LONDON: For millions of people around the world, the Mediterranean conjures images of the perfect holiday destination — pretty waterfront villages, great food, beautiful beaches and, above all, clear blue waters. Beneath this picture-postcard surface, however, the Mediterranean Sea is in the throes of a man-made environmental crisis.
At the IUCN World Conservation Congress in Marseille, France, in September, the Mediterranean plastic crisis was firmly on the agenda. Representatives from tourist-sensitive countries, including France, Italy, Greece and Cyprus, lined up to bemoan the level of plastic pollution and to highlight their own efforts to combat the problem.
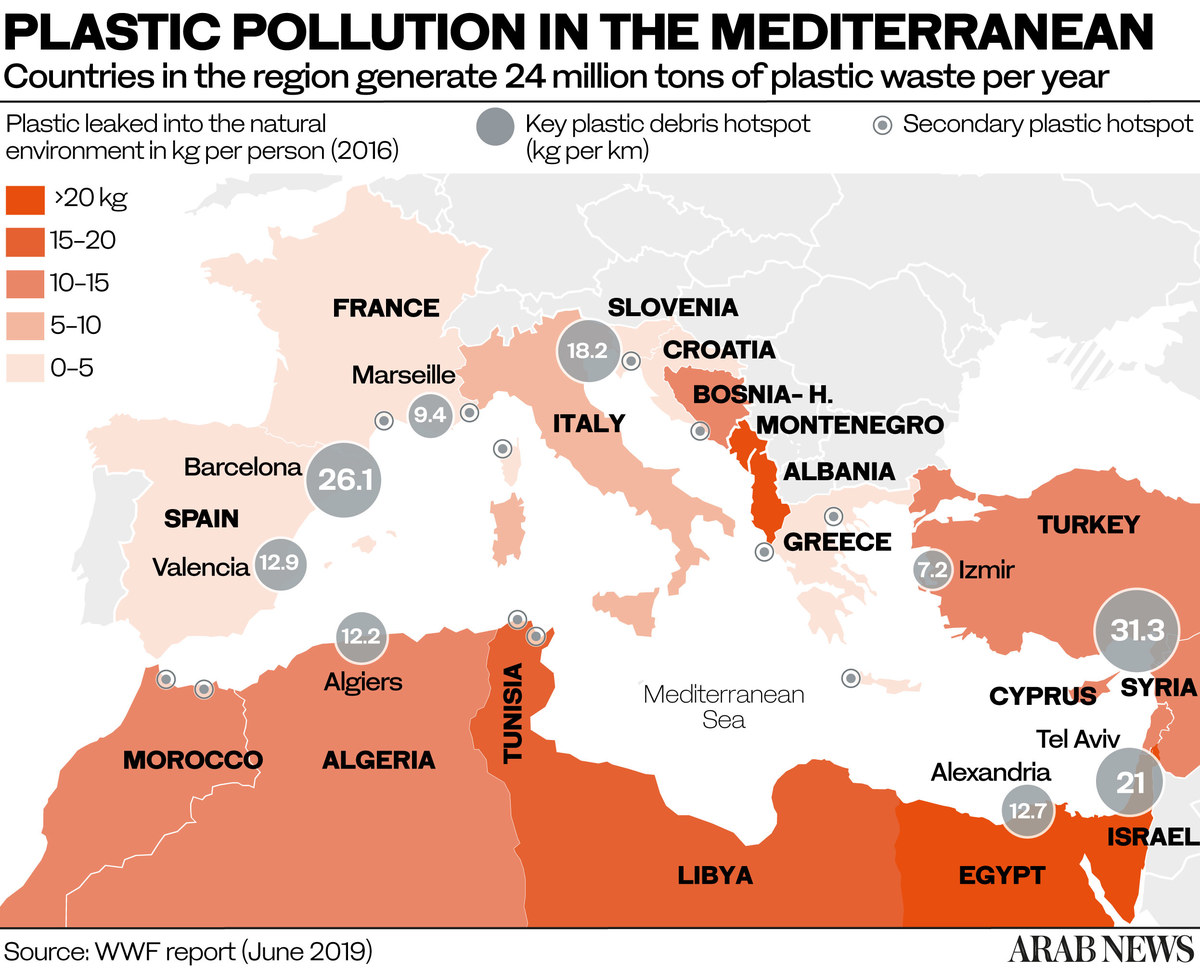
According to a report last year by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, the total volume of plastic waste in the Mediterranean, found mostly beneath the waves, could be as much as 3.5 million tons, with anything between 150,000 and 610,000 additional tons finding its way into the sea every year.
For the 21 countries that share the 28,000 km Mediterranean coastline, the half a billion people who live on the sea or along the 1,693 watersheds that feed it, and the 340 million tourists who typically visit in a normal year, this is a growing problem.
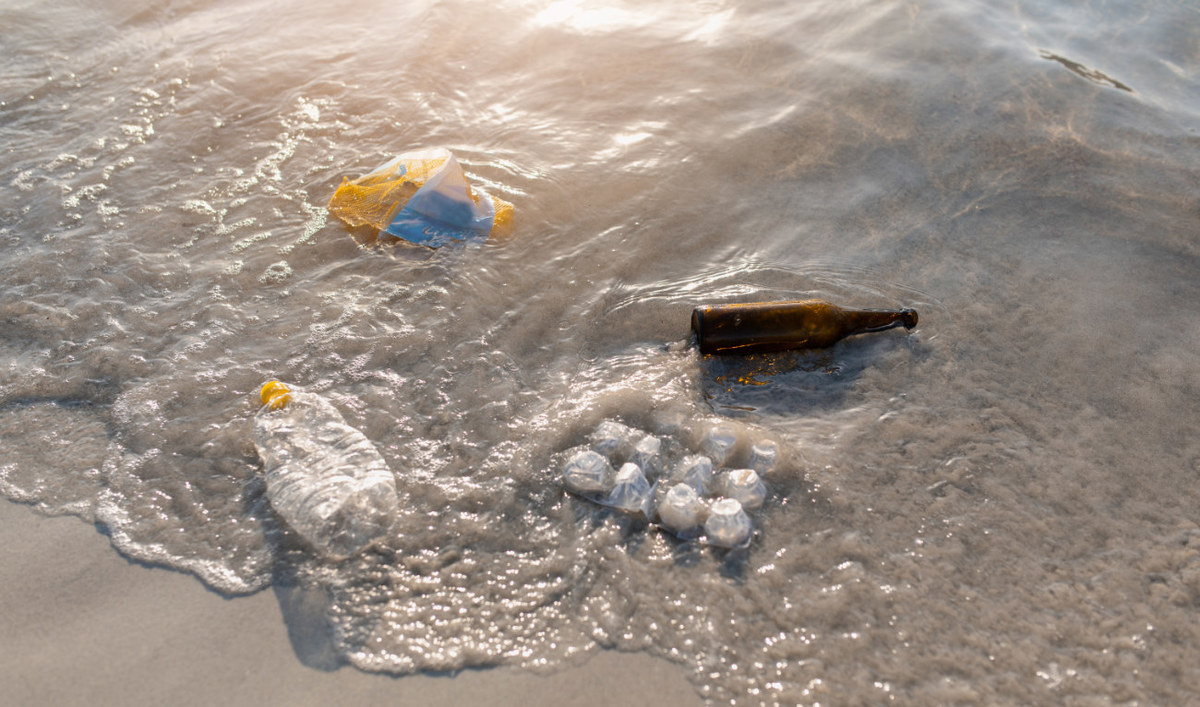

The Mediterranean Sea is in the throes of a man-made environmental crisis. (AFP)
But of all those countries, just one has been singled out as the biggest single source of the problem. The finger of blame is pointing squarely at Egypt, which the IUCN says is responsible for releasing more plastic into the sea than any other nation, and twice as much as the second-worst offender.
According to the IUCN report “The Mediterranean: Mare Plasticum” — Latin for “the plastic sea” — is “widely regarded as one of the most threatened environments in the world” and “is subject to a now ubiquitous, man-made disaster: Plastic pollution.”
The worst offender, says the IUCN, is Egypt, responsible each year for the “leakage” of over 74,000 tons of macroplastics — pieces with a diameter greater than 5 mm — followed by Italy (34,000 tons) and Turkey (24,000 tons).
Together, these three “hotspot” countries contribute more than 50 percent of the 216,269 tons of macroplastics that end up in the Mediterranean Sea each year, overwhelmingly as a result of “mismanaged waste.”
When it comes to microplastics — over 13,000 tons of which finds its way into the sea — Egypt fares little better, ranking second only to Italy (3,000 tons a year), with 1,200 tons. Tyre dust accounts for more than half of the total of microplastics, followed by textiles (33 percent) and the plastic microbeads used in cosmetics (12 percent).
Although bottles and other plastic waste is omnipresent on Mediterranean beaches, most of the polluting plastic is beneath the surface, fouling sediment and disrupting the life cycles of multiple species of fish and aquatic plants.
Perhaps the most shocking statistic is that of the top 100 locations in the Mediterranean basin contributing to the annual leakage of macroplastics, no fewer than 75 are in Egypt, but what is not clear is exactly how much Egypt is actually to blame for the statistics laid at its door.
After all, the Nile watershed, which alone contributes an astonishing 25 percent of the total leakage of plastics into the Mediterranean, is shared by Egypt with 10 other upstream countries, all doing their bit to pollute the mighty river system on its way to the sea.
Marine Moulin, a spokesperson for the Union for the Mediterranean — of which Egypt is a member and whose secretary-general, Nasser Kamel, is a former Egyptian diplomat — said: “Many coastlines have been identified as places in the Mediterranean most polluted with plastic, but as we know the plastic, once in the sea, doesn’t know any borders.”
A spokesperson for the ecological action charity WWF added that “as the Mediterranean is a semi-closed basin, it’s crucial that all countries put in place strong policies to reduce plastic consumption, ensure 100 percent collection of waste and increase recycling and reuse systems.”
Furthermore, “EU countries should support southern Mediterranean countries to increase investments aimed at increasing collection and recycling facilities. At the same time, EU countries should ensure that the countries importing their waste have enough facilities to effectively manage all their waste, internal as well as imported.”
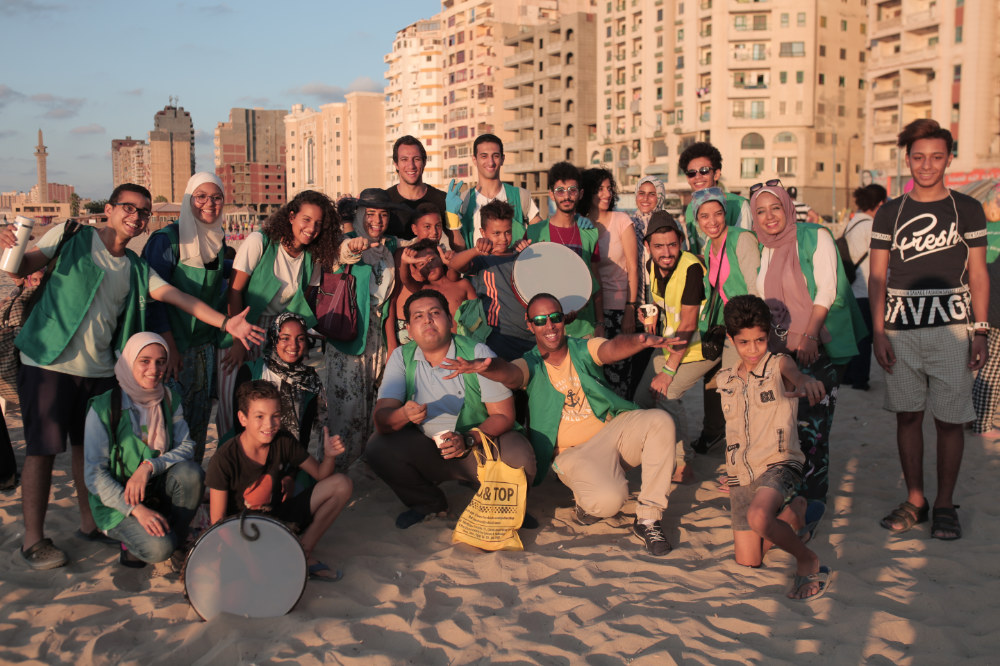

Greenish has organized a number of beach cleanups targeting plastic waste. (Supplied)
It was hardly realistic, added the Union for the Mediterranean, to expect Egypt to deal with the problem singlehandedly, and there is a strong case for wealthier European Mediterranean states, with so much to lose in terms of tourism, to help out their poorer southern neighbors.
“Governments, the private sector, research and financial institutions all need to work collaboratively to redesign processes and supply chains, invest in innovation and adopt sustainable consumption patterns and improved waste management practices to close the plastic tap.”
Egypt is keenly aware of the plastic-pollution problem. Last year, the country’s environment agency said that Egyptians use about 12 billion plastic bags a year, causing “severe problems” in the Nile, the Mediterranean and the Red Sea.
Greenish, a social enterprise running educational activities aimed at achieving sustainable development, has organized a number of beach cleanups targeting plastic waste. Co-founder Shady Khalil said that “Egyptians are becoming more aware of the plastic that we use, and also the littering on the beaches and in the resorts around Egypt.”
Nevertheless, he said, “waste management in Egypt is a work in progress.” He, too, believes northern Mediterranean countries should help Egypt with funding and, equally importantly, should be putting pressure on European companies, such as Nestle and L’Oreal, to reduce the use of plastics in their products.
“During our cleanups we find a lot of these companies’ products, in the Nile and also on the Mediterranean,” Khalil said. “Much of the plastic waste in Egypt belongs to companies from a northern country.”

Mediterranean is “widely regarded as one of the most threatened environments in the world.” (AFP)
In April 2019, Egypt’s Red Sea province, home to some of the country’s most popular tourist destinations, such as the popular diving center Hurghada, announced it was imposing a ban on the use of disposable plastic items, such as straws, plastic bags and cutlery.
And, in a little-publicized side event at last month’s World Conservation Congress, Egypt was one of seven nations (along with France, Greece, Algeria, Morocco, Italy and Monaco) behind a new initiative, “The Mediterranean: A model sea by 2030,” which aims to “end overfishing, limit plastic pollution and develop sustainable maritime transport by 2030.”
But the crisis in plastics is not Egypt’s only environmental problem, and far from its most pressing. The environmental challenges facing the country are legion, with many demanding urgent action and at least one posing an existential threat.
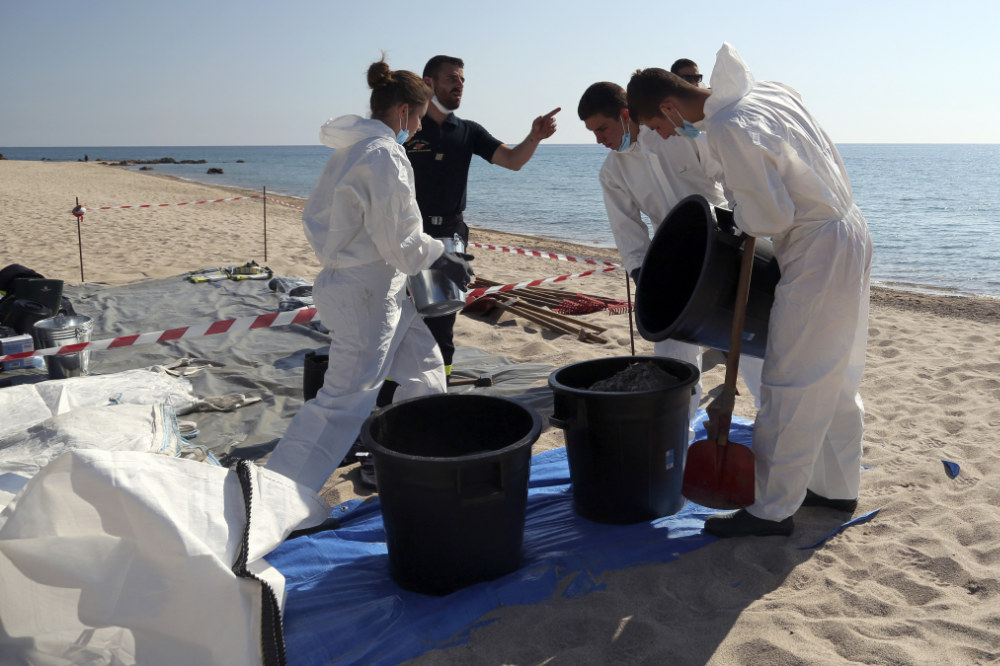

Plastic waste is a growing problem for the 21 countries that share the 28,000 km Mediterranean coastline. (AFP)
Top of the crisis list is Egypt’s chronic water shortage, a worsening problem as populations in the 10 rapidly developing upstream nations along the Nile multiply, placing increasing demands on the finite flow of the river.
Egypt is rapidly heading toward what the UN defines as “absolute water scarcity,” the point at which the annual water supply for each person drops below 500 cubic meters. With only 20 cubic meters of water available from internal resources, Egypt’s population and all-important agricultural industry is utterly dependent on the Nile for its freshwater and, says the UN, the country is on course to hit absolute water scarcity by 2024.
Coastal erosion and the gradual sinking of the Nile delta is another problem, closely related to the increasingly impossible demands being placed on the river.
Part of the problem is the rising level of the Mediterranean, predicted to only accelerate as a consequence of climate change. But scientists have also found that the Nile delta, which on average is only one meter above sea level, is slowly sinking, thanks in large part to the reduction in the amount of sediment deposited in the delta as a consequence of the reduced flow of Nile water.
Other environmental problems are clamoring for the government’s attention. In August, the country was hit by an unusually fierce heatwave, which the Egyptian Meteorological Authority attributed to climate change, and the country continues to struggle with the seasonal curse of the “Black Clouds,” the recurring annual smog that gathers over its cities between September and November.
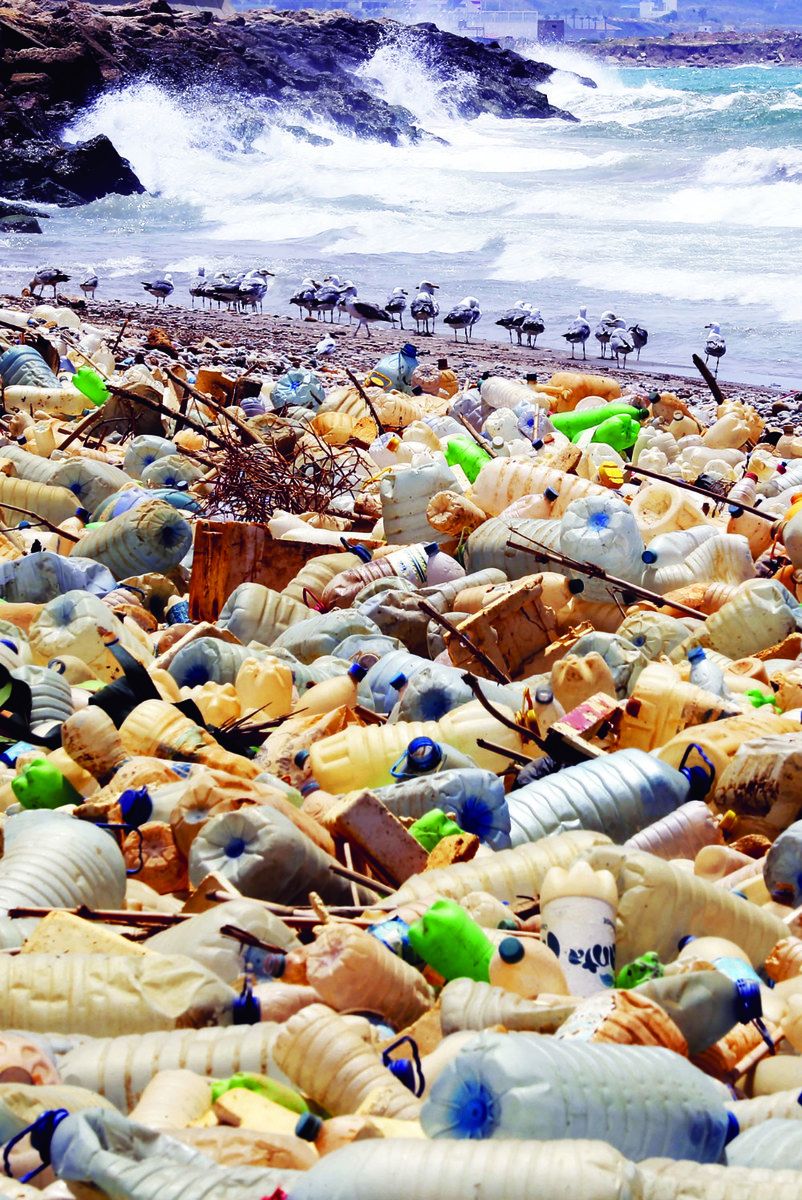

Most of the polluting plastic is beneath the surface, fouling sediment and disrupting the life cycles of multiple species of fish and aquatic plants. (AFP)
A breakdown by the Environment Ministry of the causes of the phenomenon gives an idea of the multiple issues the government must tackle if it is to make progress toward its climate goals. The burning of farming waste accounts for 42 percent of the problem, factory emissions 23 percent, vehicle exhaust fumes 23 percent and the municipal burning of waste 12 percent.
Climate change is, of course, at the top of everyone’s agenda, but even for this there is only so much money to go round.
When the 42 member countries of the Union for the Mediterranean met to discuss environmental issues and climate action in Cairo on Oct. 5, the main focus was on the failure of developed nations to make good on the pledge they made back in 2009 to allocate $100 billion a year, up to 2020, to help developing countries tackle the climate crisis.
Regardless, at that same meeting Egypt’s environment minister committed her government to “greening” half of its programs by 2024. This is an enormous task, given the current volume of Egypt’s CO2 emissions and general levels of pollution.
It was announced in October that Egypt wants to host next year’s COP27 session of the UN Climate Change Conference in Sharm El-Sheikh — great news for the hotels and restaurants of the Red Sea resort town, which were hard hit by the loss of tourism to the global pandemic.
But hosting the world’s leading climate-change event will cast a harsh light on the multiple environmental challenges facing Egypt. As Cairo intensifies its focus on these ahead of COP27, the hope is that the plastic-pollution crisis lurking beneath the surface of the Mediterranean will rise to the top of the government’s green agenda.
Twitter: @JonathanGornall

























