WATERLOO, Canada: As the last US troops departed Kabul on Aug. 31, drawing 20 years of war in Afghanistan to a dispiriting end, Taliban commanders were quick to declare victory. Little did they know, amid their jubilation, that a new and much more complex battle was about to begin.
It is often said it is easier to acquire power than it is to hold on to it. After conquering the capital, Kabul, during a lightning-fast summer offensive, the victorious Taliban now faces the gargantuan task of reviving the economy while addressing a worsening food crisis, fighting a Daesh insurgency and healing a rift within its own ranks.
Addressing these simultaneous challenges will be no easy feat. The US, the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund have severed Kabul’s access to more than $9.5 billion in loans, funding and assets, hobbling the new regime.
At the same time, and despite its best efforts to the contrary, the Taliban has also failed miserably in its attempt to gain international recognition as the official government of Afghanistan, leaving the country precariously isolated.
“The real risk for the Taliban is to remain unrecognized by the international community, just like the last time they were in power, from 1996 to 2001,” Torek Farhadi, who was an adviser to Afghanistan’s former president, Hamid Karzai, told Arab News. “This would not be good for the Taliban and it would not be good for the millions of Afghans.”
Indeed, without international recognition and access to capital, the Taliban cannot fulfill its promises of development.
“It would put a stop to the region’s hopes for economic collaboration,” Farhadi said. “Both Central Asia and Pakistan’s plans for economic integration will remain in jeopardy, as the necessary financing from international institutions to upgrade and invest in Afghan infrastructure will remain on hold.”
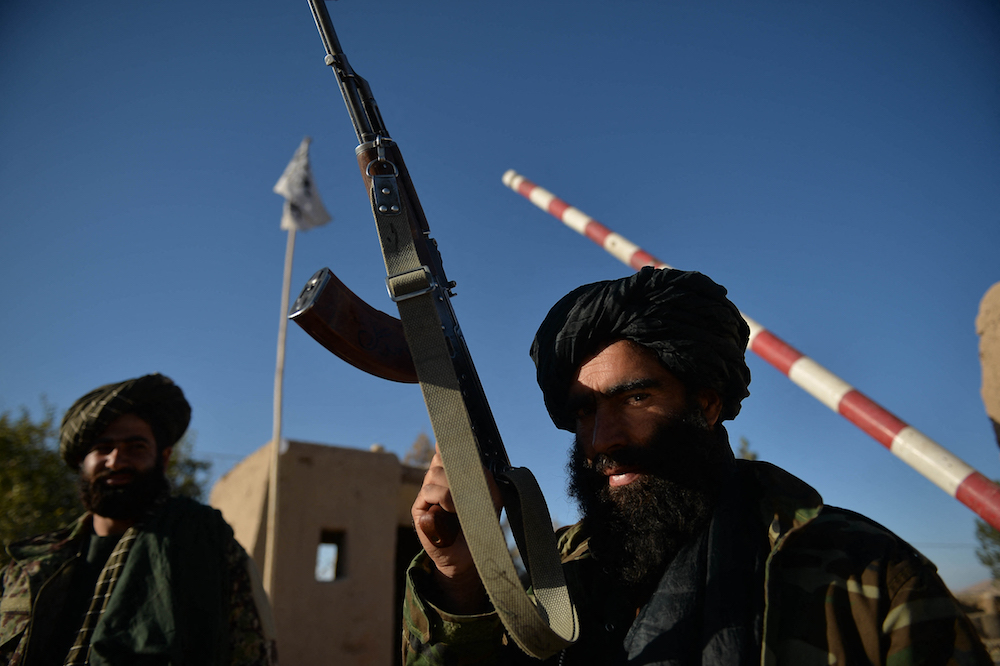

Taliban fighters stand guard at a police station gate in Ghasabha area in Qala-e-Now, Badghis province on October 14, 2021. (AFP/File Photo)
Against this backdrop, Muslim nations pledged on Sunday to set up a fund to help Afghanistan avert an imminent economic collapse they say would have a “horrendous” global impact.
At a special meeting in Pakistan of the 57-member Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), delegates also resolved to work with the United Nations to try to unlock hundreds of millions of dollars in frozen Afghan assets.
The promised fund will provide humanitarian aid through the Islamic Development Bank (IDB), which would provide a cover for countries to donate without dealing directly with the country’s Taliban rulers.
For ordinary Afghans, the return of the Taliban has been a double-edged sword. On the one hand it eliminated the corrupt warlords who had long treated whole tracts of the country as their own private fiefdoms. It has also made the country more secure overall.
On the other hand it has turned back the clock 20 years on personal freedoms and civil liberties.
As a result, tens of thousands of Afghans are now trying to leave the country, following in the footsteps of more than 123,000 civilians who were evacuated from Kabul airport by US forces and their coalition partners in August.
In mid-November, the Norwegian Refugee Council reported that about 300,000 Afghans have fled to neighboring Iran since August and up to 5,000 continue to illegally cross the border every day.
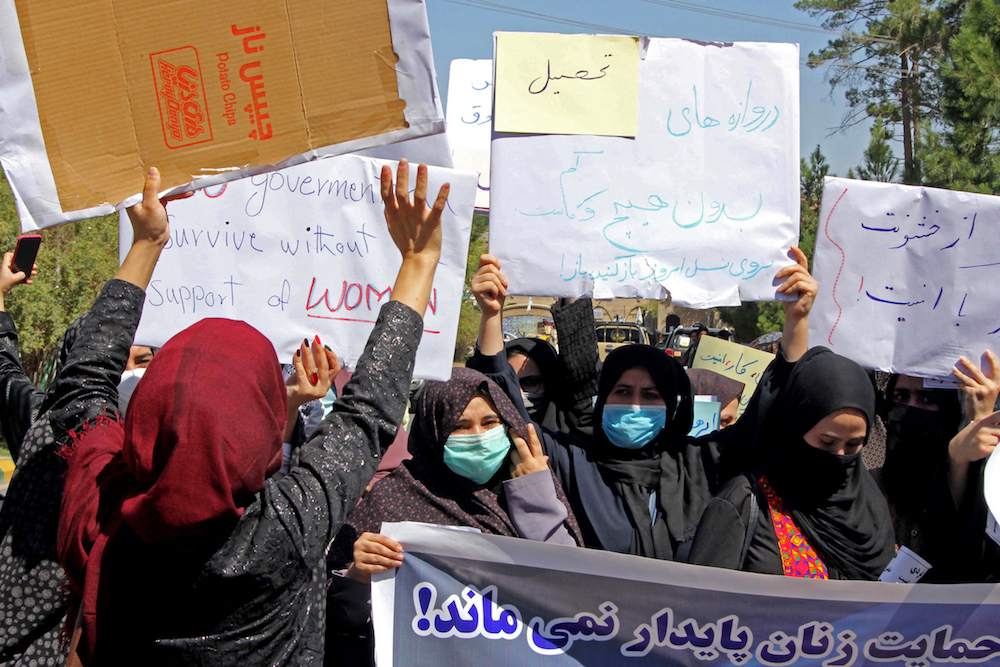

Defiant Afghan women held a rare protest on Sept. 2 saying they were willing to accept the burqa if their daughters could still go to school under Taliban rule. (AFP/File Photo)
One of the primary reasons for this mass exodus, and the Taliban’s ongoing isolation, is the group’s ultraconservative views on women, ethnic minorities and freedom of expression.
“The Taliban have defeated their rivals militarily, but on the political, social, economic and academic fronts, they have failed Afghanistan tremendously,” Ahmad Samin, a former World Bank adviser based in the US, told Arab News.
“They have not earned the support of Afghans and the international community. They have established the government of the Taliban, by the Taliban, for the Taliban. They want recognition with minimum commitments but I do not think the international community will compromise in this regard.”
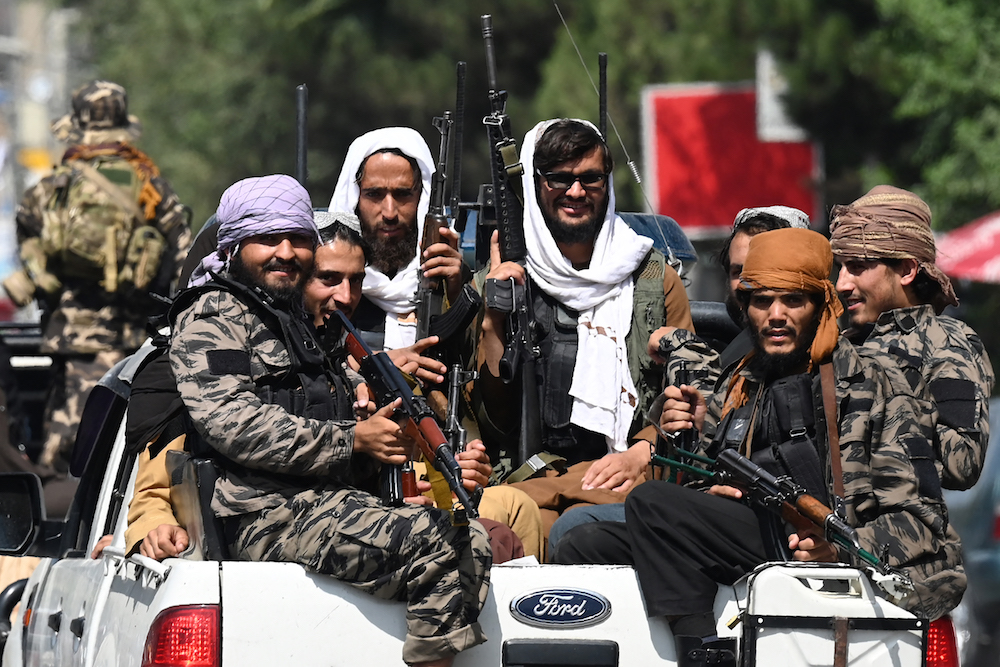

Taliban fighters patrol on vehicles along a street in Kabul on September 2, 2021. (AFP)
As a result of its isolation, Afghanistan finds itself on the brink of humanitarian catastrophe. With foreign exchange reserves depleted, granaries empty, hospitals running out of drugs, and international aid reduced to barely a trickle, ordinary Afghans face a winter of hunger and misery.
What is more, without foreign capital to pay for electricity from neighboring countries, Kabul and other major cities are likely to face rolling blackouts.
INNUMBERS
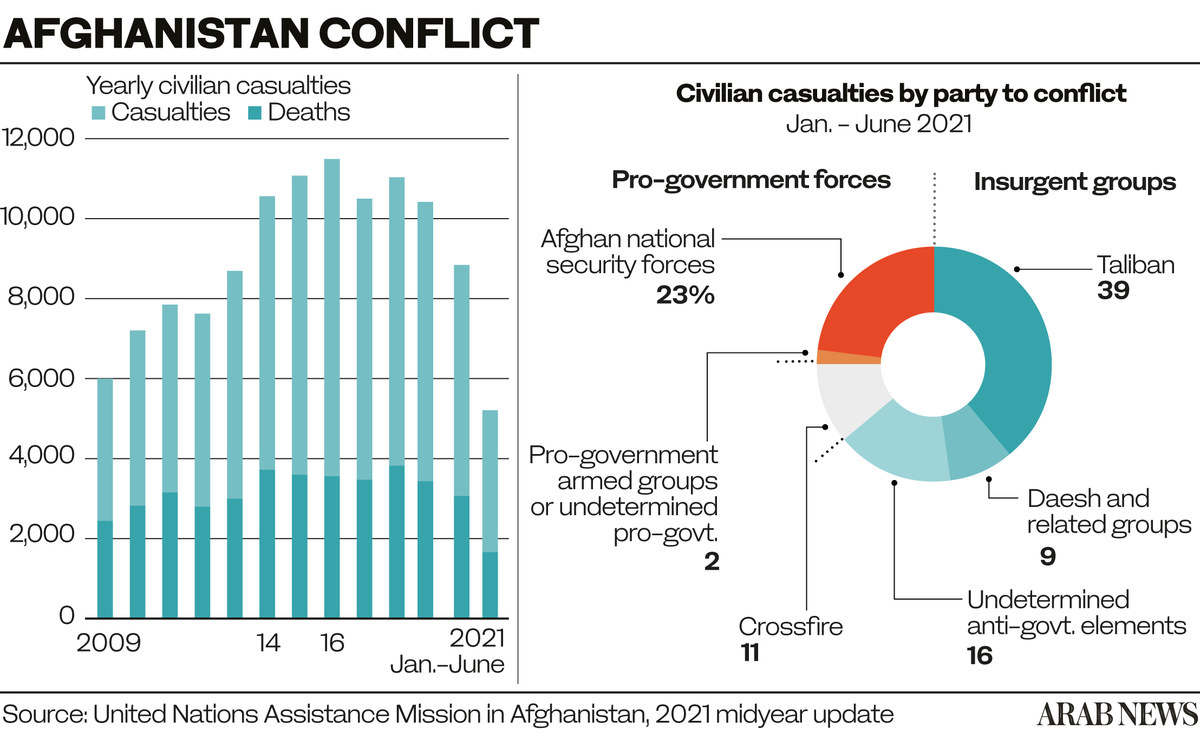
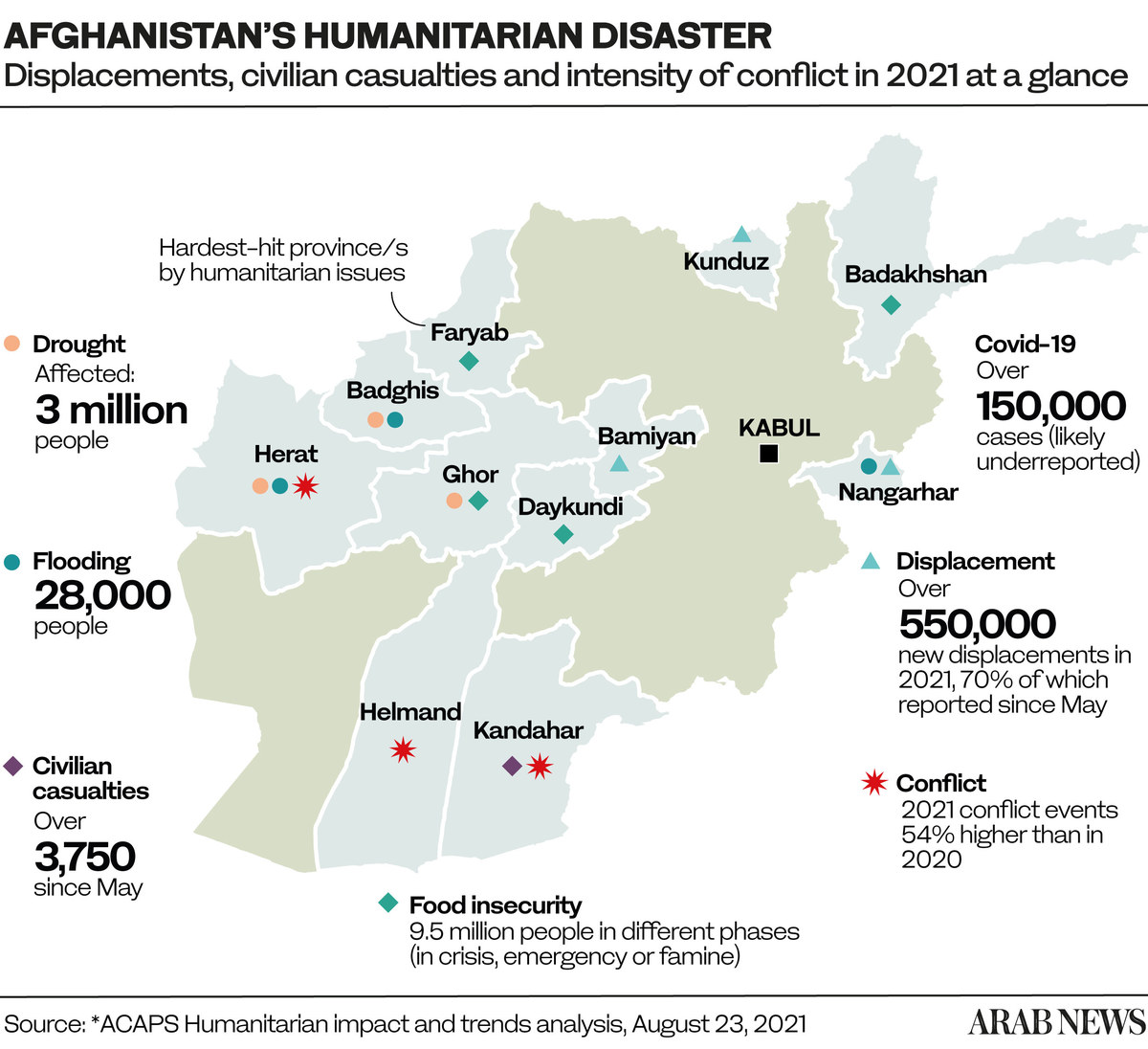
* 3,750 civilian casualties since May 2021.
* 9.5 million people with food insecurity.
In a report from the city of Bamiyan in central Afghanistan last month, headlined Afghans facing “hell on earth” as winter looms, John Simpson of BBC News wrote: “Before the Taliban took power in Afghanistan in August, there was confidence that the government of President Ashraf Ghani would be able to cope with the threat of a bad winter, given the help of the international community. That help evaporated when Mr. Ghani’s government collapsed.
“Western countries have cut off their aid to the country, since they don’t want to be seen to help a regime which bars girls from education and is in favor of reintroducing the full range of Sharia punishments.”
Speaking to Arab News, Taliban spokesman Ahmadullah Wasiq conceded that Afghanistan faces dire economic and health challenges, but blamed the crisis on the loss of aid and the freezing of the country’s assets.
On Nov. 17, the Taliban’s foreign minister, Amir Khan Muttaqi, wrote an open letter to the US Congress warning that there would be a mass exodus of refugees from Afghanistan unless Washington releases the country’s assets and lifts sanctions.
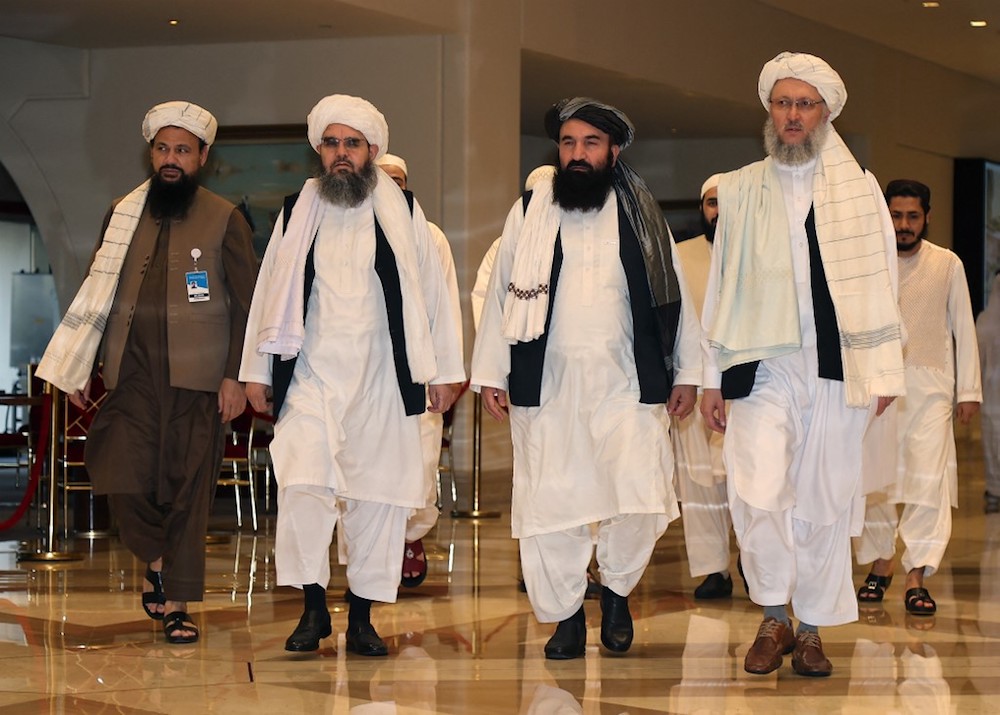

Head of the Taliban delegation Abdul Salam Hanafi (R), accompanied by Taliban officials (2R to L) Amir Khan Muttaqi, Shahabuddin Delawar and Abdul Latif Mansour, walks down a hotel lobby during the talks in Qatar's capital Doha in August 2021. (AFP/File Photo)
“Currently the fundamental challenge of our people is financial security and the roots of this concern lead back to the freezing of assets of our people by the American government,” he wrote.
But with no sign that the Taliban is ready to change its ideological course, UN officials said Afghanistan is hurtling toward disaster.
“The Afghan people now feel abandoned, forgotten and, indeed, punished by circumstances that are not their fault,” Deborah Lyons, the UN secretary-general’s special representative for Afghanistan, told delegates in New York last month.
“To abandon the Afghan people now would be a historic mistake — a mistake that has been made before, with tragic consequences.”
David Beasly, executive director of the World Food Program, said about 23 million Afghans are on the brink of starvation, a challenge the aid community is ill-equipped to address.
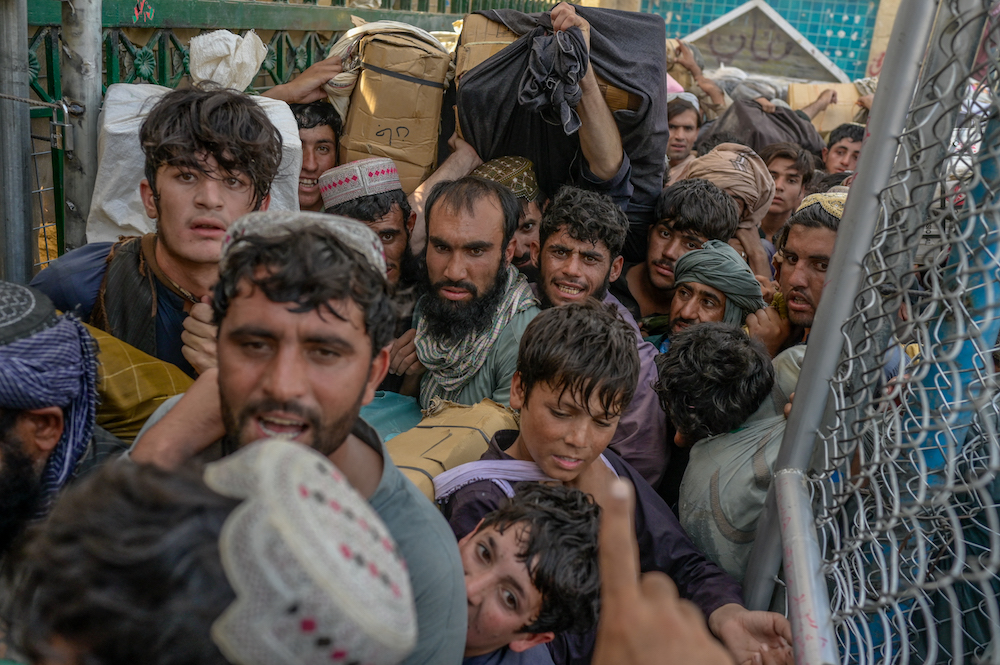

Thousands of Afghans trying to escape the misery at home have flocked to their country's southern border with Pakistan, but their attempts to get across have been stopped by the Taliban. (AFP)
“WFP does not have the money we need to feed them. We have to choose who eats and who doesn’t,” he said in a video message posted on Twitter last month. “How many children must starve until the world wakes up? None of these children should die.”
Nikolai Patrushev, the secretary of Russia’s Security Council, said the situation in Afghanistan is becoming critical and warned that the country could slide back into civil war unless the Taliban and the international community reach an agreement.
“The situation unfolding today in Afghanistan is unprecedented both in military-political and socioeconomic terms,” Patrushev said last month.
“If the new authorities in Kabul fail to normalize the situation, and the international community fails to provide effective support to the Afghan people, the scenario could become catastrophic, involving a new civil war, the general impoverishment of the population, and famine.”
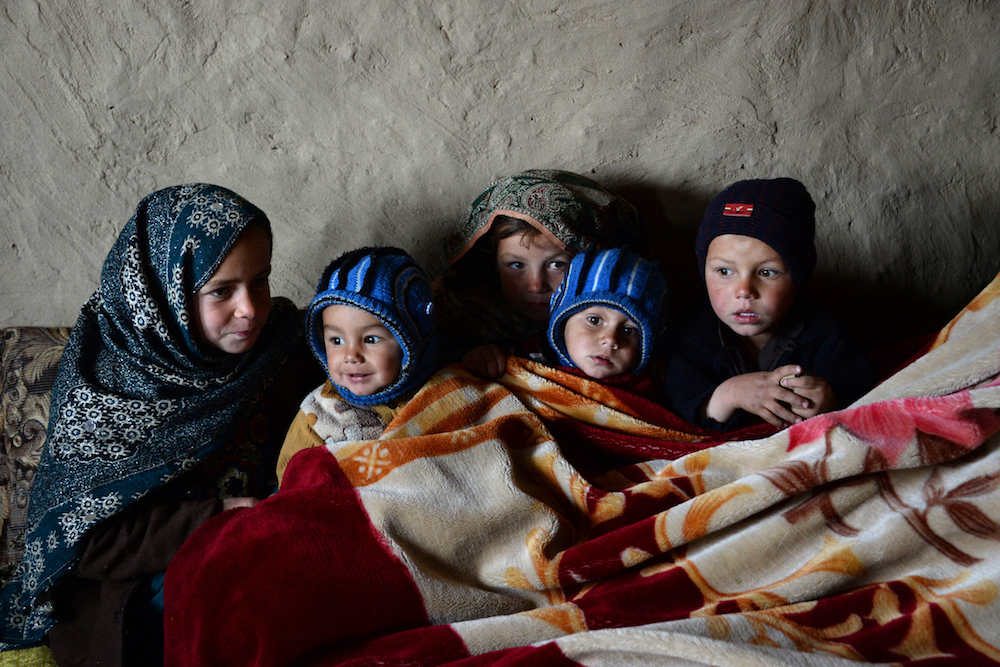

Afghan children warm themselves with a blanket inside a mud house at a refugee camp on the outskirts of Laghman. (AFP/File Photo)
Kamran Bokhari, the director of the US think tank Analytical Development, agrees that the Taliban faces a serious dilemma which, in the absence of a compromise, could plunge the country into a new conflict.
“The Taliban need the world to provide financial assistance, hence the feverish effort to convince the world that the Taliban are pragmatic, despite being a radical Islamist entity,” Bokhari told Arab News. “But the Taliban cannot be both at the same time. The Taliban have to change but can’t without causing internal ruptures. Therefore, we are looking at more conflict.”
Farhadi agrees that the Taliban faces the prospect of internal strife and challenges to its power unless it can urgently resolve this dilemma and remove the barriers to its economic salvation.
“These are the risks for Afghanistan; they are real,” he said. “The Taliban refuses to recognize the link between extreme poverty and political instability in Afghanistan. The risks caused by extreme poverty are real. The Taliban risks new violence in the face of instability and risks losing control.”

























