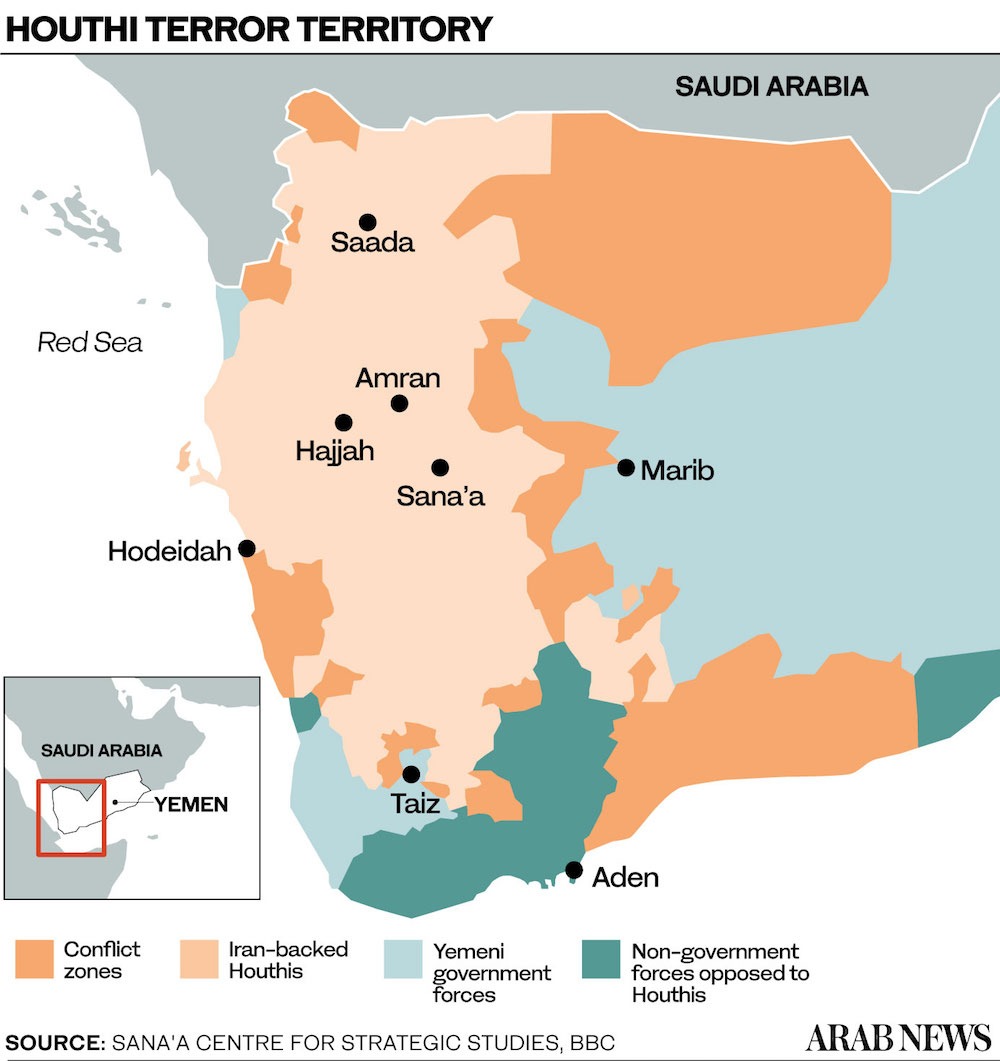
LONDON: Seven months after the US removed the Houthis from its list of designated foreign terrorist organizations, the militia is killing more people than before and intensifying its efforts to bring the entire country of Yemen under its extremist doctrine, according to experts.
Within days of their removal, the Houthis escalated their assault on Yemen’s Marib, a province that provides temporary shelter to thousands of internally displaced people and acts as a bastion of the UN-backed government’s pushback against the Houthis’ religious tyranny.
Six months later, the siege of Marib continues to claim lives daily — on both sides — and perpetuates Yemen’s twin humanitarian and economic crises.
If these developments in Yemen are anything to go by, one of Joe Biden’s first acts as US president has backfired badly.
“I am revoking the designations of Ansar Allah, sometimes referred to as the Houthis, as a Foreign Terrorist Organization,” Biden said on Feb. 12.
Citing the “dire humanitarian situation in Yemen,” he said the group’s inclusion on the list would only obstruct the delivery of aid.
“By focusing on alleviating the humanitarian situation in Yemen, we hope the Yemeni parties can also focus on engaging in dialogue.”
Granted, hindsight is always 20/20 but the Biden team never really tried to defend the rationale behind the move with evidence.
“The delisting gave the Houthis and, more importantly, their Iranian sponsors a sense of impunity,” Michael Rubin, a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, told Arab News. “The delisting also eviscerated international efforts to prevent Houthi supply and finance.”
In fact, Rubin says, the Biden administration’s justification for the delisting of the Houthis — to facilitate the delivery of humanitarian aid — never made sense in the first place.
“There was already an inspection regime” in place, Rubin said. “The UN had repeatedly reported on the delivery of humanitarian goods. Ironically, it was often the Houthis which prevented the delivery of goods to cities like Taiz not under Houthi control.”
In Rubin’s view, Biden’s decision to delist the Houthis may have had more to do with domestic American politics than what was best for the Yemeni people — and it may have emboldened other regional terrorist groups in the process.
“The Biden administration’s delisting had more to do with reversing what (former president Donald) Trump had done than with any consideration of the realities on the ground,” he said.
“As such, Biden’s delisting for purely political reasons undermined the legitimacy of US listings and also encouraged other terrorist groups to demand delisting as a diplomatic concession.”
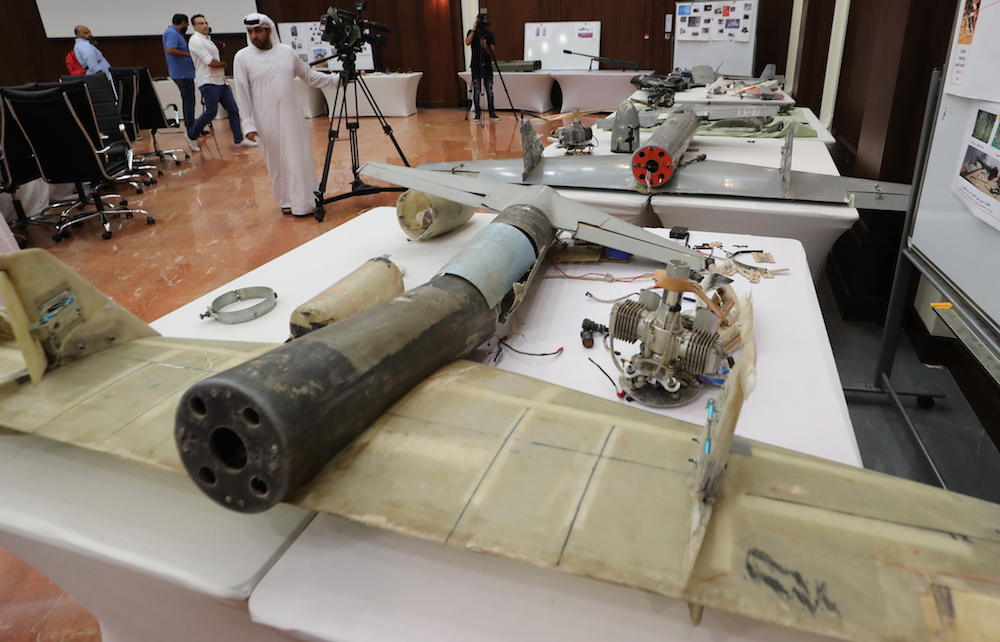

Drone missiles used by Houthis in Yemen in battles against the coalition forces led by Saudi Arabia and UAE. (AFP/File Photo)
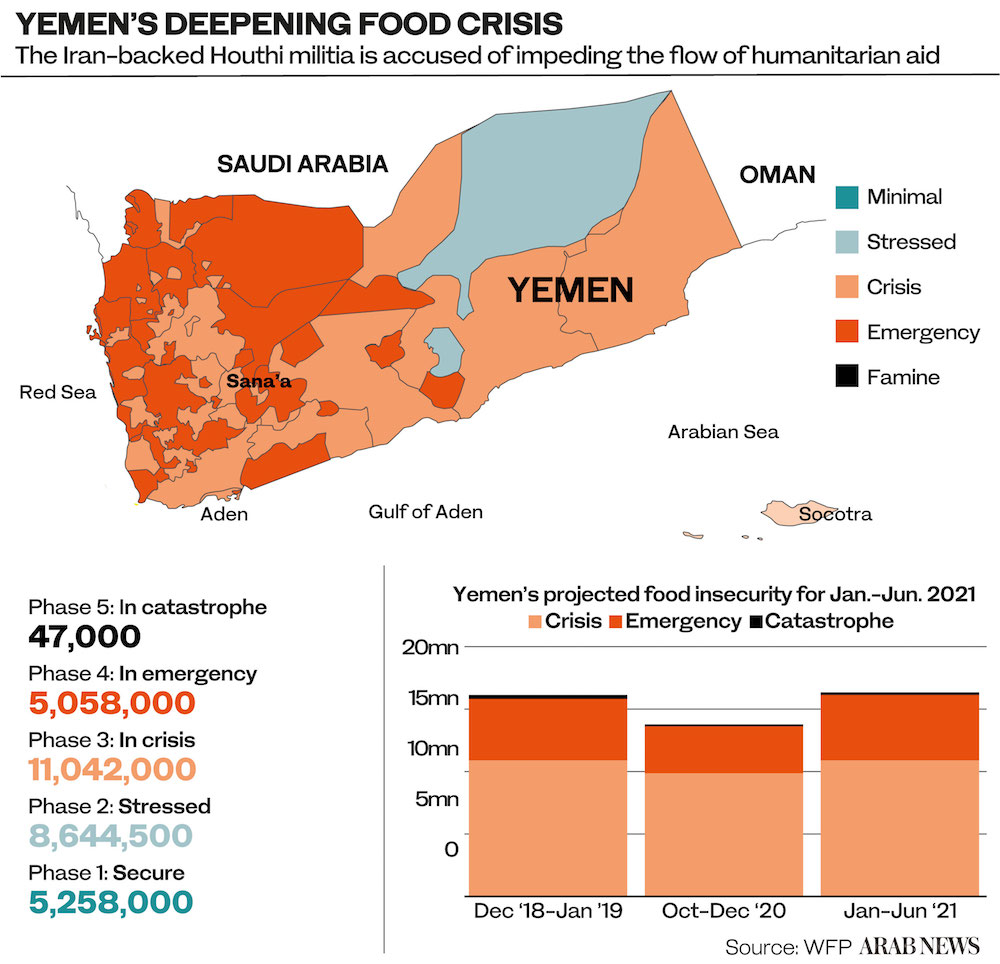
Not only has the delisting failed to concretely resolve the humanitarian situation in Yemen, but it may also have cost more people their lives.
Alexander Jalil is a Middle East and North Africa analyst at the Armed Conflict Location Event Data Project, a highly specialized organization dedicated to recording instances of fatal and non-fatal violence in conflicts or politically unstable locations across the world.
Jalil told Arab News that ACLED’s data, painstakingly collected and verified based on local sources, suggests that not only were the Houthis involved in a higher proportion of the fighting in Yemen after they were removed from the terror list, but they were actually responsible for the deaths of more people.
“The events in the six months after the group was removed from the US terror designation list were also deadlier, as our fatalities count saw an increase between Feb. 12, 2021, and Aug. 12, 2021, compared to Aug. 12, 2020, and Feb. 12, 2021,” Jalil said.
INNUMBERS
* 7,998 - Number of fatalities attributed to Houthi activity in the 6 months prior to delisting.
* 9,312 - Number of fatalities attributed to Houthi activity in the 6 months since delisting.
(Source: ACLED)
ACLED’s data shows that in the six months preceding the Houthis’ removal from the terror blacklist, 7,998 fatalities were attributed to Houthi activity. In the six months after, that number was 9,312 — a rise of more than 1,314.
It is not clear exactly what caused this jump in fatalities, but Asif Shuja, a senior research fellow who specializes in Iran at the National University of Singapore’s Middle East Institute, told Arab News “the delisting of the Houthis by the Biden administration tilted the balance in favor of Iran.”
Iran has long supported the Houthis, who are ideologically aligned with Tehran’s doctrine of velayat-e faqih — or guardianship of the Islamic jurist. This ideology places supreme control of the state in the hands of Ayatollah Ali Khamenei on the basis of a religious worldview prescribed by his revolutionary predecessor Ruhollah Khomeini.
Saudi Arabia’s 2015 intervention in Yemen was launched in order to uphold the legitimate Yemeni government, which was forced from the capital Sanaa by the Houthis earlier that year, and to prevent further attacks on the Kingdom.
Tehran now provides funding, arms, training, and ballistic missiles to the Houthis — many of which have been turned against Saudi Arabia, its citizens, and its allies.
The Houthis unleashed a wave of ballistic missile and drone attacks against the Kingdom on Sept. 4, defying calls by the international community for a return to the negotiating table.
All of the missiles and drones were intercepted and destroyed, but falling debris from a missile shot down over Eastern Province injured a boy and a girl in Dammam city.
Falling debris also caused damage to 14 residential houses, coalition spokesman Brig. Gen. Turki Al-Maliki said in a statement carried by the Saudi Press Agency.
A second missile targeted the southwestern region of Najran followed by a third on the adjacent region of Jazan. Earlier that same day, coalition air defenses intercepted three booby-trapped drones launched by the Houthis.
Houthi attempts to target civilians and civilian objects are not only hostile and barbaric but also “incompatible with heavenly values and humanitarian principles,” Al-Maliki told SPA.
Another attack at the end of August struck an airport in Abha, wounding eight civilians and damaging a commercial airliner.
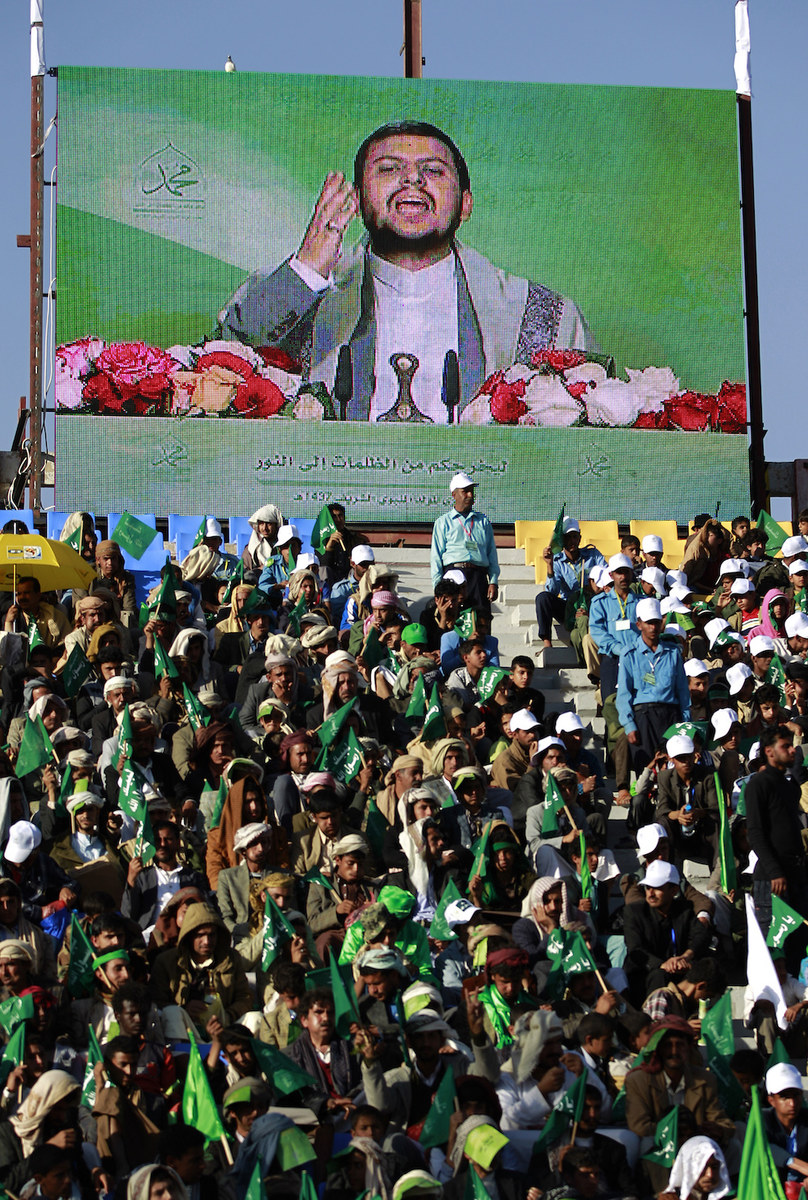

A speech by Shiite Houthi leader Abdul-Malik Al-Houthi is screened as supporters take part in a rally. (AFP/File Photo)
“Houthi attacks are perpetuating the conflict, prolonging the suffering of the Yemeni people, and jeopardizing peace efforts at a critical moment,” US Secretary of State Antony Blinken said in a statement at the time.
Abdullah Al-Mouallimi, Saudi Arabia’s Ambassador to the UN, told Arab News the Kingdom is actively working to expose the Houthi militia’s true nature as a terrorist organization through the UN Security Council.
“When we send letters to the UNSC or to the secretary-general regarding the various attacks that the Houthis try to launch against Saudi Arabia, our main objective is simply to record the fact,” he said.
Al-Mouallimi added: “We are repulsing these attacks, foiling them well before they hit targets in most cases, and we are exposing them to the international community. We are making them well known to the international community and the world at large.”
Saudi Arabia has confronted the Houthis with force but has also consistently pushed for a peaceful resolution to the war in Yemen that places the people at the heart of any political settlement. But a peaceful end to the conflict is not a goal shared by the Houthi militia.
In his speech to the UN General Assembly on Wednesday, King Salman of Saudi Arabia said: “The peace initiative in Yemen tabled by the Kingdom last March ought to end the bloodshed and conflict. It ought to put an end to the suffering of the Yemeni people. Unfortunately, the terrorist Houthi militia rejects peaceful solutions.”
------------------
Twitter: @CHamillStewart























