NEW YORK CITY: Although the world is understandably preoccupied with the coronavirus pandemic, climate change, and regional conflicts, it would be wrong to assume that the threat of nuclear war had vanished. In fact, the probability of nuclear annihilation remains perilously high.
At the beginning of the year, the pandemic claimed yet another casualty — the 10th Review Conference of the parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, which had been scheduled to take place on Jan. 4.
The postponement of the meeting until August went largely unreported at the time because, it would appear, the perceived threat posed by nuclear weapons had lost its urgency in recent decades.
However, the development came as tensions escalated between Western countries and Russia over Ukraine as well as between the US and China over Taiwan.
The non-proliferation treaty, or NPT, which forms the foundation of the non-proliferation regime, was signed in 1968 and came into force in 1970. It is the single most important instrument that the 191 states-parties have to prevent further proliferation and lead the world toward total disarmament.
The bargain that underpins the NPT is very simple: The nuclear states under the treaty commit to reduce their nuclear arsenals with the ultimate goal of eliminating them, and the non-nuclear states adhere to their commitments enshrined in the treaty to not acquire nuclear weapons.
Not everyone has adhered to this. India, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea are not signatories, while Iran, although an NPT signatory, is nevertheless enriching uranium and is locked in a battle with the West over its nuclear program.
It is the second time the 10th RevCon has been rescheduled due to the pandemic. The 2020 conference, which would have coincided with the NPT’s 50th anniversary, was also delayed, scuttling hopes of getting the non-proliferation regime back on track and breathing new life into the arms control and disarmament process.

Iran, although an NPT signatory, is nevertheless enriching uranium and is locked in a battle with the West over its nuclear program. (AFP/File Photo)
The three pillars of the NPT — non-proliferation, disarmament, and the peaceful use of nuclear technologies — have seen varying degrees of success.
While the non-nuclear states kept their end of the bargain and adhered to the treaty, bar a couple of exceptions, the nuclear states have been less faithful. They have not fulfilled their obligations, as stipulated by article six of the NPT, to rid the world of nuclear weapons. This has led to tensions and placed a strain on the whole non-proliferation regime.
Looking for an alternative, the non-nuclear states pushed for a process in the UN General Assembly, which culminated in the adoption of a Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons on July 7, 2017, coming into force on Jan. 22, 2021.
However, the conference’s postponement could not have come at a worse time, as anxiety over the fraying of the architecture of arms control is mounting.
Experts believe the risk of nuclear war is greater than ever. The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists has set its Doomsday Clock at 100 seconds to midnight — the closest the timepiece has been to symbolic doom in its more than 70 years of its existence.
FASTFACTS
* With 191 signatories, the NPT is the world’s most widely ratified nuclear arms control agreement.
* The NPT Review Conference was supposed to start on Jan. 4 at the UN HQ.
* Review conferences, to take stock of compliance and commit to further steps, are supposed to happen every 5 years.
* The postponed 10th Review Conference was initially scheduled to start in April 2020.
A speech by former US Senator Sam Nunn, an authority on nuclear weapons, on the 50th anniversary of the NPT in 2020 described the danger in stark terms.
“We are moving into an era of enhanced nuclear risk,” he said, as a result of the “stalled progress on North Korea, the uncertain future of the Iran agreement and their nuclear program, the continued failure to bring the Comprehensive Test-Ban Treaty into force, and the understandable frustration by the non-nuclear states about the slow pace of nuclear disarmament.”
Today, even as the pandemic rages, nuclear states have continued to modernize and upgrade their arsenals. According to the International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons, the world’s nine nuclear states spent $72.6 billion on modernizing their arsenals in 2020 — up $1.4 billion on 2019 spending. In doing so, many of these states have violated the NPT.
The Stockholm International Peace Institute has estimated that the world’s nuclear states collectively possessed approximately 13,080 nuclear weapons as of January 2021. That figure represented a small decrease on the 13,400 estimate of 2020.
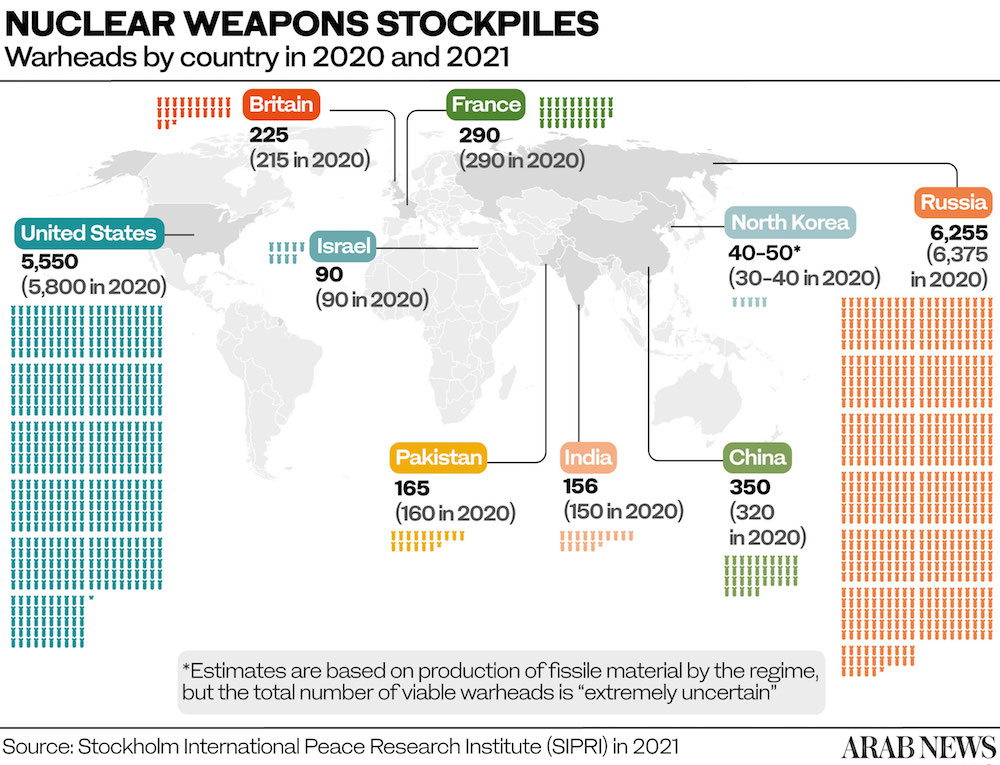

However, this has been offset by the increase in the number of nuclear weapons deployed with operational forces, from 3,720 in 2020 to 3,825 in 2021. Of these, around 2,000 were “kept in a state of high operational alert,” the institute said in its 2021 report.
All of this has occurred in the absence of a credible arms control process because of growing tensions between the US and Russia over Ukraine, and America and China over Taiwan, Hong Kong, and the Indo-Pacific.
Although they were disappointed by the conference postponement, the non-nuclear states were heartened on Jan. 3 when the US, Russia, China, France, and the UK, a group of powers known as the P5, put out a joint statement claiming they “consider the avoidance of war between nuclear-weapon states and the reduction of strategic risks as our foremost responsibilities.
“We affirm that a nuclear war cannot be won and must never be fought. As nuclear use would have far-reaching consequences, we also affirm that nuclear weapons — for as long as they continue to exist — should serve defensive purposes, deter aggression, and prevent war. We believe strongly that the further spread of such weapons must be prevented.”
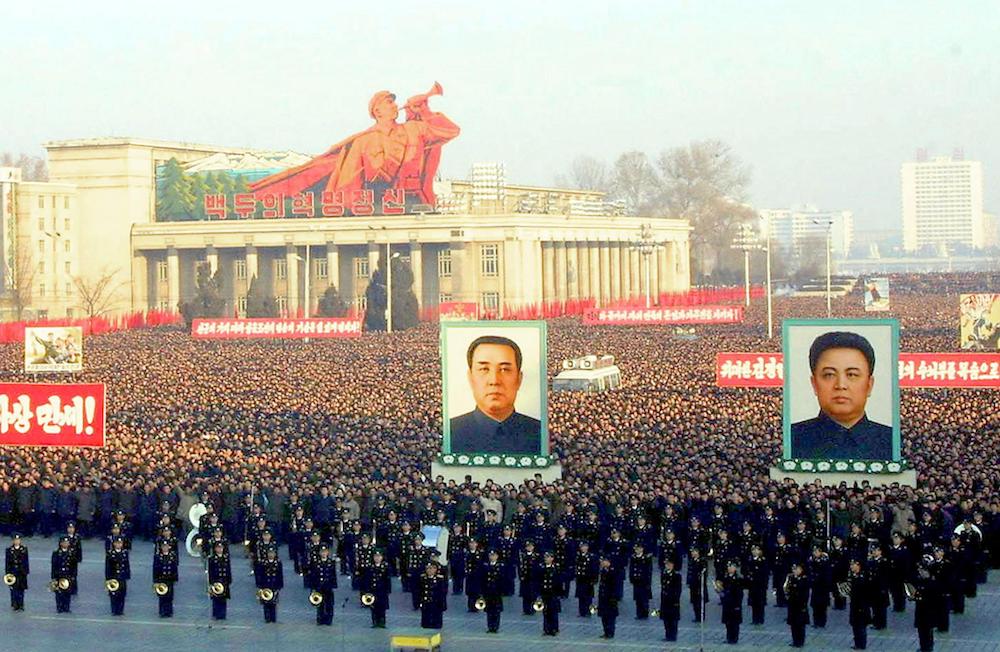

More than one million people gathered on Kim Il Sung Square in Pyongyang 11 January 2003, to hear political leaders hail North Korea's dramatic decision to withdraw from the nuclear non-proliferation treaty (NPT). (AFP/File Photo)
They also committed to “maintain and further strengthen our national measures to prevent unauthorized or unintended use of nuclear weapons.”
Perhaps most importantly, they reaffirmed their commitment “to our Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty obligations, including our Article VI obligations to pursue negotiations in good faith on effective measures relating to cessation of the nuclear arms race at an early date and to nuclear disarmament, and on a treaty on general and complete disarmament under strict and effective international control.”
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres, said he was “encouraged” by the commitments voiced by the nuclear states “to pursue measures to prevent nuclear war,” with the added caveat that “the only way to eliminate all nuclear risks is to eliminate all nuclear weapons.”
Non-proliferation groups and experts also applauded the joint statement, but want to see the nuclear powers take genuine, concrete action.
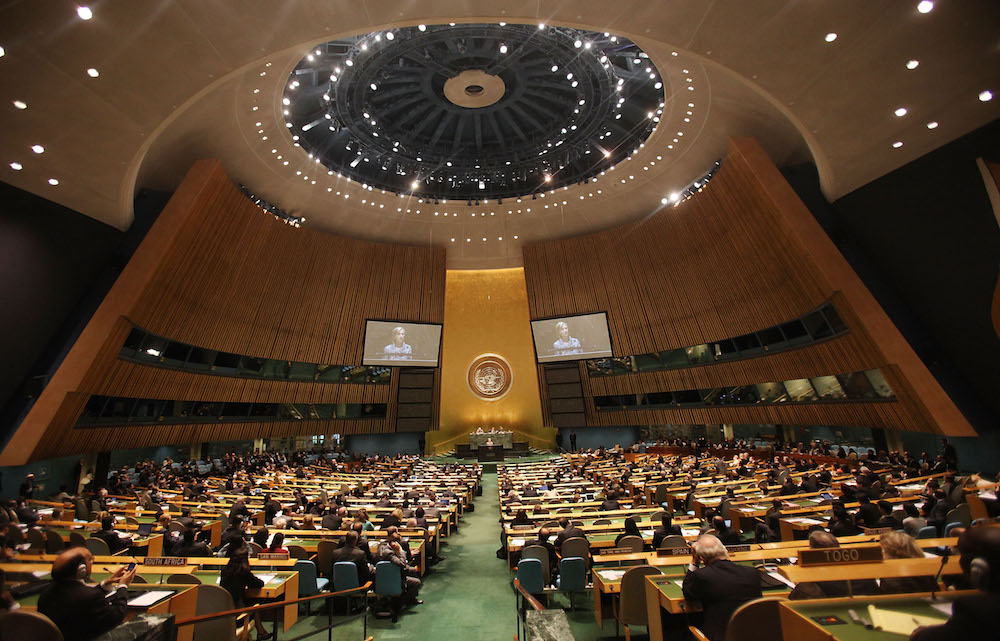

US Secretary of State Hillary Clinton speaks at the UN 2010 High-level Review Conference of the Parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons at its New York headquarters in 2010. (AFP/File Photo)
From the standpoint of Arab countries, there was also an important element missing from the joint statement, which failed to mention the 1995 NPT resolution introduced by the US, the UK, and Russia agreeing in support of the principle of a Middle East region free from all weapons of mass destruction.
It had been hoped that the 10th RevCon would provide an opportunity to acknowledge the progress made in this regard. The first Conference on the Establishment of a Middle East Zone Free of Nuclear Weapons and Other Weapons of Mass Destruction took place at the UN headquarters in New York in 2019, chaired by Jordan, and again in 2021, chaired by Kuwait.
Israel, the only state in the Middle East thought to possess nuclear weapons, did not attend any of the sessions, nor did the US, despite being one of the main sponsors of the 1995 resolution.
Supporters of arms control therefore have little choice but to wait until August to see whether the P5 will back up their words with action and deliver a “meaningful outcome” that will preserve the integrity of the NPT.




























