JERUSALEM: Israeli troops conducted a series of arrest raids against suspected Hamas militants across the occupied West Bank early Sunday, sparking a pair of gunbattles in which five Palestinians were killed and two Israeli soldiers were seriously wounded.
It was the deadliest violence between Israeli forces and Palestinian militants in the West Bank in several weeks. The region has seen an increase in fighting in recent months, with tensions fueled by Israeli settlement construction, heightened militant activity in the northern West Bank and the aftermath of a bloody war between Israel and Hamas militants in the Gaza Strip last May.
Israeli officials said they had been tracking the Hamas militants for several weeks and that the raids were launched in response to immediate threats.
Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett said the militants were about to carry out attacks “in real time.” He praised the Israeli forces, saying they acted “as expected. They engaged the enemy and we back them completely.”
Lt. Col. Amnon Shefler, an Israeli army spokesperson, said Israeli forces came under fire while carrying out the arrest raids. He said at least four Hamas operatives were killed and several others were arrested in the overnight operation.
The Palestinian Health Ministry said two Palestinians were shot dead near the northern West Bank city of Jenin and three others were killed in Biddu, north of Jerusalem. The Israeli military said an officer and soldier suffered serious injuries during the arrest in Burqin, near Jenin, and were airlifted to a hospital for medical treatment.
Hamas confirmed that four of the dead, including all three killed in Biddu, were members of the Islamic militant group. Palestinian officials said a 16-year-old boy was also among the dead, though it was not immediately known if he was a militant.
The Palestinian Authority, which administers semi-autonomous areas in the West Bank, condemned the killings and said the Israeli government was “fully and directly responsible for this bloody morning and the crimes committed by the occupation forces.”
But Hamas also criticized the Palestinian Authority, which maintains security coordination with Israel in a shared struggle against the Islamic group.
Hamas spokesman Abdulatif Al-Qanou said that recent meetings between Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas and Israeli officials “encouraged the occupation again to pursue the resistance.”
Hamas, which rules the Gaza Strip after seizing it from the Palestinian Authority in 2007, praised those killed as “heroic martyrs.” It called on its supporters to “devise tactics and means that harm the enemy and drain it with all possible forms of resistance.”
Also Sunday, Israel released Khalida Jarrar, a prominent Palestinian lawmaker, after nearly two years in prison. Jarrar, a senior figure in the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine, has been in and out of Israeli prisons for years — often without being charged.
The PFLP has an armed wing and is considered a terrorist group by Israel and Western countries, but Jarrar has not been implicated in attacks. She was sentenced to two years in prison in March for membership in a banned group but given credit for time already served. She was freed several weeks before her sentence was to end.
Recent months have seen a rise in violence in the West Bank, with more than two dozen Palestinians killed in sporadic clashes with Israeli troops and during protests.
Many of the clashes have occurred near Beita, a Palestinian village where residents regularly demonstrate against an unauthorized settlement outpost, and near Jenin, which is known as a militant stronghold.
Last month, Israeli troops clashed with Palestinian gunmen during a late night raid in Jenin, killing four Palestinians. Sunday’s clashes came a week after Israel recaptured the last of six Palestinian fugitives who tunneled out of a maximum-security Israeli prison earlier this month. The escapees were from Jenin, and two were caught there after an extensive search.
Israel captured the West Bank in the 1967 Mideast war and has established dozens of settlements where nearly 500,000 settlers reside. The Palestinians seek the West Bank as part of their future state and view the settlements as a major obstacle to resolving the conflict.
Israeli troops kill 5 Palestinians in West Bank gun battles
https://arab.news/vnr2a
Israeli troops kill 5 Palestinians in West Bank gun battles

- Deadliest violence between Israeli forces and Palestinian militants in the West Bank in several weeks
- Hamas confirmed that four of the dead were members of the militant group
White House says ceasefire agreement between Lebanon, Israel to continue until Feb 18

WASHINGTON: The White House said in a statement on Sunday that the arrangement between Lebanon and Israel would continue to be in effect until Feb 18, after Israel said on Friday it would keep troops in the south beyond the Sunday deadline set out in a US-brokered ceasefire that halted last year’s war with Hezbollah.
The White House also said the governments of Lebanon, Israel and the United States would begin negotiations for “the return of Lebanese prisoners captured after October 7, 2023.” (Reporting by Daphne Psaledakis and Humeyra Pamuk; editing by Diane Craft)
Arab League says Palestinian displacement would be ‘ethnic cleansing’

- Egypt earlier expressed objection to Trump's suggestion to “clean out” the Gaza Strip and move its population to Egypt and Jordan
- Egyptian President El-Sisi has repeatedly warned that any planned displacement would threaten Egypt’s national security
CAIRO: The Arab League on Sunday warned against “attempts to uproot the Palestinian people from their land,” after US President Donald Trump suggested a plan to “clean out” the Gaza Strip and move its population to Egypt and Jordan.
“The forced displacement and eviction of people from their land can only be called ethnic cleansing,” the regional bloc’s general secretariat said in a statement.
“Attempts to uproot the Palestinian people from their land, whether by displacement, annexation or settlement expansion, have been proven to fail in the past,” the statement added.
Earlier Sunday, Egypt vehemently expressed its objection to Trump's suggestion.
Cairo’s foreign ministry in a statement expressed Egypt’s “continued support for the steadfastness of the Palestinian people on their land.”
It “rejected any infringement on those inalienable rights, whether by settlement or annexation of land, or by the depopulation of that land of its people through displacement, encouraged transfer or the uprooting of Palestinians from their land, whether temporarily or long-term.”
After 15 months of war, Trump said Gaza had become a “demolition site” and he would “like Egypt to take people, and I’d like Jordan to take people.”
Moving Gaza’s inhabitants could be done “temporarily or could be long term,” he said.
Since the start of the Israel-Hamas war in October 2023 both countries have warned of plans to displace Palestinians from Gaza into neighboring Egypt and from the West Bank into Jordan.
Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi, with whom Trump said he would speak on Sunday, has repeatedly warned that said displacement would aim to “eradicate the cause for Palestinian statehood.”
El-Sisi has described the prospect as a “red line” that would threaten Egypt’s national security.
The Egyptian foreign ministry on Sunday urged the implementation of the “two-state solution,” which Cairo has said would become impossible if Palestinians were removed from their territories.
Canadian veteran released in Afghanistan after Qatari mediation, official says

- David Lavery is now in the Qatari capital, Doha, where he has undergone a medical assessment
DOHA: Canadian veteran David Lavery has been freed following his arrest in Afghanistan’s capital Kabul on Nov. 11 after mediation by Qatar, an official with knowledge of the release said on Sunday.
The circumstances surrounding Lavery’s arrest remain unclear. The Veterans Transition Network, where Lavery worked, said last year that he had frequently traveled to Afghanistan to carry out humanitarian work.
“Mr. Lavery’s release was secured following a request from the Canadian government to Qatar, asking for their support given their past experience as mediators in Afghanistan,” the official added, speaking on condition of anonymity.
Lavery is now in the Qatari capital, Doha, where he has undergone a medical assessment, the official said.
What to know about Israel’s ban on UN agency for Palestinians

- Replacing UNRWA, therefore, is seen as impossible, even though beneficiaries and NGOs have been searching for alternatives for weeks
JERUSALEM: As a law banning the UN agency for Palestinian refugees from operating on Israeli territory is set to take effect, the future of the vital services it offers is shrouded in uncertainty.
Israeli politicians have accused UNRWA of being linked to Palestinian militants, and in October voted to ban it. The order will come into force at the end of January.
Lawmakers have celebrated the legislation as a political victory, but it has raised questions about what would replace the work of the crucial aid agency.
UNRWA operates across the Middle East, particularly in Palestinian refugee camps.
The areas that would likely be affected by the Israeli ban are the Palestinian territories — the occupied West Bank and annexed east Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip.
UNRWA provides education, sanitation and health services, and has been the main agency coordinating aid during the Gaza war.
The legislation bans Israeli officials from working with UNRWA and outlaws its activities “on Israeli territory,” which under Israeli law would include east Jerusalem, occupied and annexed by Israel in 1967.
UNRWA has a large compound in east Jerusalem and works in the Shuafat refugee camp there.
According to Jonathan Fowler, a spokesman for the agency, 750 children attend UNRWA schools in east Jerusalem, while it conducts 8,000 medical consultations each year for patients who have no access to other options.
In the Gaza Strip, devastated by more than 15 months of war between Israel and Hamas, the agency employs 13,000 people and coordinates the humanitarian response for other organizations, which means it is regularly in contact with the Israeli authorities.
In the West Bank, UNRWA provides services for hundreds of thousands of people living in refugee camps.
To operate in the territory, the agency must coordinate with an Israeli defense ministry agency.
Under the Israeli law, UNRWA must cease its operations in east Jerusalem and vacate all its buildings by January 30, Israeli ambassador to the UN Danny Danon wrote in a letter to Secretary-General Antonio Guterres on Friday.
Apart from that letter, “no one knows what is going to happen,” said Fowler.
“We will continue everything we can while awaiting further details. We are not giving up.”
Emphasising the uncertainty that surrounds the agency, Fowler said it wasn’t clear whether UNRWA staff passing through Israeli checkpoints across the West Bank could “be considered contact with the Israeli authorities” and therefore banned.
He said that during Israeli military raids, UNRWA staff have maintained contact with Israeli officials to protect the people it serves, especially children in refugee camps.
“If we lose that contact, that would be a big problem,” he said. “It is very dangerous.”
In the Gaza Strip, UNRWA “provides logistical support” for other UN agencies and remains “the backbone of UN operations on the ground,” said Muhannad Hadi, the UN’s humanitarian coordinator for the Middle East, recently returned from Gaza.
Replacing UNRWA, therefore, is seen as impossible, even though beneficiaries and NGOs have been searching for alternatives for weeks.
Human rights group Adalah petitioned the Israeli supreme court on January 15, in the name of 10 Palestinian refugees, arguing that the legislation banning UNRWA “violates fundamental human rights and Israel’s obligations under international law.”
Fowler said that “under international law, it is incumbent on an occupying power to ensure the well-being... of an occupied population.”
The Palestinian Red Crescent on Thursday said it “absolutely” rejected the idea of replacing UNRWA “despite ongoing attempts by various parties” to convince it to take on the UN agency’s work or receive funds that currently go to the agency.
It said “the most recent of these attempts was by the Israeli health ministry which sought to hand over UNRWA’s Bab Al-Zawiya clinic in Jerusalem to the (Red Crescent) in exchange for financial support — a proposal that the Society categorically rejected.”
Some have suggested that UNRWA’s mission be taken over by foreign governments or other UN agencies.
Some UN staff, speaking to AFP on condition of anonymity, said that their organizations lacked both the human and material resources to replace UNRWA.
Other UN agencies “don’t have the capacity, on the ground, to do the distribution like we do,” said Fowler.
COGAT, the Israeli defense ministry agency overseeing civilian affairs in Palestinian territories, has repeatedly said that it works with other organizations, UN agencies and NGOs to organize the humanitarian response in the Gaza Strip.
How war’s toll on schools is creating a bleak future for millions of children

- War has kept 18 million children in Sudan and 658,000 in Gaza out of school for nearly two years, with no immediate hope of returning
- School closures in conflict zones, experts warn, put children at greater risk of exploitation, abuse, and mental health challenges
LONDON: In wartime, the destruction of a school is more than collateral damage — it represents the theft of a child’s future. The past year has been especially bad in this regard, with one in three children in conflict zones or fragile states deprived of schooling.
With wars taking place in Gaza, Lebanon, Sudan, Ukraine, and elsewhere around the globe, the UN children’s fund, UNICEF, described 2024 as “one of the worst years” in its history for children in conflict.

“By almost every measure, 2024 has been one of the worst years on record for children in conflict in UNICEF’s history — both in terms of the number of children affected and the level of impact on their lives,” said Catherine Russell, the agency’s executive director.
“A child growing up in a conflict zone is far more likely to be out of school, malnourished, or forced from their home — too often repeatedly — compared to a child living in places of peace.
“This must not be the new normal. We cannot allow a generation of children to become collateral damage to the world’s unchecked wars.”
Nearly one in six children worldwide live in conflict zones, with more than 473 million enduring the highest levels of violence since the Second World War, according to the Peace Research Institute Oslo.

In contexts like Gaza and Sudan, where many educational facilities have been damaged or destroyed by fighting and where teachers have been forced to flee, learning and play have been replaced by trauma and loss.
In Gaza, at least 658,000 school-aged children remain out of classrooms for the second consecutive academic year, with around 96 percent of school buildings damaged or destroyed since October 2023, despite their protected status under international humanitarian law.
The Oct. 7, 2023, Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, which saw 1,200 killed and 250 taken hostage, triggered the devastating war in Gaza, which killed at least 47,000 Palestinians and displaced 90 percent of the population, according to Gazan officials.
Despite the fragile Israel-Hamas ceasefire deal reached earlier this month, a return to classrooms in Gaza remains a distant hope. UNICEF said in November that at least 87 percent of the enclave’s schools will require extensive reconstruction before they can reopen.
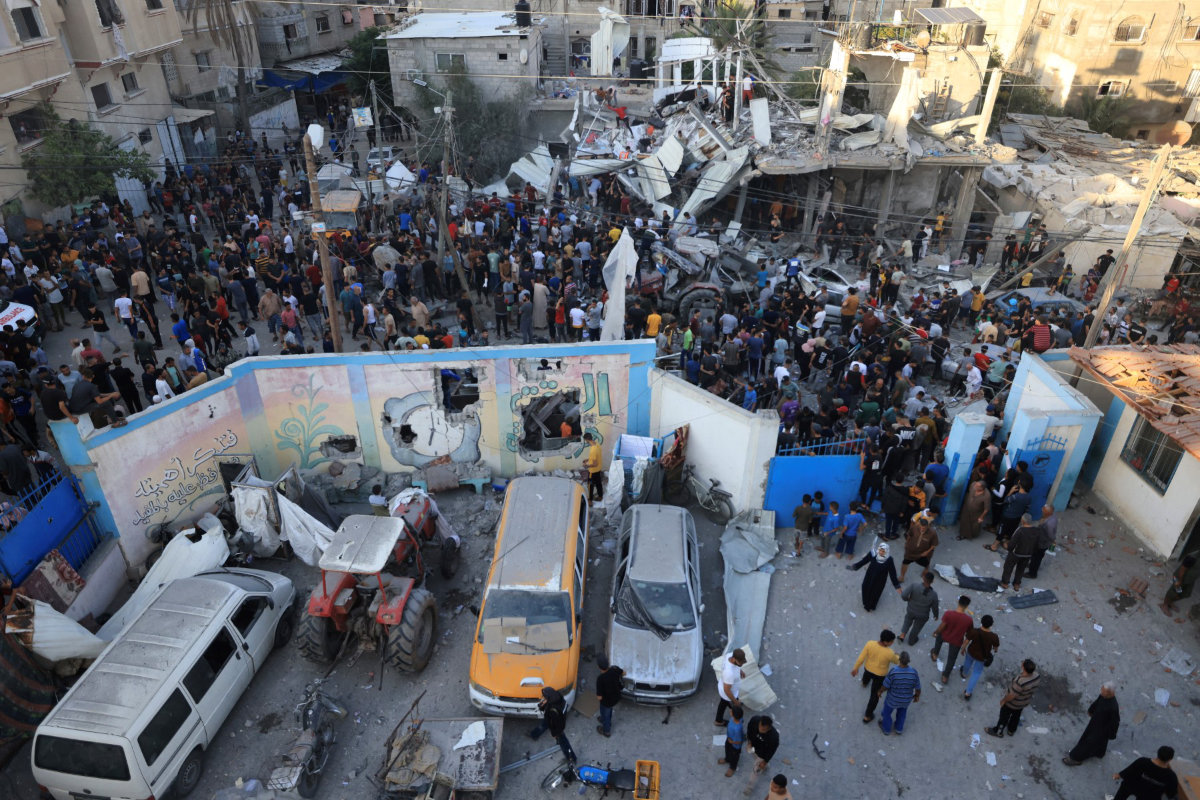
Although Israel says it does not deliberately target civilian infrastructure, few educational institutions have been spared damage, including UN-run schools sheltering displaced civilians.
UN experts voiced concern last year over what they considered the systematic destruction of education in Gaza, not only through the crippling of schools and colleges but also the arrest and killing of teachers.
“It may be reasonable to ask if there is an intentional effort to comprehensively destroy the Palestinian education system, an action known as scholasticide,” the UN experts said in a joint statement.
“These attacks are not isolated incidents. They present a systematic pattern of violence aimed at dismantling the very foundation of Palestinian society,” the statement added, lamenting that “when schools are destroyed, so too are hopes and dreams.”
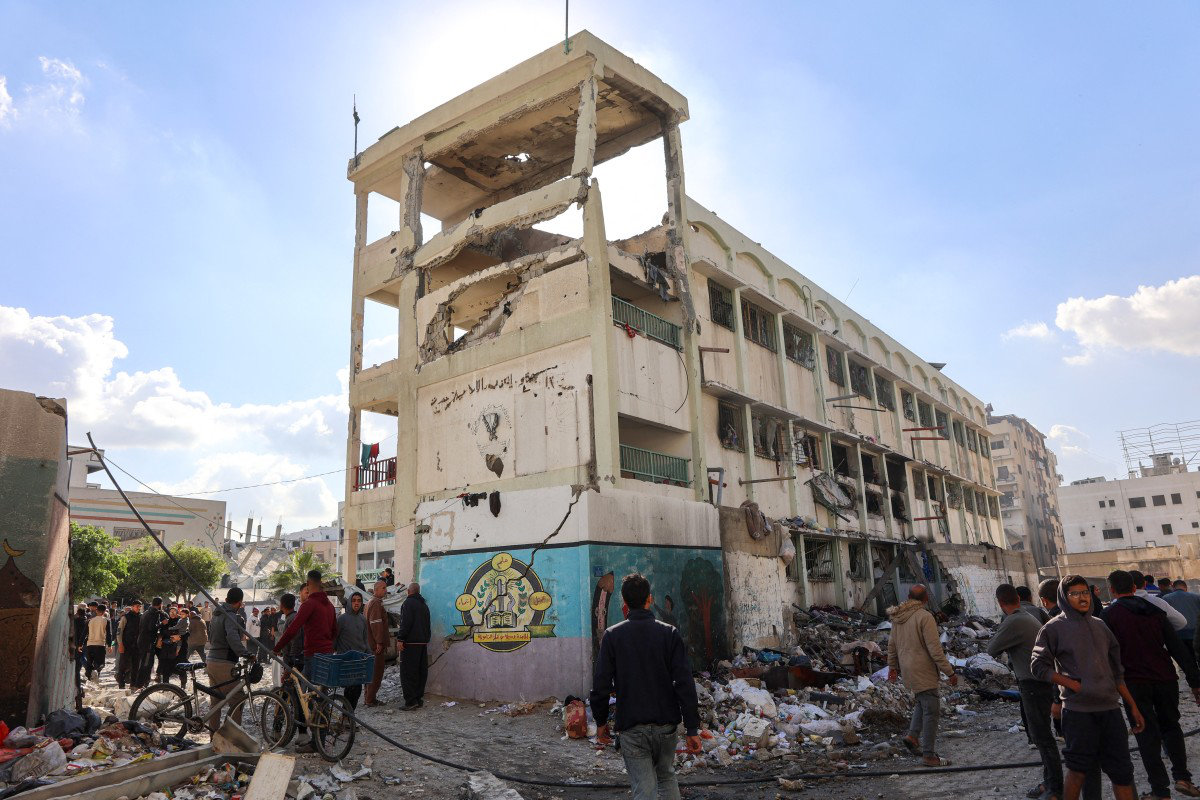

By September last year, at least 10,490 school and university students and more than 500 schoolteachers and university lecturers had been killed, according to Gaza’s Ministry of Education.
In October alone, the UN documented at least 64 Israeli attacks on schools in Gaza, averaging almost two attacks per day.
“Schools should never be on the front lines of war, and children should never be indiscriminately attacked while seeking shelter,” UNICEF’s Russell said in early November.
“The horrors we are seeing in Gaza are setting a dark precedent for humanity, one where children are hit with bombs at record numbers while looking for safety inside classrooms. Trauma and loss have become their daily norm.”
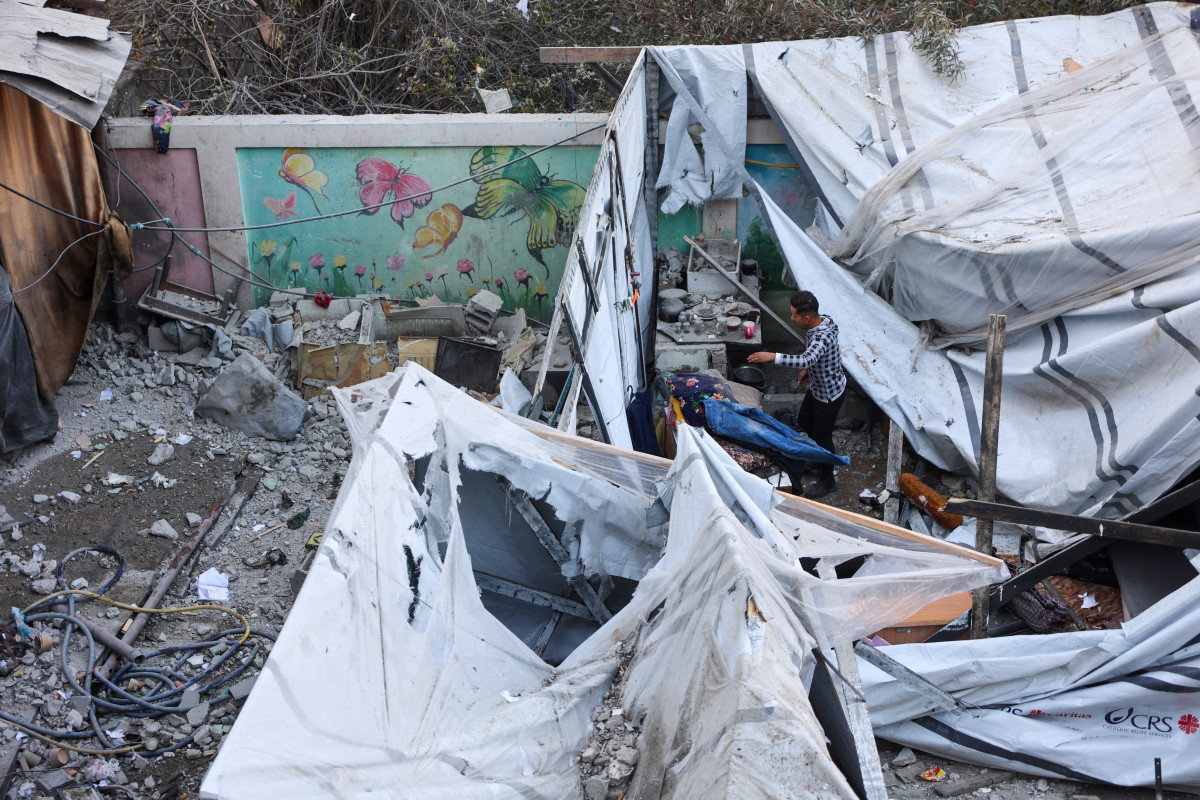

The situation is equally dire in Sudan, where a brutal civil war has wrought havoc on civilians and critical infrastructure since April 2023, killing tens of thousands and displacing more than 11.4 million, according to UN figures.
Attacks on schools, which Save the Children reports have increased fourfold since the conflict began, have forced most institutions to close, leaving more than 18 million of the country’s 22 million children without a formal education for more than a year.
Such attacks, Save the Children says, include airstrikes on schools, the abduction, torture, and killing of teachers, and sexual violence against students inside education facilities.
Other violations include armed groups occupying schools, using them to store weapons, and fighting battles on school grounds.
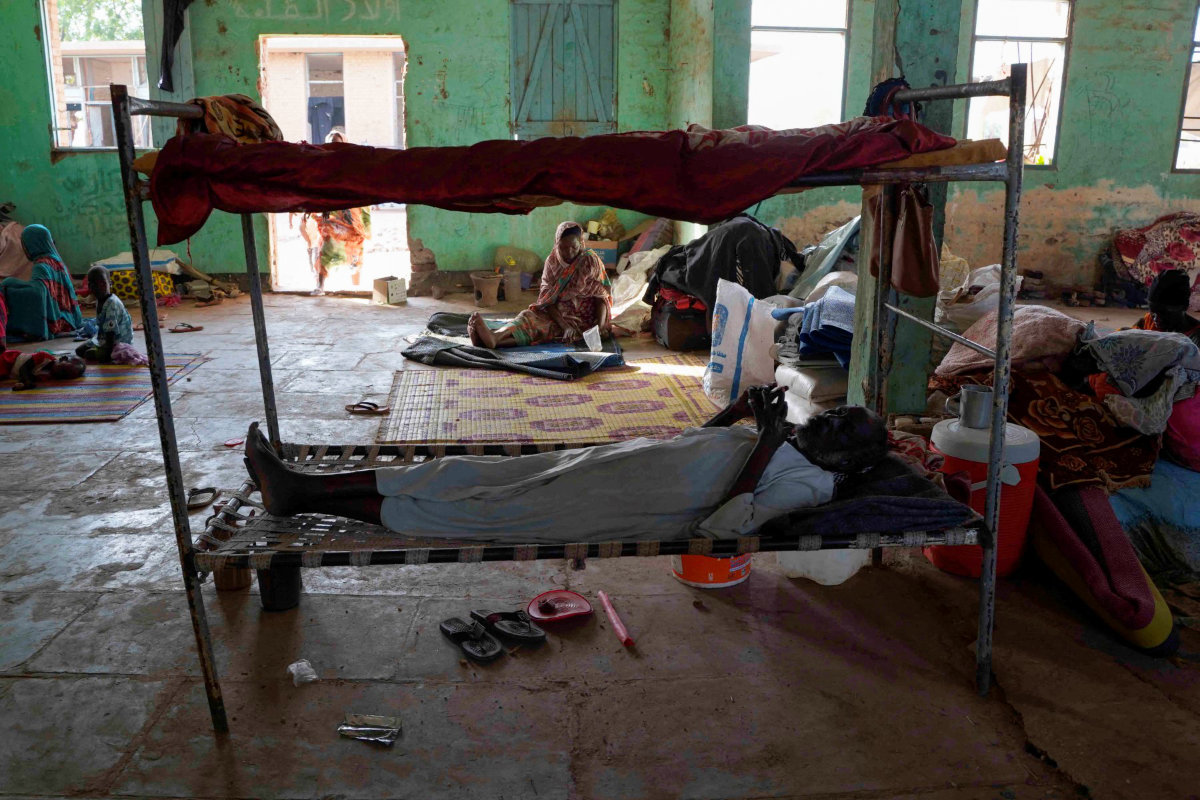

Adil Al-Mahi, MedGlobal’s Sudan country director, believes that even if the violence ends, a full return to normal education is unlikely in the near future.
“Cities controlled by the Rapid Support Forces are badly damaged, including education facilities in those areas,” Al-Mahi told Arab News.
By early 2024, the paramilitary RSF had seized most of the capital, Khartoum, and much of Al-Jazirah state, Sudan’s agricultural heartland.
INNUMBERS
• 25 million Children in 22 conflict-affected countries who are out of
• 103 million Children in 34 conflict-affected countries denied schooling in 2024.
(Source: Save the Children)
However, in January, the Sudanese Armed Forces announced they had advanced into Omdurman, Sudan’s second-largest city, located in Khartoum state, reclaiming some areas previously held by the RSF.
Schools in these areas have been “used by the RSF as warehouses for military equipment,” and therefore many have been targeted by the air force, Al-Mahi said. “Around 70 percent of the facilities might not be safe for children’s education.”
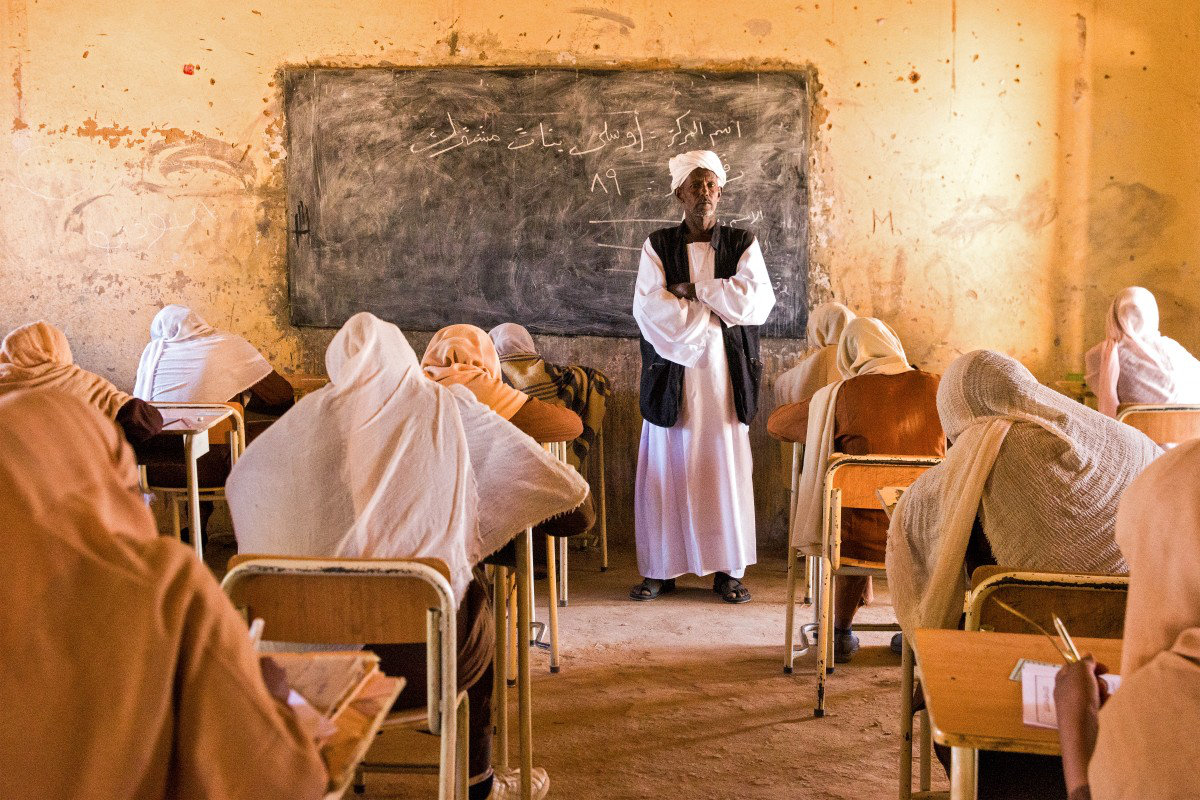

Aid agencies warned in May that Sudan is on the brink of the world’s worst education crisis. Displacement has compounded the already dire situation, even in areas where schooling remains relatively accessible.
With no formal camps for internally displaced persons, many families have sought refuge on school grounds, disrupting the education of local children, said Al-Mahi.
In the eastern coastal city of Port Sudan, for example, “some schools have reopened,” but they face significant challenges as “the schools themselves were used as shelters for IDPs arriving from the conflict area.”
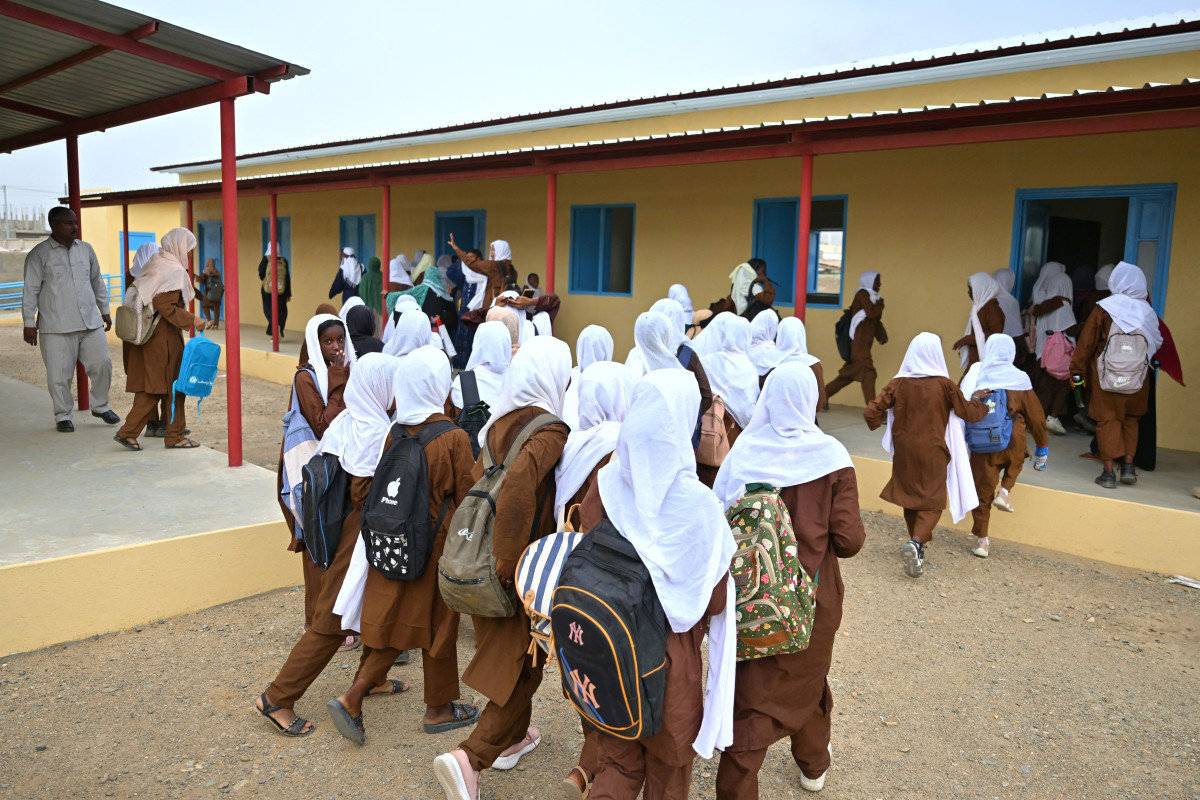

Al-Mahi said the situation has created tensions with local communities, who wanted to reclaim the spaces and reopen the schools.
A similar issue emerged in the River Nile state. However, according to Al-Mahi, “the problem was resolved to get the families out of the classrooms and have them in proper tents in the open areas within the school — the playgrounds — and then have the schools also operate.”
Nevertheless, facilities in these areas continue to struggle with overcrowding. “Most of the cities that received IDPs have seen their populations increase three or fourfold, making it very difficult to accommodate children, even if the school is no longer housing IDPs,” Al-Mahi said.

The disruption of formal learning in conflict zones has cast a shadow over children’s futures, leaving many with mental health issues and at an increased risk of child labor and child marriage.
“Education is lifesaving,” James Cox, Save the Children’s global education policy and advocacy lead, told Arab News.
“School protects children from things like child labor, early marriage and pregnancy, recruitment into armed forces, and helps build critical thinking, healthy social relationships, and mental wellbeing.
“Children being denied their right to education on any scale has significant implications for society as well as the individual children. Studies have shown that in low- and middle-income countries, the probability of conflict has almost tripled when the level of educational inequality doubled.”
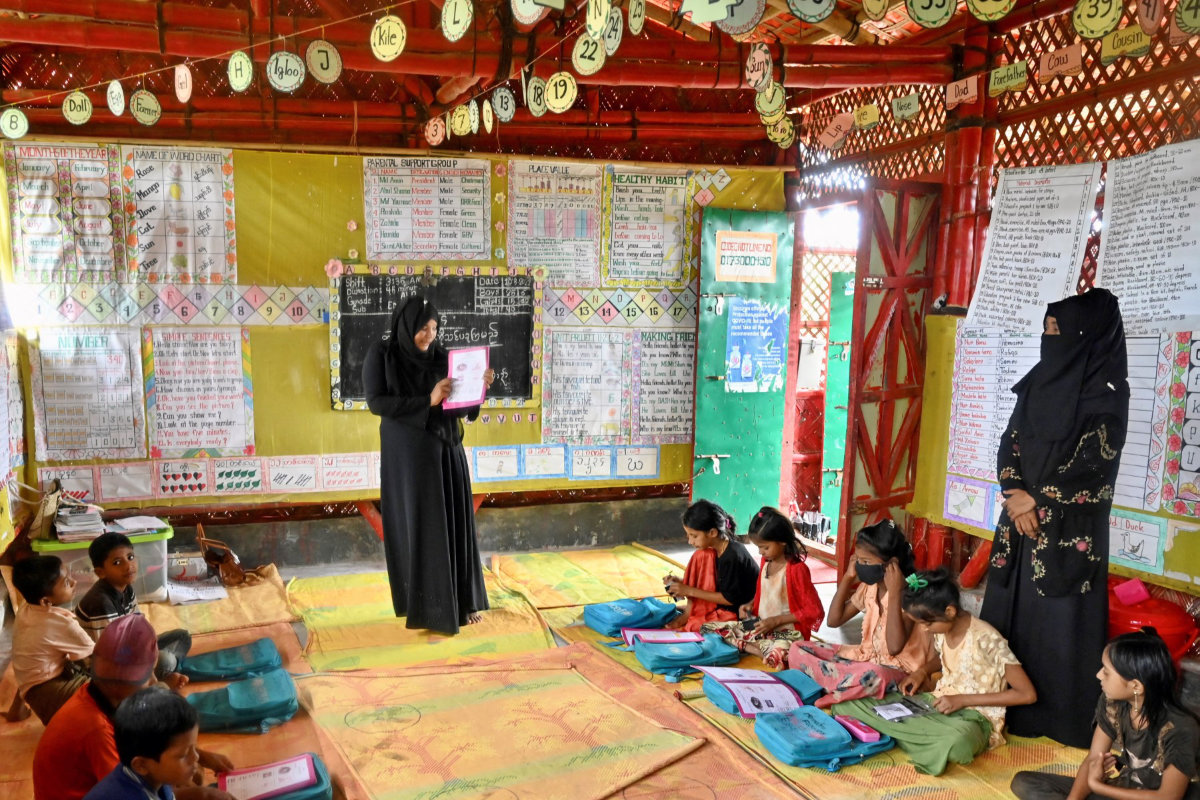

It also impacts economic prosperity. UNESCO estimates that by 2030, the annual global social costs of children who leave school early will reach $6.3 trillion — or 11 percent of global gross domestic product.
Cox also warned that “when children are prevented from attending school for a long period, learning is significantly impacted — and can often regress.”
He said: “The longer children are out of school, the greater the risk that they never return — and, without the right support, of dropping out for those who try to return.”
For school-age children in conflict zones, the mental health impact can be immense. Jeeda Al-Hakim, a specialist counseling psychologist at City University of London, described being out of school as “an emotional wound that goes beyond missed lessons.
“School offers much-needed stability, a sense of normalcy, and a safe space to form friendships and express themselves,” she told Arab News. “Without it, children are left isolated and burdened by uncertainty, often grappling with feelings of fear, loss, and despair.”
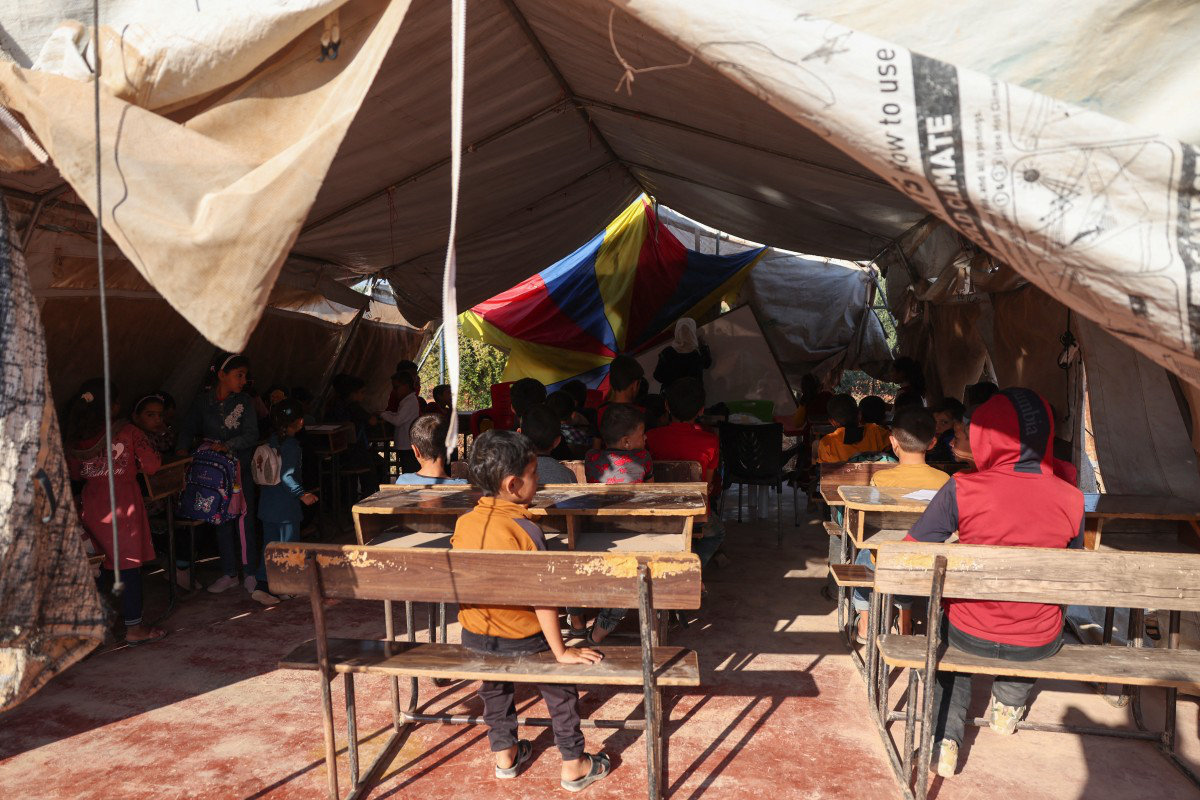

Many of those children “are thrust into adult responsibilities — caring for siblings or finding ways to survive — while their own emotional needs are sidelined,” she said.
“Premature adultification can lead to profound feelings of loneliness and anxiety, as children miss out on the freedom to simply be children.”
Stressing that “the emotional cost of these experiences cannot be understated,” Al-Hakim said: “While informal learning or community support can provide glimmers of hope, nothing replaces the emotional security and opportunities that come from a stable environment.
“To truly support these children, we must prioritize ending the conflicts that strip them of both their childhoods and their futures.”


















