DUBAI: Blood-donation awareness has been steadily increasing in Saudi Arabia, thanks in part to an innovative smartphone app called Wateen, which tells people about their nearest blood bank, when they are due to give, and how many times they have donated.
Ahmad Alhesayani, one of Wateen’s young Saudi co-founders, helped launch the service in early 2019. Today it is used by the Kingdom’s Ministry of Health under Sehhaty, the national platform for blood donation.
“Wateen not only makes donating easier, but also automates more than 150 private and public blood-bank systems in the country, making them more productive, helpful and organized,” Alhesayani told Arab News.
“The service encourages and enables voluntary blood donation in Saudi Arabia. It has a humanitarian approach, and what shapes it is the vision of creating a robust health infrastructure around blood, plasma and platelets donation. The concept is both ambitious and feasible, and at the same time imperative.”

Wateen has become a recruitment tool for the ministry to motivate potential donors
Blood and its components are used by hospitals to treat patients with medical conditions such as anemia, cancer and blood disorders, as well as those having surgery. Nations try to maintain a stockpile of blood so that their health systems can provide lifesaving transfusions during mass-casualty events. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has refocused minds on health-system preparedness.
However, blood stocks need to be replenished constantly because blood components have a limited shelf life. Red blood cells can be stored for up to 35 days, platelets for up to seven days, and plasma for up to three years.
Blood banks rely on regular voluntary donations. Despite shifting attitudes in the Kingdom toward blood donation and a growing number of donors, including many women, blood banks occasionally run short, especially when it comes to rarer blood types, which can be a matter of life and death for patients.
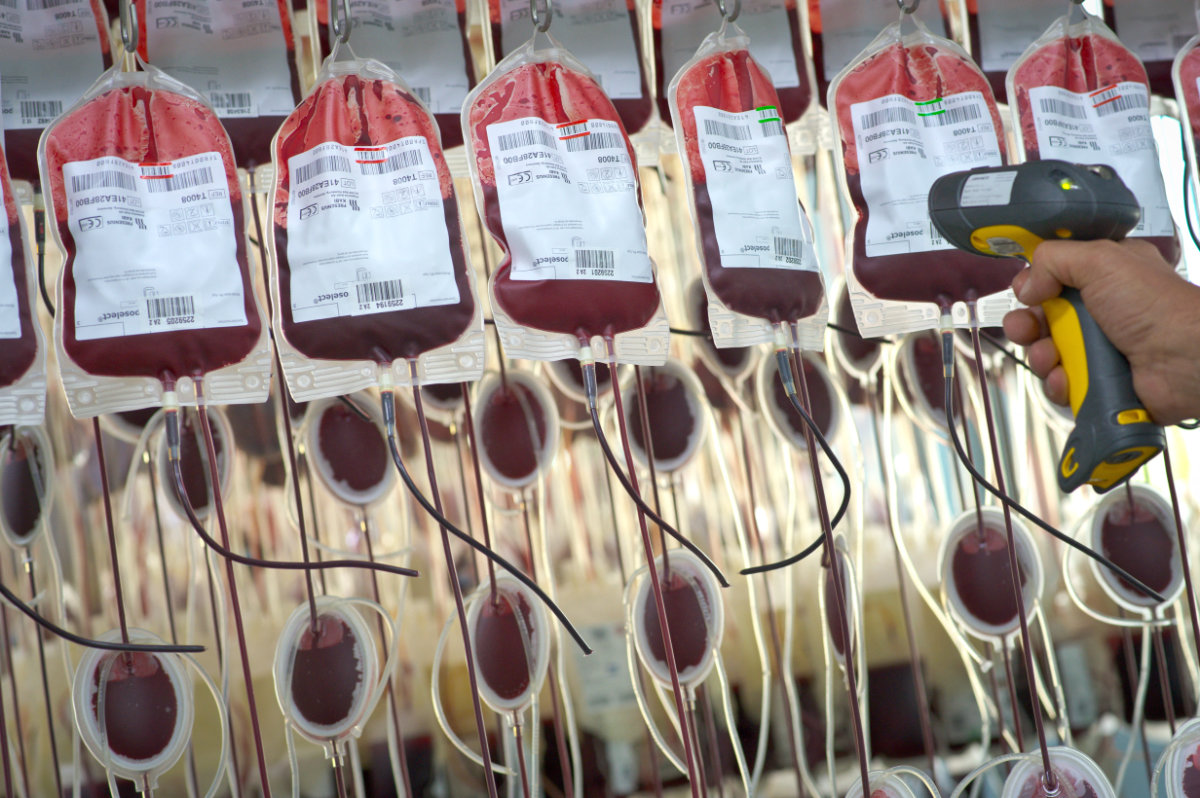
Blood stocks need to be replenished constantly because blood components have a limited shelf life. (AFP file photo)
Saudi health officials have introduced measures to ensure adequate stocks in blood banks, including those run by the health ministry and dedicated centers. These include a large facility at King Fahad Medical City and the country’s Central Blood Bank.
Donors in the Kingdom must be aged over 17, weigh more than 50 kg and have passed a brief medical examination.
Wateen provides a seamless interface where people can locate their nearest blood bank and other facilities without having to trawl the internet, which often provides “useless and superficial” information, according to Alhesayani.
“The approach is to tap Saudis’ inherent compassion and brotherhood, and turn it into a tangible service. Freeing people of their reservations and misunderstandings regarding blood donations, and partnering with like-minded individuals and organizations is at the heart of our business model.”

Ahmed Alhesayani (foreground) was one of the young Saudi co-founders of Wateen and helped to launch the service in early 2019. (Supplied)
Alhesayani belongs to a generation of young Saudis responsible for a wave of innovations in health-tech solutions — a trend that has been nurtured by the Kingdom’s Vision 2030 reform agenda, which seeks to diversify national industries away from oil and build a dynamic, knowledge-based economy.
“I found myself in this project when I finished my first semester in the college of law,” said Alhesayani, a graduate of King Saud University in Riyadh.
“It started after an invitation from a friend to leave my part-time job as a bookseller and join a team driven by the desire to make an impact, with a clear vision to change the blood-bank system and help the community. I was impressed by a short conversation I had with him, so I left my job and joined in the early stages of the project.”
As the startup grew and its destination became clearer, Alhesayani was handed the operational lead in recognition of his energy and passion for the project. “I was a 19-year-old student, but it is possible to handle it if you are hungry to learn and achieve,” he said.
FASTFACTS
56 Ideal gap between whole blood donations in days.
3 Lives that can be saved by a single donation.
10 Average adult’s blood volume in pints.
1 Typical whole-blood donation volume in pints.
(Source: Cedars-Sinai)
Leading operations was one of the most complex parts of the project, with responsibility for more than 150 blood banks in over 20 regions, thousands of users and more than 40 health ministry representatives — all at least 10 years older than Alhesayani.
“I have funny stories about dealing with older people from hugely different backgrounds,” he said. “The operations were not only about that, but the platform would have been useless if it were not integrated with all blood banks.”
Qualified training, including data entry, appointments and donation requests, was needed for nurses, doctors and the staff providing the service for donors. The work meant Alhesayani often had to travel while continuing his university studies.
“At Wateen, we have weekly, monthly and yearly key performance indicators that help us achieve our targets and grow rapidly,” he said. “I was committed to achieving more than what they were looking for, and my team and I completed the annual target after only four months of hard work.”
Wateen acts as a platform with a growing number of features and is integrated under the name of Sehhaty and Blood Bank Management System.
Alhesayani said that the Qimam Fellowship — an intensive 12-day training program launched in 2018 to empower the Kingdom’s high-potential university students through one-to-one mentoring and career guidance — was a vital step in his career development.
One of the student participants, Ahmed Alenzi, joined Wateen’s operations team in early 2019 after being recommended by his mentor.
“I worked with Alenzi for a while, and saw how clever, hard working and smart he was, with a real passion for success,” Alhesayani told Arab News. “Later on, I asked him about Qimam, how to apply and the benefits it offers.”
The young entrepreneur added: “Qimam is not only a period program but also provides friends and colleagues for life — people you will always be proud of, learn from, and potential and promising partners you will love to work with.”
At the end of 2019, as a culmination of his work at Wateen, Alhesayani and his team applied for the King Khalid Award for the nonprofit sector in the GCC, and won, gaining the recognition of King Salman.
Today, Wateen acts as a platform with a growing number of features, including additional information from other health ministry platforms, and is integrated under the name of Sehhaty and Blood Bank Management System.

Wateen has become a recruitment tool for the ministry to motivate potential donors. (AFP file photo)
With 520,000 users, 962,000 donations and 440,000 appointments, Wateen has become a recruitment tool for the ministry to motivate potential donors and meet the needs of blood banks.
“Wateen has come to fruition for the overall advancement of Saudi Arabia’s healthcare infrastructure,” Alhesayani said.
“The country has an advanced infrastructure on many counts, but there is plenty of scope for improvement when it comes to blood donation. Saudi Arabia is growing and progressing rapidly in such areas as artificial intelligence, data and innovation, which will create a seamless customer experience in people’s daily or seasonal needs.
“The healthcare system is one of them. Wateen is just one example of the vast tech transformations occurring in Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Health.”
__________________
• Twitter: @CalineMalek

































