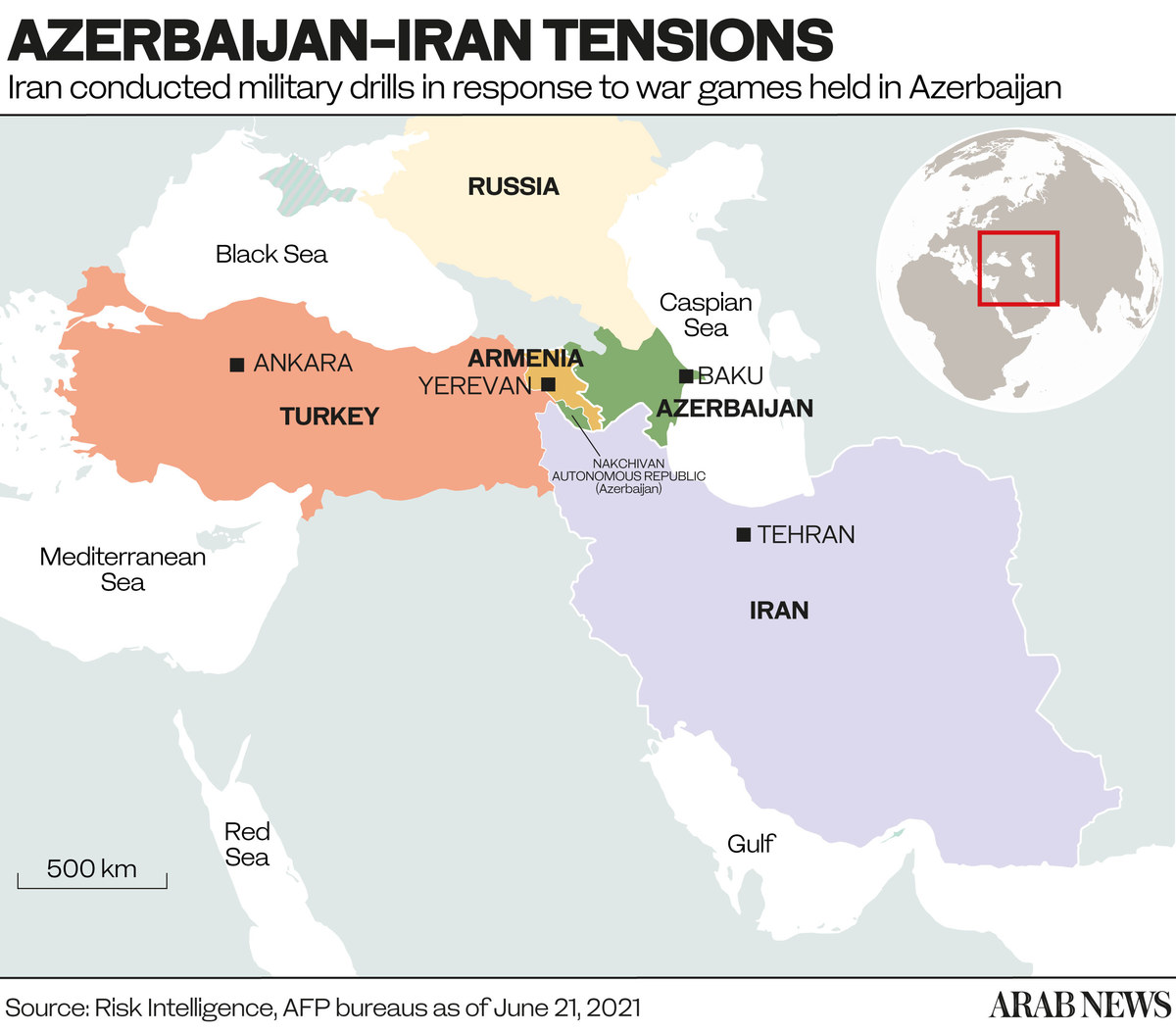
WASHINGTON D.C.: Tensions between Iran and Azerbaijan are high amid a diplomatic spat that is approaching crisis point, according to regional observers.
Although the two countries normally enjoy cordial relations, they are drifting apart owing to divergent strategic interests and political visions.
Azerbaijani authorities, long frustrated by Iran’s support for its neighbour and rival, Armenia, have launched a crackdown on cross-border trade that was a lifeline for an Armenian separatist holdout in the Nagorno-Karabakh region.
In 2020, following a Russian-brokered ceasefire, Armenian forces agreed to hand over much of Nagorno-Karabakh to Azerbaijan, which marked a significant victory for Baku after a 44-day war.
In Nagorno-Karabakh, Armenian separatists protected by Russian peacekeepers still control the city of Khankendi, also known as Stepanakert, and a handful of surrounding villages.
The entirety of Iran’s shared border with what had once been Armenian-occupied Nagorno-Karabakh is now under the control of Azerbaijani authorities.
However, Iranian trucks allegedly continued to enter Nagorno-Karabakh without paying the requisite customs fees to the Azerbaijani government.

The Iranian army's ground forces began holding manoeuvres near the country's border with Azerbaijan recently, despite criticism from its northwestern neighbor. (AFP/Iranian Army Office/File Photo)
“This is not the first time that Iran’s trucks have illegally traveled to the Karabakh region,” Azerbaijan’s President Ilham Aliyev said this week.
“This is something that happened repeatedly during the occupation period. Around 60 Iranian trucks entered Azerbaijan’s Karabakh region without permission between Aug. 11 and Sept. 11 this year after Azerbaijan called on Iran to put an end to the practice.
“Then we started to control the road passing through Azerbaijani land, and the trucks sent by Iran to Karabakh came to an end.”
Tensions have been stoked further by joint military drills held by the Azerbaijani army with Turkey and Pakistan 500 kilometers from the country’s border with Iran.
Aliyev also inaugurated a new military base in the city of Jabrayil in Nagorno-Karabakh, right on the border with Iran, making sure to be filmed standing beside a line of Israeli-made Harop combat drones that Azerbaijan used to devastating effect during the 2020 war.
Iran claimed Azerbaijan was allowing Israel to establish a base on Iran’s border.
“Iran will not tolerate the presence of the Zionist regime near our borders,” said Saeed Khatibzadeh, the Iranian foreign ministry spokesman.

A handout picture provided by the office of Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei on November 1, 2017 shows him (R) meeting with Azerbaijan's President Ilham Aliyev in Tehran. (AFP/File Photo)
Iran then conducted a multi-day military exercise along its border with Azerbaijan.
According to Iran’s Tasnim news agency, the Azerbaijani government ordered the closure of a mosque in Baku linked to Iran’s supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei.
“The mosque and representative office of Seyyed Ali Akbar Ojaghnejad, representative of supreme leader (Ayatollah) Ali Khamenei in Baku, were sealed and closed today by order of the authorities of the Republic of Azerbaijan,” Tasnim said.
Azerbaijan claimed the move was necessary because of “a surge in COVID-19 cases in several locations in Baku,” saying that the mosque’s operation had been “suspended temporarily.”
Iran’s embassy in Baku said there had been no advanced warning of the move.
Speaking to Arab News, Farid Shafiyev, chairman of the Baku-based Center of Analysis of International Relations, said: “Only Iran will suffer from these statements. Tehran, first of all, should see the Caucasus as a region of potential cooperation.
“Iran’s statements about ‘third-country’ or ‘foreign’ forces stationed in Azerbaijan are mainly aimed at Israel and Turkey, but they must understand that we are not hiding.
“Azerbaijan has military-political cooperation with Israel and with Turkey, as well as strong economic ties. It is designed, first of all, to ensure the security of Azerbaijan and not against Iran.”

Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev tours the Military Trophy Park in Baku that showcases military equipment seized from Armenian troops during last year’s war over the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region. (AFP/File Photo)
Shafiyev believes there are two key reasons why Iran fears Azerbaijan’s growing regional clout. The first is the Zangezur Corridor — an overland corridor Baku plans to establish across southern Armenia to link up with the Nakhchivan enclave bordering Turkey.
According to Shafiyev, Iran fears the plan, which was agreed under the terms of the ceasefire deal, will leave it cut off from the wider region.
The second factor at play is Azerbaijan’s longstanding relationship with Israel, which has angered Iran at a time when its nuclear program has been set back by a string of suspected Israeli covert operations.
Shafiyev says Azerbaijan is unlikely to back down in the face of Iranian saber-rattling.
“This is our sovereign right,” he said. “Our cooperation with Israel is more about security. Israeli weapons have shown their effectiveness during the Patriotic (Nagorno-Karabakh) War.
“As a former diplomat, I would like the issues to be resolved diplomatically and Iran should (instead) consider this region as a potential region of cooperation.”
Ahmad Obali, a US-based Azerbaijan analyst and founder of Gunaz TV, also believes the outcome of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war is driving Iranian policy in the region.

An Iranian army helicopter during a military exercise in northwest of the country, close to the Iranian-Azerbaijani border. (AFP/Iranian Army Office/File Photo)
“Iran does not want to accept the fact that Azerbaijan won the Karabakh war and liberated the border between Iran and Azerbaijan from Armenian occupation,” he said.
“Iran lost significant revenue when Azerbaijan regained Karabakh from the Armenians. The border area in that region was used extensively for narcotics smuggling and exports. Now Azerbaijan is in control.
“Iran is also opposed to Azerbaijan’s ambitions to build the Zangezur Corridor, which would further cost Iran revenue that it would have otherwise collected.”
He added: “Iran was caught red handed. The Iranian truck drivers were arrested by Azerbaijani authorities after delivering goods. That has now been stopped, which has further angered Iran.
“The fact that the Turkey-Azerbaijan relationship has grown bothers Iran. Iran is more aggressive now and they’re frustrated that Azerbaijan is becoming stronger.”
Obali says Baku’s victory in the Nagorno-Karabakh war has lifted the morale of an estimated 20 million ethnic Azerbaijanis in Iran who are opposed to Tehran’s policies towards their ethnic kin.

Iranian army tanks lined up during a military exercise in northwest of the country, close to the Iranian-Azerbaijani border. (AFP/Iranian Army Office/File Photo)
“Iran has been emboldened by the thinning US presence in the region, including its withdrawal from Afghanistan and the softer approach of the current US administration regarding Iran and the potential reinstatement of the JCPOA,” said Efgan Nifti, CEO of the Caspian Policy Center, referring to the 2015 Iran nuclear deal.
“Iran feels it can challenge Western partners with minimal pushback from the US and European powers. Baku’s regaining of control of its sovereign territory has interrupted Iran’s illicit trafficking and trade.
“In addition to this, the opening of the Zangezur Corridor and regional east-west communication links will cause Iran to lose control over trade and transit.”
Nifti added: “Iran is also frustrated by economic difficulties and growing popular discontent, which make it feel insecure about its ethnically diverse population. This tension with Baku helps the regime divert popular attention away from real domestic issues.”
Undoubtedly, Azerbaijan’s recent territorial and strategic gains, coupled with its ability to win both Israeli and Turkish support, could act as a deterrent against future Iranian encroachment.
“Azerbaijan is strengthening relations with Turkey and Israel,” said Nifti. “Iran sees the latter as an existential threat.”
-----------------
Twitter: @OS26























