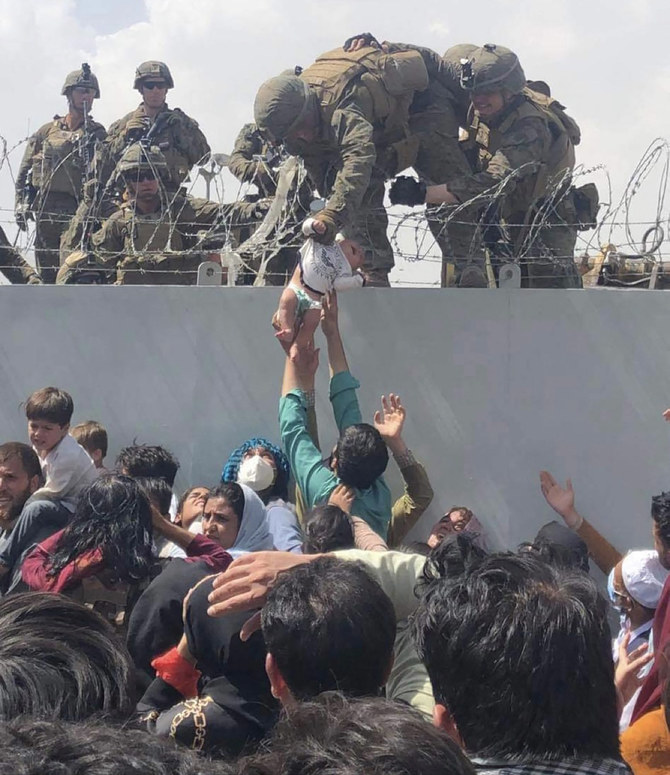
WASHINGTON D.C.: Images of the chaotic last days of the US mission in Afghanistan have been compared widely to the scenes of the final evacuation from Saigon in 1975 as the victorious North Vietnamese Army rolled into the capital of South Vietnam.
Iconic photos of desperate Vietnamese trying to scale the walls of the US embassy bear a striking resemblance to those of civilians clambering up the gates of Kabul airport last month in hopes of catching one of the last flights out of the country.
In hindsight, the parallels between the American experience in Vietnam and Afghanistan are too many to ignore. Just like the US began a rapid military drawdown in Vietnam after signing the Paris Peace Accords with North Vietnam in 1973, the February 2020 Doha deal between the US and the Taliban set the scene for America’s rush for the exits in Afghanistan.
By 1975, the only US soldiers remaining in South Vietnam were the Marines who guarded the embassy in Saigon and a small contingent at a nearby air base. By the end of April that year, the city, later renamed Ho Chi Minh City, had fallen to the North VIetnamese Army (NVA).
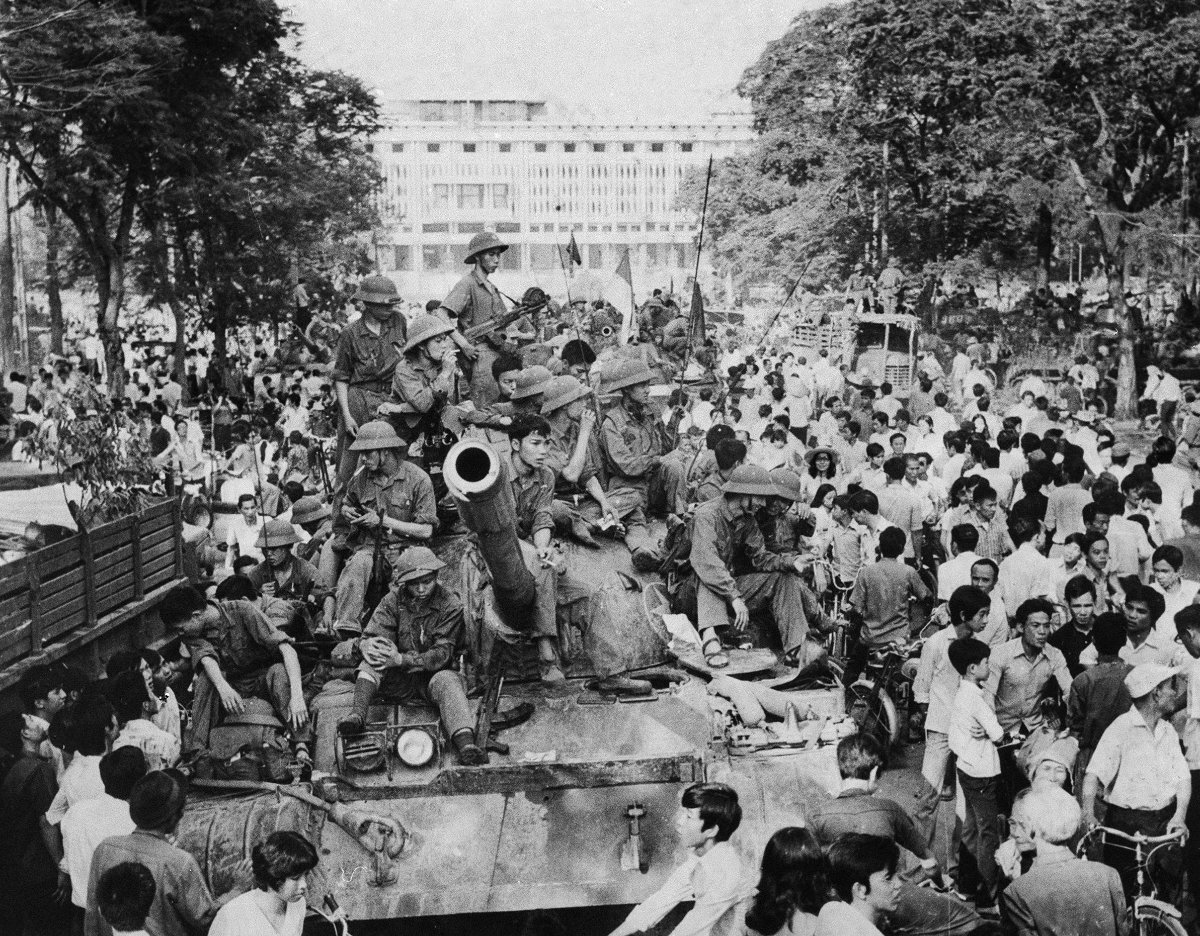

Jubilant communist troops atop tanks make their way to the center of Saigon as the city fell under their control on April 30, 1975. (Vietnam News Agency photo via AFP)
The US had hoped that the peace accords would allow for the “Vietnamization” of the conflict, transferring combat operations and security away from the US military to the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN).
But just like the Afghan National Army — in which Washington had invested billions in training and equipment — proved incapable of securing the country on their own, the ARVN crumbled in the absence of the full complement of US ground combat units and field advisers.
For a long time after the humiliating end to the Vietnam War, the US seemed to suffer from a crisis of confidence, questioning its strength, the appeal of its values and its role in the world.
“This will be the final message from Saigon station,” wrote Thomas Polgar, the last serving CIA station chief in Saigon, before his evacuation. “It has been a long and hard fight and we have lost. This experience, unique in the history of the US, does not signal, necessarily, the demise of the US as a world power.”
He added: “Those who fail to learn from history are forced to repeat it. Let us hope that we will not have another Vietnam experience and that we have learned our lesson. Saigon signing off.”
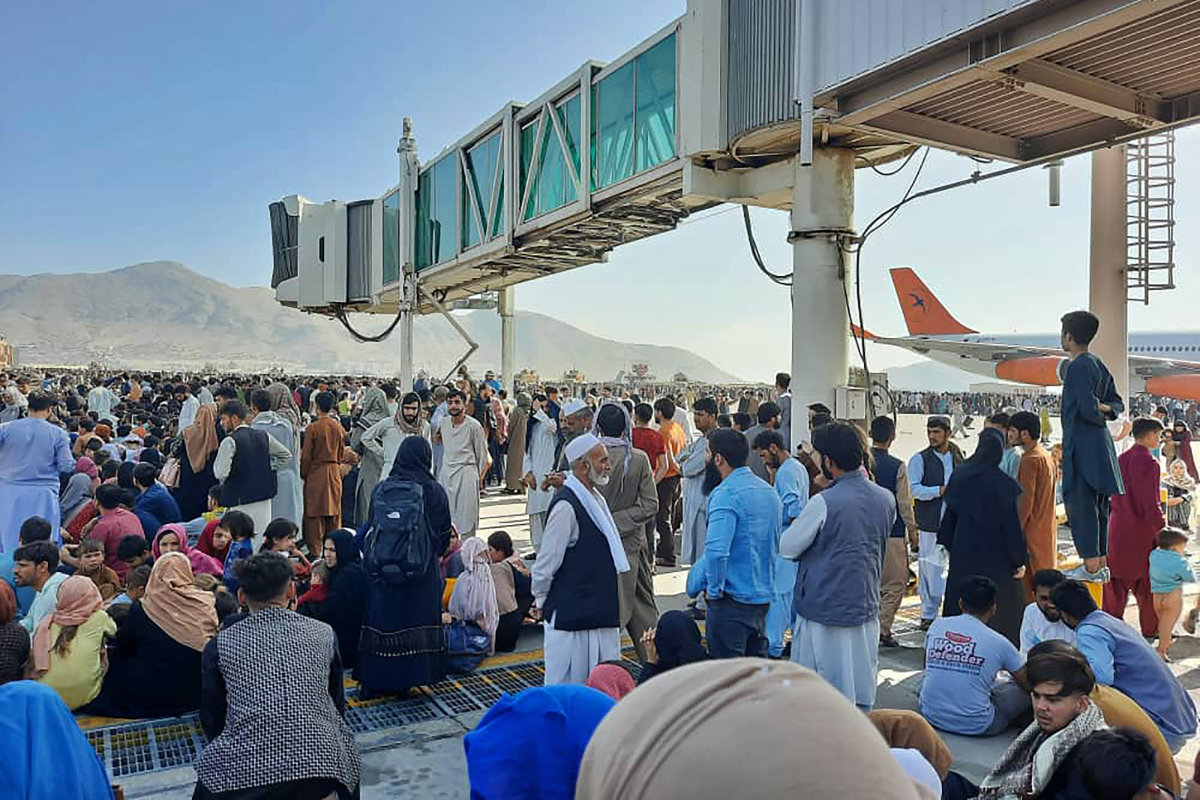

Afghans crowd at the tarmac of the Kabul airport on August 16, 2021, to flee the country as the Taliban took control of Afghanistan. (AFP file)
American military historians would be right to assess that the lessons of Vietnam were lost when the US pursued another open-ended war whose initial limited objectives were overtaken by a zeal for nation-building.
As with Saigon in the late 1960s and early 1970s, the government in Kabul supported by the US military lacked the competence and broad legitimacy to combat an insurgency on its own.
In a now declassified 1969 memo to former president Richard Nixon, his national security adviser, Henry Kissinger, expressed deep concern that the war was unlikely to be won militarily.
“I am not optimistic about the ability of the South Vietnamese armed forces to assume a larger part of the burden than current plans allow,” he wrote, adding: “Hanoi’s adoption of a strategy designed to wait us out fits both with its doctrine of how to fight a revolutionary war and with its expectations about increasingly significant problems for the US.”
In both the Vietnam and Afghanistan missions, time and lack of strategic patience were America’s main weaknesses in the face of a stubborn insurgency. Of the four different administrations that have guided US foreign policy since the Afghan war began, none took a step back to assess the likelihood of success as rationally and impartially as Kissinger did in the 1969 memo.
Although the Afghanistan mission did not produce the kind of civil disturbance and political turmoil synonymous with the Vietnam War, there was a broad consensus among US politicians for some time now that an indefinite military involvement in the culturally distant Central Asian country was not desirable.
Now that the Afghanistan chapter is closed, some point to the fact that the post-1975 period has seen a slow but remarkable rapprochement between the US and Vietnam.
Within the space of 20 years, the former belligerent nations were able to forge a relationship that today has evolved into a veritable strategic partnership, symbolized by the US-Vietnam Comprehensive Partnership of 2013.
A quarter of a century after the establishment of bilateral relations in 1995, the US and Vietnam are thus partners with a friendship grounded in mutual respect and suspicion of China’s geopolitical motives.
The partnership now spans political, economic, security and people-to-people ties. Tens of thousands of Vietnamese citizens study in the US and contribute almost $1 billion to the US economy.
“We must remember that the immediate consequences of the Vietnam War were horrible. Many in South Vietnam were sent to camps and murdered, resulting in a huge human-rights tragedy,” James Carafano, a fellow at the Heritage Foundation, told Arab News. “Today, Vietnam is a different place. Vietnamese are terrified of China and they need the US to defend them.”
A strong, prosperous and independent Vietnam is very much in Washington’s interest as Hanoi and Beijing remain locked in a standoff over competing territorial claims in the South China Sea.
Bilateral trade between the two nations has grown from $451 million in 1995 to more than $90 billion in 2020. US goods exports to Vietnam were worth more than $10 billion in 2020, while imports were worth a whopping $79.6 billion. US investment in Vietnam touched $2.6 billion in 2019.
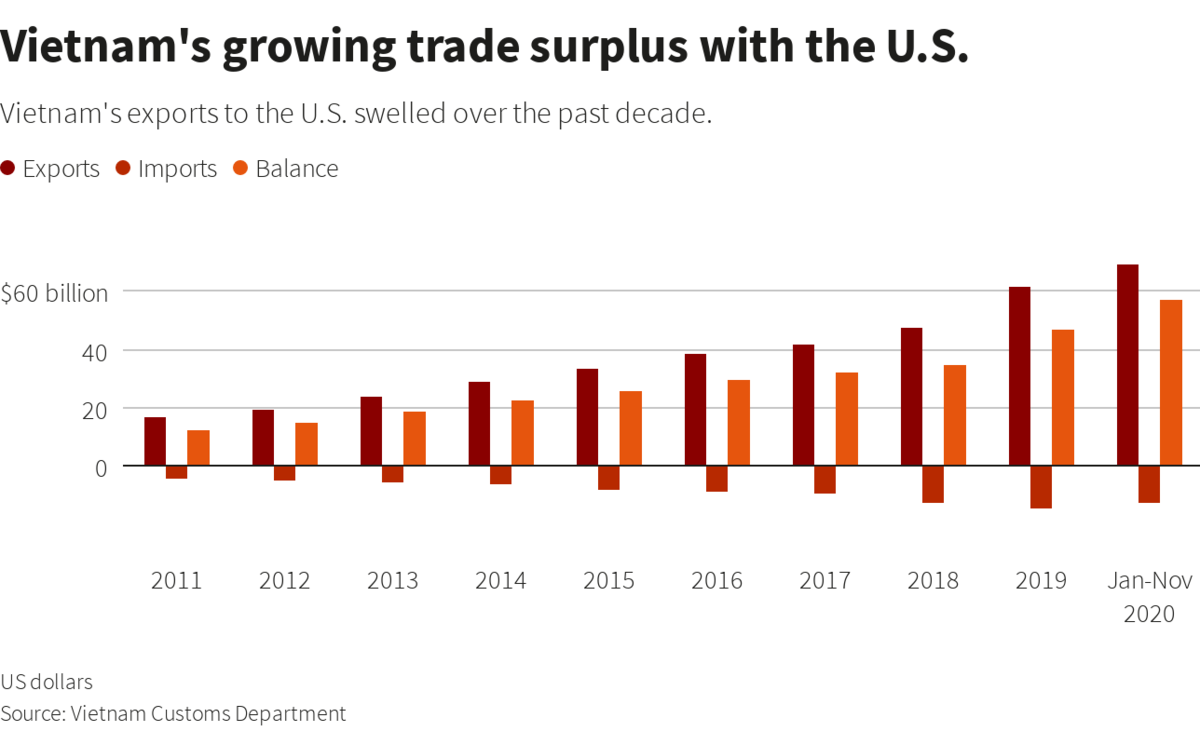
Vietnam's exports to the US swelled over the past decade. (Reuters file photo)
Now that the war in Afghanistan is over and discussions between the Taliban and regional countries toward diplomatic normalization are ongoing, the evolution of US-Vietnamese relations from enmity to a flourishing partnership can prove instructive.
Could economic leverage, common security interests and deft diplomacy achieve in Afghanistan what the expenditure of billions of dollars in building a defense force in the mold of Western militaries failed to do?
The Taliban have been keen to signal that they are ready to engage diplomatically with regional powers, including China, the Arab Gulf states, Turkey and even India.
For the US, the immediate security objective is to make sure that neither Al-Qaeda nor Daesh establishes a base of operations to plot transnational terror attacks from. To this end, the US will have to make use of all the tools at its disposal: Soft power, diplomacy and economic incentives.
The worst-case scenario at the time of the 1975 US defeat was a communist victory in South Vietnam having a “domino effect,” leading to the collapse of Southeast Asian governments allied with the US. But such an eventuality did not come to fruition.
The dramatic turnaround in US-Vietnam relations means there is room for hope in the case of Afghanistan, too, but with a number of caveats.
“There were two reasons why the US remained in Afghanistan: One, to prevent another space for transnational terror again, and two, to prevent the destabilization of South Asia. Both were legitimate US interests,” said Carafano.
“Now we have no presence, no visibility on the terrorist situation and no deterrent against actors in the region. We have lost the trust of allies.”
As for the future, Carafano said: “The Taliban are not going through an evolution like Germany post-Second World War. It’s a ridiculous notion that the Taliban will normalize as a government. Daesh are useful idiots who do not have the capacity to threaten anybody. They are a bigger threat to the Taliban than to us.
“Will the Taliban break with the Haqqani network and Al-Qaeda? They won’t. The Taliban may not plan the next 9/11, but Al-Qaeda and Haqqani will.”
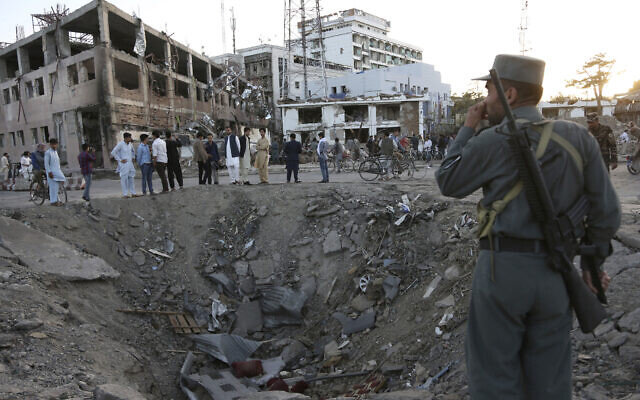

In this photo taken on May 31, 2017, Afghan security forces stand at the site of a deadly explosion blamed on the Haqqani network. (AP file)
Clearly, the time-worn tribal partnership between the Haqqani network, which is an integral part of the Taliban, and Al-Qaeda, will be a major complicating factor in the Taliban’s ability or willingness to prevent the international terror group from rebounding.
For the moment, the Taliban seem to be making all the right noises. The political leadership has emphasized that they are pursuing a nationalist vision, not a transnational one.
What remains to be seen is whether the group can prioritize the needs of running the affairs of state, which will require significant outside financial support and technical expertise, over a wild-eyed “revolutionary” vision that includes terror sanctuaries.
“In Vietnam, military victory over the US did not translate to a strategic defeat of the US and the anti-communist bloc globally,” Carafano told Arab News.
“Both Republican and Democratic administrations have taken successive steps toward strengthening Washington’s commitment to a security partnership with Vietnam. Previously unthinkable, US Navy aircraft carriers are now allowed to dock in Vietnamese ports.

US Vice President Kamala Harris meets with Vietnam's Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh din Hanoi on August 25, 2021. (REUTERS/Evelyn Hockstein/Pool)
“Whether the US and Taliban-controlled Afghanistan can develop some level of security arrangement based on a common threat perception is an open-ended question.
“But already, China and Russia have signaled that they are ready for a bigger role in Afghanistan in the wake of the US withdrawal. Though they are likely to engage cautiously. Both powers’ interest in Afghanistan lies in winning without fighting. But they’ll take their time in Afghanistan.”
In the final analysis, time was the overarching factor in America’s military defeat by the insurgency in both Vietnam and Afghanistan. But it also was the passage of time following the Vietnam War that enabled the adversaries to grow into friends based on common interests and threats.
It remains to be seen what American policymakers have learnt from the two humiliating withdrawals in order to avoid a third. With Vietnam, the US was able to salvage a measure of diplomatic victory from its military defeat. In Afghanistan, much will depend on the Taliban leadership’s ability and willingness to make a complete break with the past.
_______________
• Twitter: @OS26





























