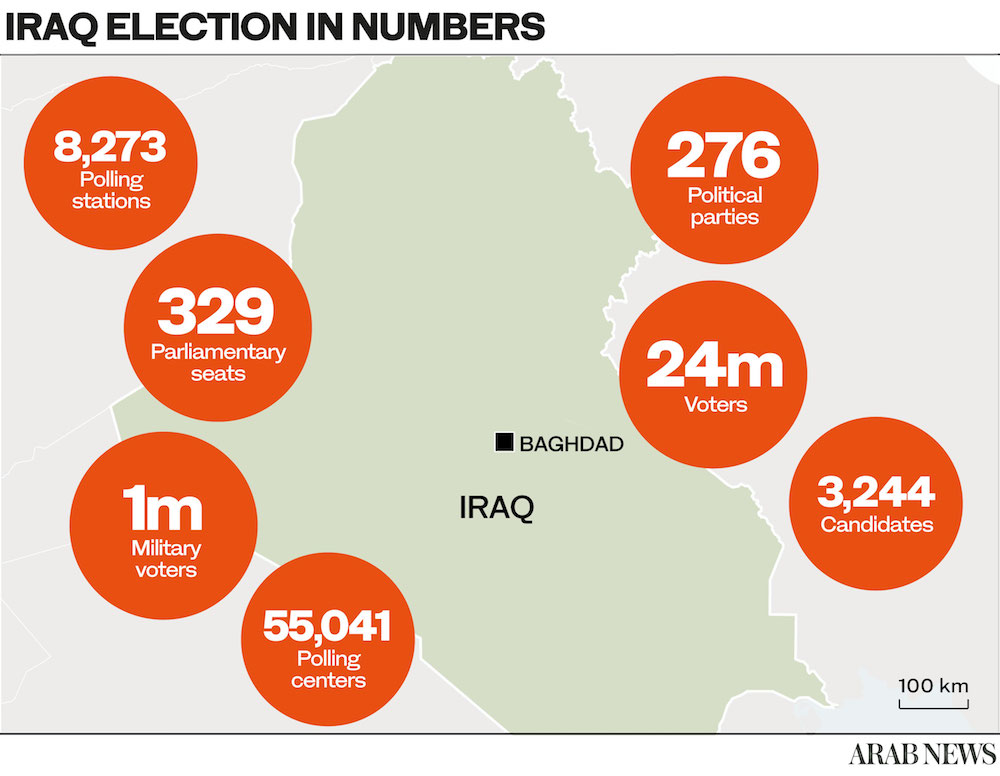
BAGHDAD, Iraq / BOGOTA, Colombia: Eighteen years since the US-led invasion of Iraq toppled the Baathist dictatorship of Saddam Hussein, a whole generation has come of age knowing only the system of parliamentary democracy built in its place.
But as election day unfolds today, many young Iraqis still feel alienated from the political process and skeptical about meaningful change happening via the ballot box.
In 2003, as part of its de-Baathification strategy, the Coalition Provisional Authority teamed up with Iraqi oppositionists, many of whom had spent decades in exile, to build the vital institutions of state almost from scratch.
However, the system they built, modeled on the West’s own time-honored institutions, was alien to many Iraqis who had for centuries conducted their affairs along tribal and religious lines and were divided along sectarian lines.
Mourtatha Al-Makhsousi, a 27-year-old unemployed graduate from the eastern Iraqi city of Kut, told Arab News: “In 2003, the Iraqi opposition was working to change the regime, but they did not address it well and they failed to analyze the consequences of the changes. As a result, we have a fragile system here.
“Here in Iraq people did not know about democracy and parliamentary systems. Moreover, we are a tribal and religious community with social contradictions that cannot be controlled by a parliamentary system.
“Therefore, it required a religious appeal in the Iraqi constitution and parliament for people to vote. I suppose a majority of Iraqis still do not know how it works or how power is distributed.”
Foreign powers, armed groups, and corrupt individuals soon took advantage of the situation and the billions of dollars in aid money lavished on the country, fashioning a system that was, for the most part, democratic in name only.

Iraqis chant slogans as they rally at Fardous square in central Baghdad, on October 1, 2021, demanding justice for demonstrators killed during the October 2020 anti-government protests, ahead of the October 10 parliamentary elections. (AFP)
Rana, a 24-year-old law graduate, also from Kut, said: “We were told there would be democracy and change. On the contrary. We had one corrupt face; now we have many corrupt faces.
“Since the invasion and until now, we have not seen real change. It is like a mafia controlling the government. They are just a group of gangsters working for their own interests, from the 2003 government until the current one.”
Former Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri Al-Maliki’s State of Law coalition, which maintained close ties with Iran, came to dominate national affairs in the years after 2003, leaving Iraq’s once pre-eminent Sunni minority and long-persecuted Kurds feeling excluded.
ALSO READ: A Mosul book cafe raises political awareness in the run-up to Iraq elections
A sectarian civil war soon enveloped the country from 2006 to 2008, followed in 2014 by the emergence of Daesh, an Al-Qaeda splinter group that went on to conquer a third of Iraq’s territory in the predominantly Sunni northwest.
Once the Iraqi security forces had reclaimed these territories in 2017 with extensive coalition air support, the country set about the gargantuan task of reconstruction and resettling millions of displaced households.
The May 2018 election was post-war Iraq’s first democratic test. But with a record low turnout, and widespread allegations of fraud, Shiite militia leaders moved almost seamlessly from the battlefields into the corridors of power, together with the followers of firebrand Shiite cleric Muqtada Al-Sadr.
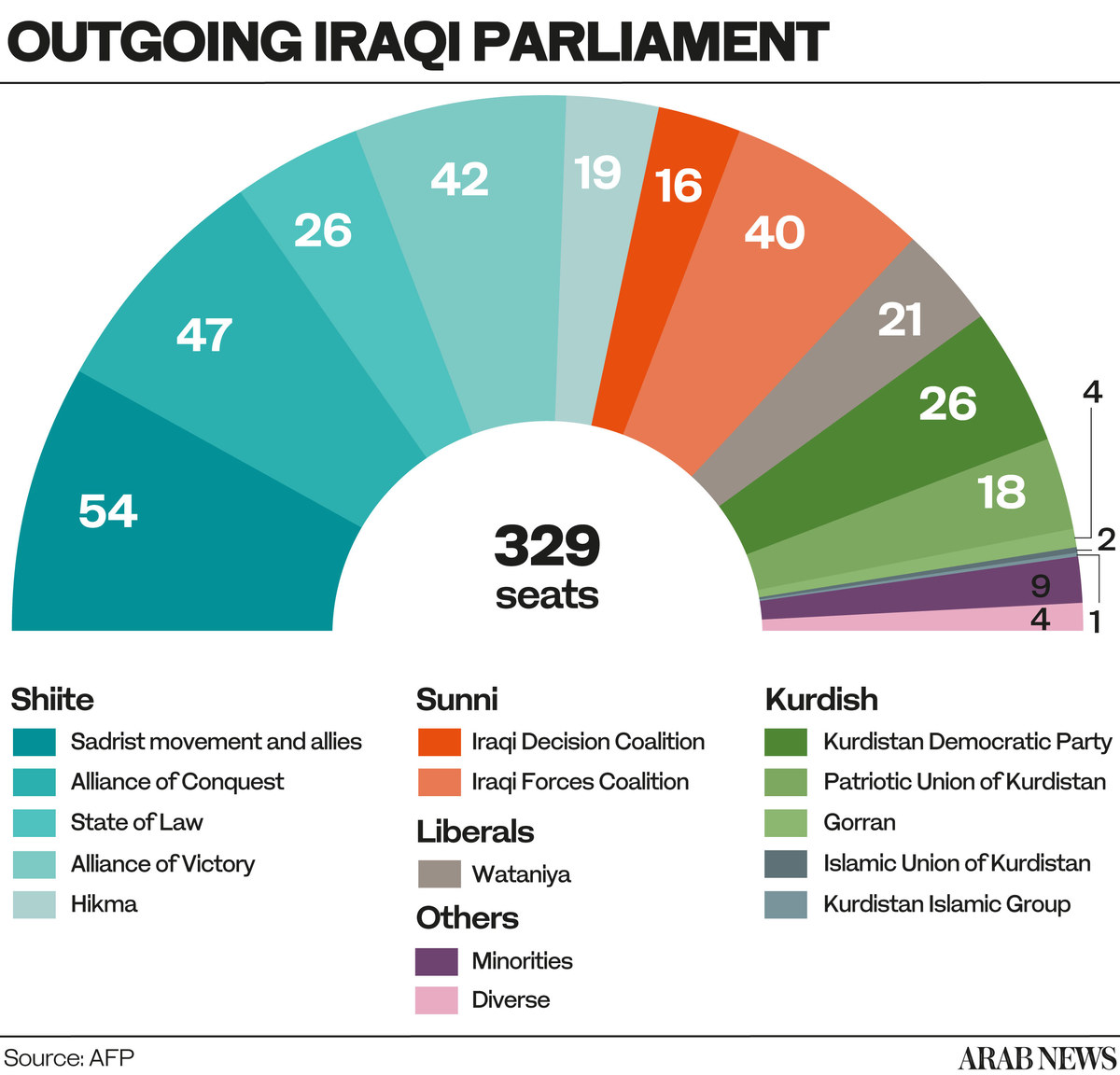
And, after months of back-room wrangling, the victors chose the mild-mannered technocrat Adel Abdul-Mahdi to form a new government.
However, slow progress on reconstruction and resettlement, rising unemployment, and rolling power outages soon stoked public anger and, by October 2019, tens of thousands of young Iraqis had taken to the streets nationwide demanding the removal of the post-2003 elite.
A violent crackdown by security forces and pro-government militias left hundreds of protesters dead and thousands injured. Although it eventually secured Abdul-Mahdi’s resignation, the movement soon fizzled out with the onset of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
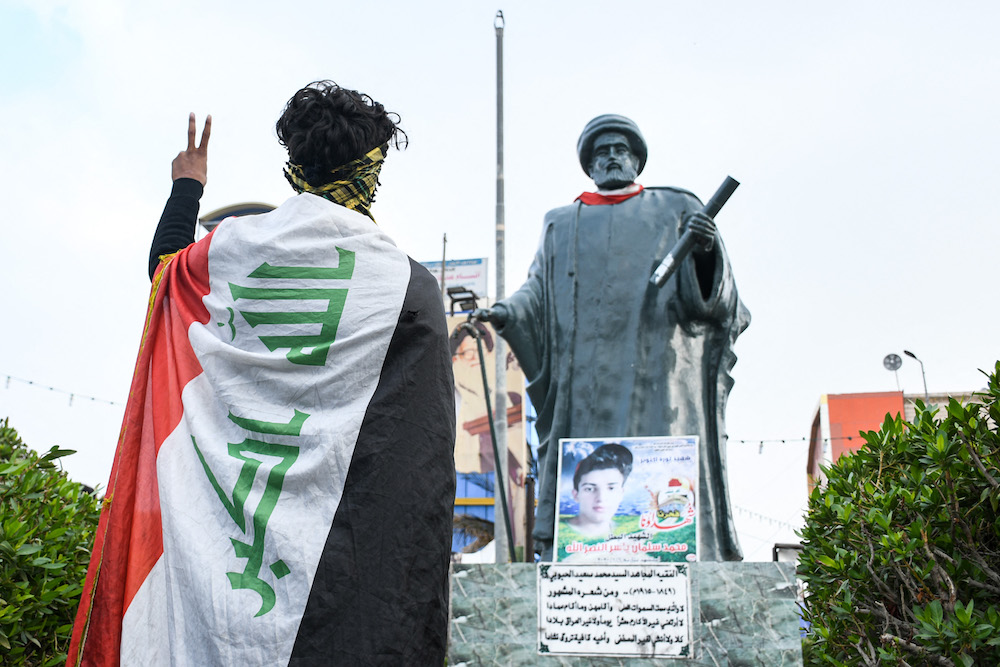

A youth draped in an Iraqi national flag flashes the victory gesture while standing before a statue of 19th century Iraqi cleric and poet Mohamed Said Al-Habboubi. (AFP/File Photo)
Rana added: “During the occupation period, people could not speak up and instead bottled up their frustrations. The grievances accumulated over the years until people could no longer hold it in. They came out on the streets in anger over the lack of services, reconstruction, security, and other injustices.
“The Iraqi youth became aware and more educated, so they came out with the revolution of October 2019. They stood against injustice and asked for the rights that have been stolen under the cover of democracy and by Islamic political parties.”
In May 2020, Mustafa Al-Kadhimi, Iraq’s former intelligence chief, was appointed the new prime minister for the period until the national elections scheduled for the following year.
Without a clearly defined political leadership heading the movement, Iraq’s young protesters were not able to translate their energy and idealism into an electoral force capable of making their demands a reality.
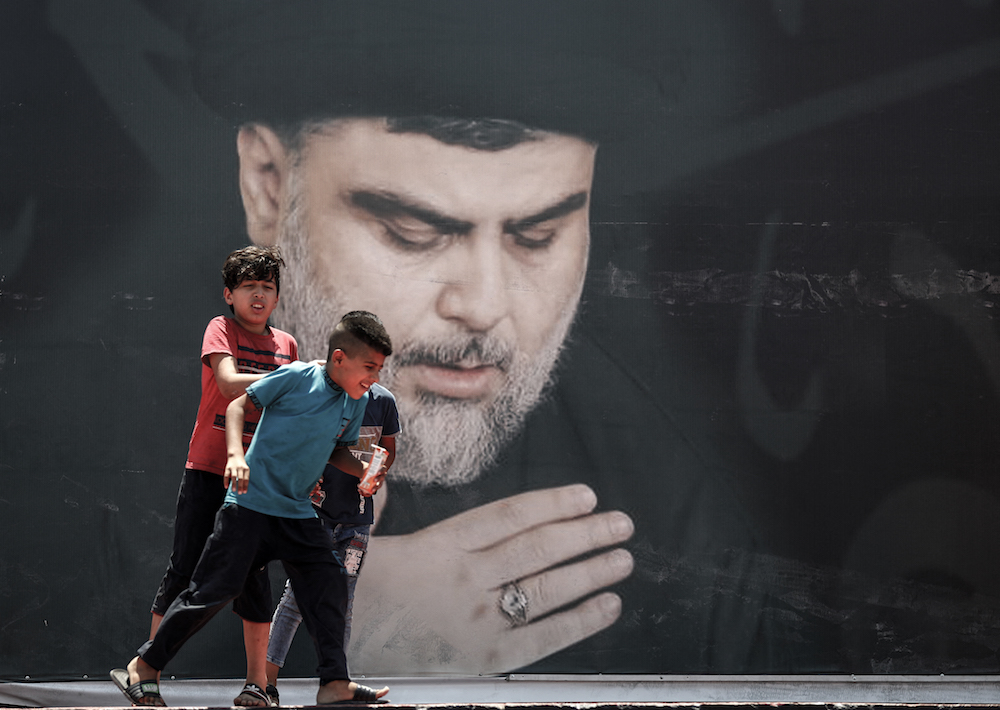

Children play in front of a large poster of Iraq's populist Shiite cleric Moqtada Sadr, in Sadr City, east of the capital Baghdad, on July 15, 2021. (AFP/File Photo)
The handful of young revolutionaries who have chosen to run as independent candidates in the Oct. 10 election stand little chance of success against the well-oiled machinery of Iraq’s establishment parties.
Zahraa Ali, a 31-year-old freelance journalist from Fallujah in western Iraq, said: “It is not easy to be involved in the democratic process here in Iraq. If you are, you will face many issues.
“If you participate in the election, they will definitely create an issue for you. The political leaders and parties that rule Iraq treat it like a dictatorship. They are imposing their will on us.”
Ali and other local activists have organized workshops to help educate Iraqis of voting age on the democratic process, their rights, and what is at stake in Sunday’s election. “In terms of change and development, it can only be achieved by Iraq’s young people,” she added.
Nevertheless, few among Iraq’s youth hold out much hope of dislodging the post-2003 order and its powerful militia-backed parties any time soon.
Zainab Jabar, a 24-year-old unemployed graduate from Basra, said: “I boycotted the last election, and I will not participate in this one either. We already know the result, so what is the point of taking part?”
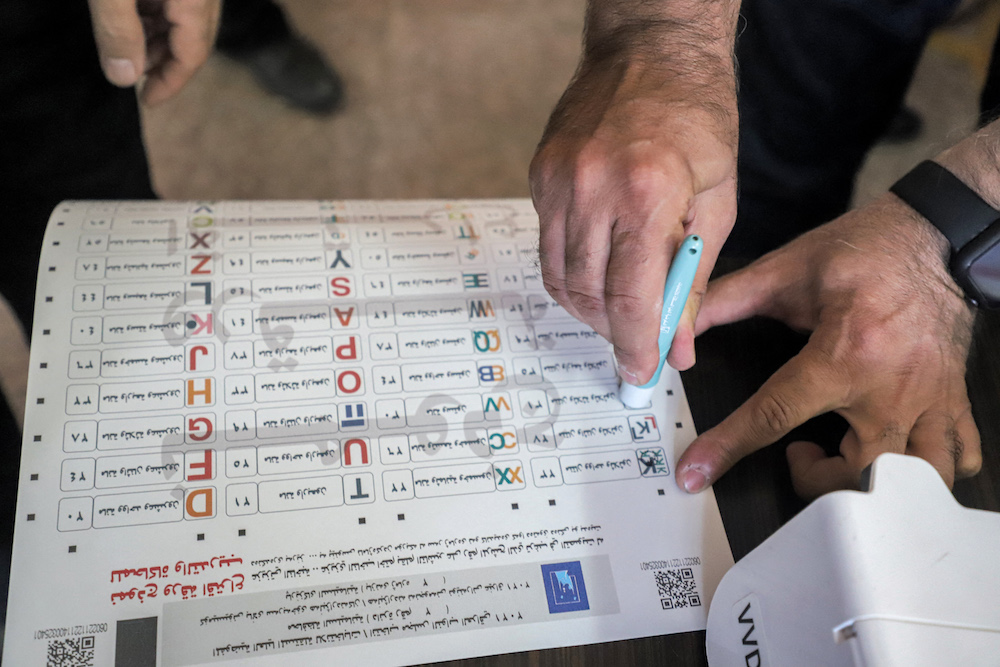

Officials of Iraq's electoral commission undergo a polling day simulation to test run its systems ahead of the upcoming parliamentary elections. (AFP/File Photo)
Jabar was among the thousands of young people who joined the protests in Iraq’s southern city of Basra in 2019. Despite its huge oil riches, Basra remains one of Iraq’s most deprived provinces, blighted by crime, poverty, and decaying infrastructure.
“We will need 50 to 100 years to change and remove the powerful political parties in Iraq. We want the change that we demanded in our revolution in October 2019. It did not happen as we hoped,” Jabar added.
Karar Al-Duaikheil, a law student from Basra, said: “Basra is the worst city in Iraq. It is dead in terms of services, construction, education, and employment, and there are militias and uncontrolled weapons on the streets. Moreover, it suffers from killings, kidnappings, threats, and arbitrary arrests.
“Unfortunately, Basra residents do not choose the candidates they want but the ones chosen by Al-Maliki, Al-Sadr, Ammar (Al-Hakim) and other political players. None of them are clean or good people.
“In addition, tribal leaders play a significant role here. They are getting stronger, with more weapons and money. Young people do not want to select a candidate who works for his party rather than for Basra.”
Al-Makhsousi pointed out that it would take time for Iraq’s democracy to fully mature and meet the needs and expectations of its young voters.

A campaign poster is seen in the Iraqi capital Baghdad on September 14, 2021, ahead of the upcoming parliamentary elections. (AFP/File Photo)
“We need more time to shape this democracy with our culture and community. We are still learning. This democracy divided us into states, regions, neighborhoods, and groups in our country.
“Wherever you go, you need a special security permit. It feels like you are not in your own country. It is as if you do not belong to it. We do not have an Iraqi nation.
“We boycotted the election in 2018. The result was very bad, and we had a regime without anything. For the upcoming election, I will be participating in order to change something, step by step.”
To this end, young people such as Al-Makhsousi have the full backing of the prime minister. In a recent tweet, Al-Kadhimi said: “Iraq counts on its youth for reform. With their persistence on a better future, the elections will be a true national triumph.
“Vote for those who preserve Iraq’s unity, sovereignty, and unique national identity. Oct. 10 is the opportunity for change.”




























