DUBAI: 2021 could go down in history as the that year when climate change made the transition from being mainly the concern of youthful activists to becoming a real and present threat for all of us, and especially for the Middle East.
The climate change agenda accelerated throughout the year, fanned by a background of raging forest fires in, for example, Australia and Turkey, extreme and fatal summer heat on the US Pacific coast, deadly floods in central Europe and South Asia, and rampaging tornadoes in the US Midwest.

Ginny Watts (C) hugs her friend as they help cleaning her destroyed home in Dawson Springs, Kentucky, on Dec. 14, 2021, four days after tornadoes hit the area. (AFP)
Each new climate disaster was received as proof, if any more were needed, of the seriousness of the climate situation; each fresh extreme event chipped away at the convictions of the deniers.
Perhaps no one better illustrates the changing sentiment on climate change better than Mark Carney. A former executive at giant US bank Goldman Sachs and governor of the Bank of England, Carney is now a UN special envoy on finance and climate change.
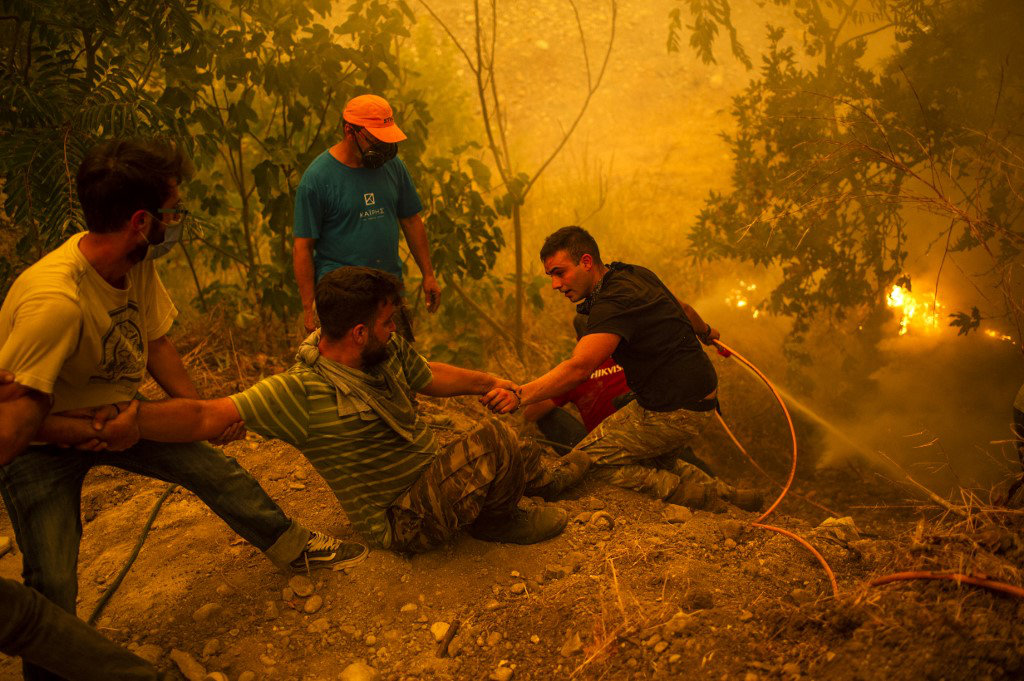

Local residents fight the wildfire in the village of Gouves on Evia (Euboea) island on August 8, 2021. (AFP)
At COP26 in Glasgow in November, he was received as a hero by environmentalists. He declared: “Finance is becoming a window through which ambitious climate action can deliver a sustainable future that people all over the world are demanding.”
And it is not just Carney. Politicians of all persuasions, multi-billion-dollar investment fund executives, and even the bosses and owners of the global oil industry — the producers of the “fossil fuels” the activists love to hate — are increasingly vocal and assertive in their demands that “something” has to be done about global warming.
One key event of 2021 was the publication in August of the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report, which — in language verging on the apocalyptic — set the tone for much of the debate for the rest of the year.

“Many of the changes observed in the climate are unprecedented in thousands, if not hundreds of thousands of years, and some of the changes already set in motion — such as continued sea level rise — are irreversible over hundreds to thousands of years,” the report said.
The authors had no doubt as to the reason for these changes.
“Emissions of greenhouse gases from human activities are responsible for approximately 1.1 degrees Celsius of warming since 1850-1900. Averaged over the next 20 years, global temperature is expected to reach or exceed 1.5 degrees Celsius of warming,” it concluded.
The Paris Agreement of 2015 set a goal of “less than 2 degrees Celsius” by 2050 if the planet were to have any chance of avoiding catastrophic warming. Now the experts have said that there was little chance that could be met.
That presents a unique challenge for the hydrocarbon-producing countries of the Arabian Gulf. Oil and gas production has been responsible for the huge advances in economic and lifestyle well-being in the region, but at the same time the abundance of hydrocarbon fuels has led to inefficient use of these fuels.
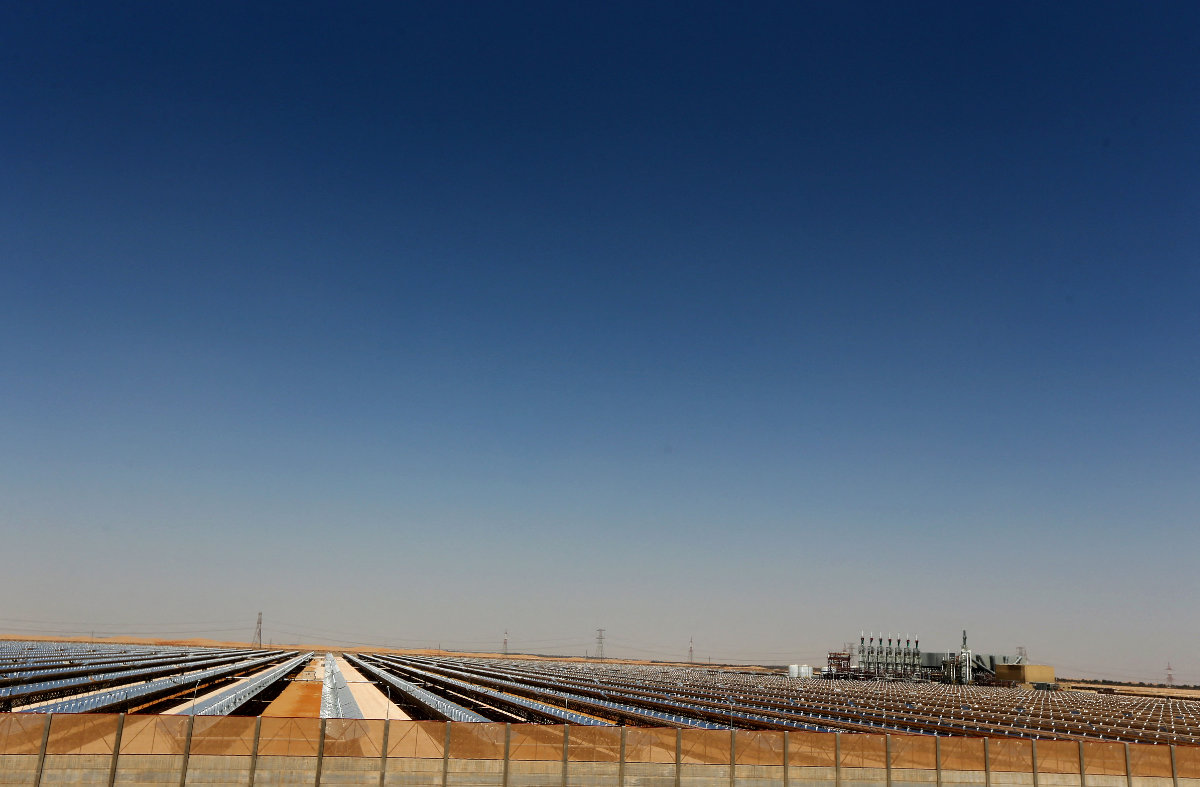

A general view shows the Shams 1, Concentrated Solar power (CSP) plant, in al-Gharibiyah district on the outskirts of Abu Dhabi, UAE. (AFP)
Gulf countries — which in the past had no second thoughts about burning oil to generate electricity — have among the highest per capita carbon footprints in the world.
The possible repercussions were highlighted in some new research by the Saudi-based energy think tank Aeon Collective. Global warming in the Gulf could lead to extreme and fatal heatwaves, a jump in atmospheric pollution and threats to public health from previously unknown diseases. It could even threaten the annual Hajj pilgrimage to Makkah, one of the fastest-warming cities in the Kingdom.

An extreme climate change could even threaten the annual Hajj pilgrimage to Makkah, one of the fastest-warming cities in the Kingdom. (SPA file photo)
Fortunately, regional policymakers appear to have developed an enhanced awareness of the specific dangers to the region’s economy and public health from global warming.
For one thing, the Vision 2030 strategy is aimed specifically at reducing Saudi Arabia’s dependence on fossil fuels — alongside similar strategies in the UAE and other GCC states.
But the Kingdom went a significant step further in October with the launch of two major initiatives designed to show that it was playing a leadership role in the global campaign against climate change.

A view of the Saudi capital, Riyadh. (AN file photo)
When Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman announced the Saudi Green and Middle East Green Initiatives at a special event in Riyadh, it was a landmark event in the region. Not only did it contain a goal for Saudi Arabia to reach net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2060, but it also stepped up the amount of harmful emissions that would be reduced under the nationally determined contributions schedule agreed with the UN and climate bodies.
In addition, the Kingdom pledged to eliminate oil from the domestic power generation cycle completely by 2030, replacing it with cleaner gas and renewables. Multi-billion-dollar investment programs to plant trees in the Kingdom were also launched, among other environmentally sound strategies.
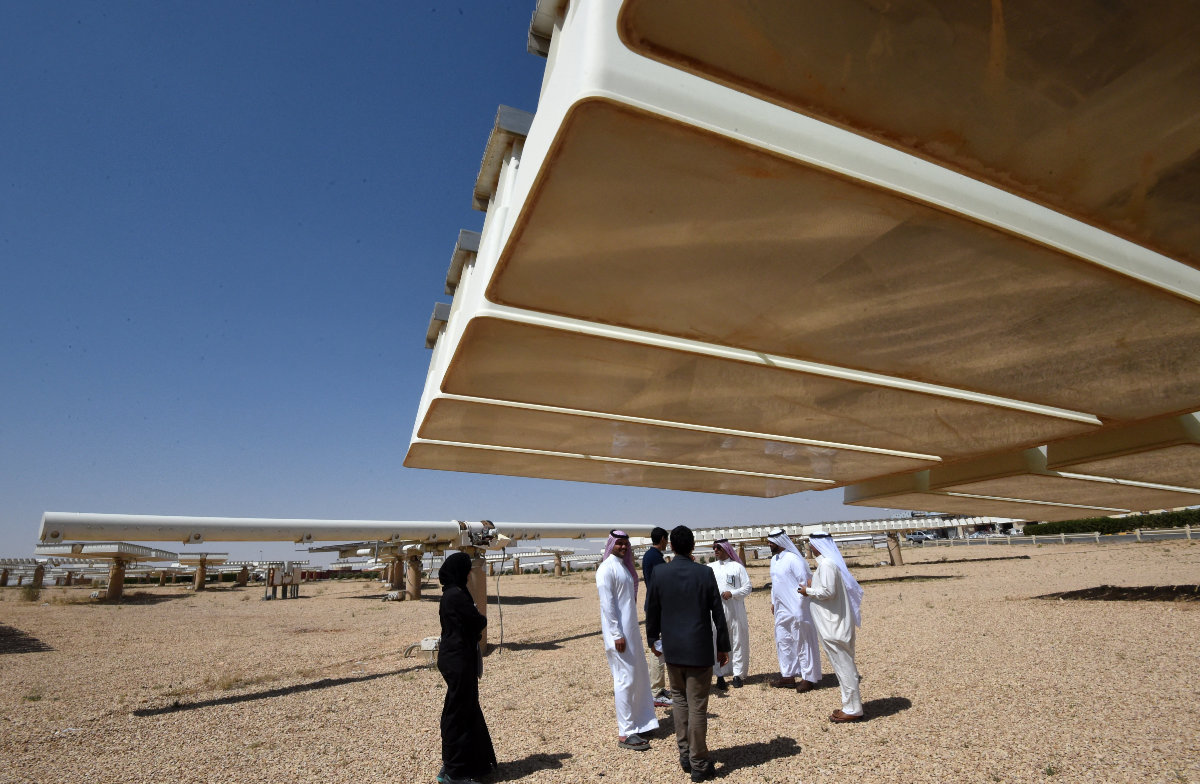

A general view shows the solar plant in Uyayna, north of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, on March 29, 2018. (AFP)
Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman, the Kingdom’s energy minister, underlined the seriousness of the campaign against global warming. “It is most daunting challenge that we are faced with. We have, I think, the most humane initiative that we could ever come up with, and we’re willing to enlarge it if everybody wants to enlarge it. I’m sure that people have noticed that we have been repositioning ourselves,” he said at the Future Investment Initiative in Riyadh in October.
These developments in the Middle East set the stage for the decisive climate change event of the year: COP26 in Glasgow, the annual gathering of energy policymakers, experts and activists. Expectations were high that the Glasgow gathering could lead an advance against climate change of comparable significance to the Paris meeting six years earlier.
Two weeks of intense negotiations eventually produced what became know as the Glasgow Climate Pact. This fell short of a commitment to a hard 1.5 degrees Celsius target by 2050 and resisted some of the wilder calls from the extreme environmentalists for an end to fossil fuel investment and production, but had enough for everybody to claim COP26 as a success.
“The Pact charts a course for the world to deliver on the promises made in Paris,” was the verdict of Alok Sharma, the UK president of COP26.
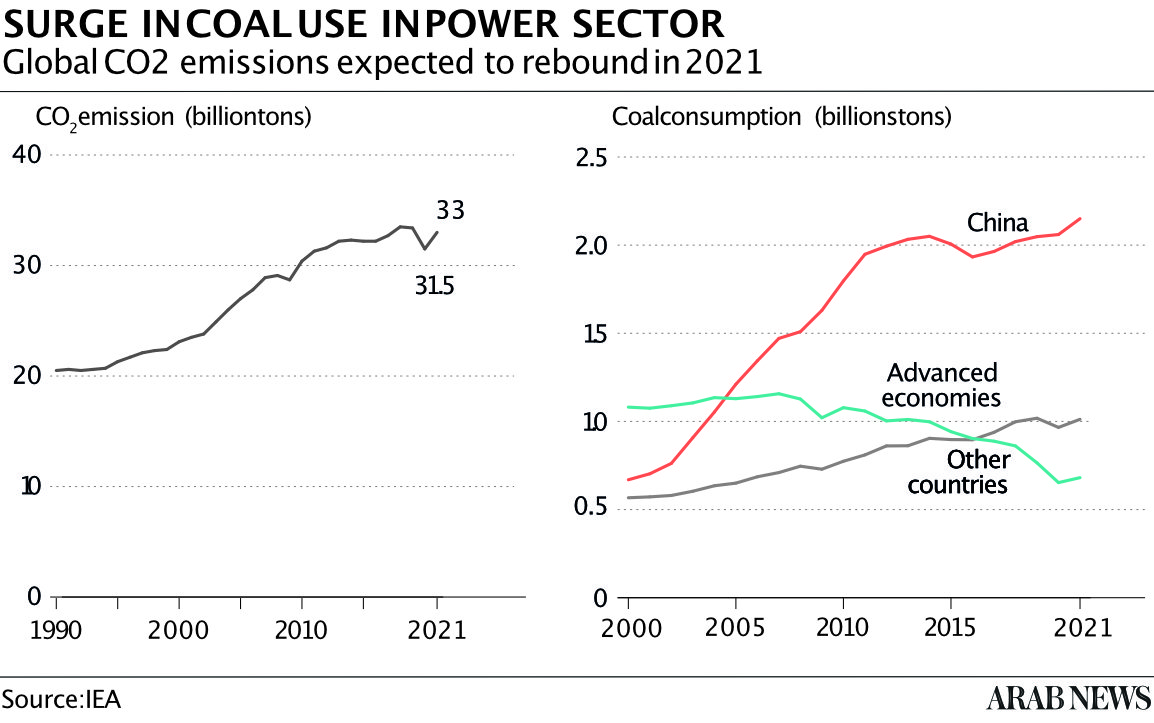
Some were disappointed that there was no commitment to “phasing out” coal as a fuel source, but — with the Glasgow event taking place in the middle of an energy crisis in which every ton of hydrocarbon was needed — the general feeling was that it was good enough, especially in view of the coal-burning necessity in places like India and China.
A few days after the COP26 delegates had departed, a rather different energy forum convened in the UAE capital, Abu Dhabi. ADIPEC is one of the biggest oil and gas gatherings in the world, but is definitely an industry event. There were no parties of Amazonian natives among the delegates there.
However, attendees noted a distinct empathy between COP26 and ADIPEC21. Badar Chaudry, senior vice president for the energy sector at UAE bank Mashreq, said: “There was enough overlap in the agendas and outcomes of both events to reach the conclusion that there is a consensus that climate change is the big issue facing the world today, and that the hydrocarbon industry has recognized that and is stepping up to play its part.”

Saudi Aramco's Shaybah plant in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. (Supplied)
For the Middle East, the climate change challenge gets very real indeed from now on. COP27 will take place next year in Cairo, and COP28 is earmarked for the UAE in 2023.
The two biggest oil producers in the region — Saudi Arabia and the UAE — are set to increase oil production in the years ahead to fuel economic growth and take advantage of their low production costs at a time of rising prices.
How they can square this strategy with the self-declared aim of reducing emissions will be a key focus for the next couple of years.
























