government in Kabul.
Afghans and the international community can do little but wait and see what kind of Taliban regime emerges in Kabul — one that is moderate in its treatment of women and minorities, or one that repeats the brutality and repression of its 1996-2001 predecessor.
“If, or when, sanctions are put in place, Afghanistan’s developing economy simply can’t sustain a nation where more than 50 percent of the population faces poverty before the recent turn of events. And it is likely that this number will increase significantly,” said Noori of AMS.
“The COVID-19 crisis, political crisis, economic crisis — all of this put together, Afghanistan is being cursed.”
---------------
Twitter: @rebeccaaproctor



























