STRASBOURG, France: A World Health Organization official warned last week of a “closing window of opportunity” for European countries to prevent their health care systems from being overwhelmed as the omicron variant produces near-vertical growth in coronavirus infections.
In France, Britain and Spain, nations with comparatively strong national health programs, that window may already be closed.
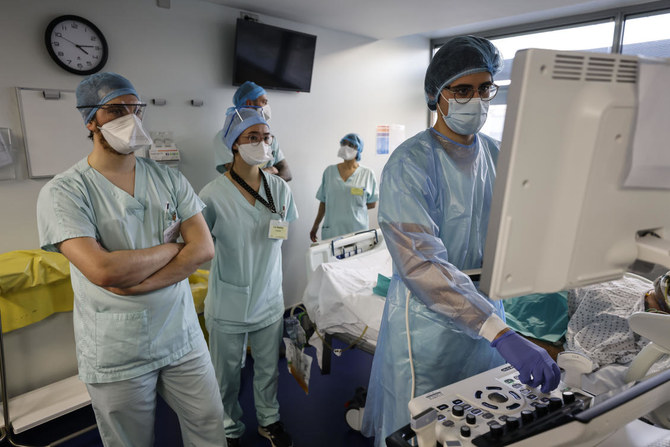
The director of an intensive care unit at a hospital in Strasbourg is turning patients away. A surgeon at a London hospital describes a critical delay in a man’s cancer diagnosis. Spain is seeing its determination to prevent a system collapse tested as omicron keeps medical personnel off work.
“There are a lot of patients we can’t admit, and it’s the non-COVID patients who are the collateral victims of all this,” said Dr. Julie Helms, who runs the ICU at Strasbourg University Hospital in far eastern France.
Two years into the pandemic, with the exceptionally contagious omicron impacting public services of various kinds, the variant’s effect on medical facilities has many reevaluating the resilience of public health systems that are considered essential to providing equal care.
The problem, experts say, is that few health systems built up enough flexibility to handle a crisis like the coronavirus before it emerged, while repeated infection spikes have kept the rest too preoccupied to implement changes during the long emergency.
Hospital admissions per capita right now are as high in France, Italy and Spain as they were last spring, when the three countries had lockdowns or other restrictive measures in place. England’s hospitalization rate of people with COVID-19 for the week ending Jan. 9 was slightly higher than it was in early February 2021, before most residents were vaccinated.
This time, there are no lockdowns. The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, a population health research organization based at the University of Washington, predicts that more than half of the people in WHO Europe’s 53-country region will be infected with omicron within two months.
That includes doctors, nurses and technicians at public hospitals.
About 15 percent of the Strasbourg hospital system’s staff of 13,000 was out this week. In some hospitals, the employee absentee rate is 20 percent. Schedules are made and reset to plug gaps; patients whose needs aren’t critical must wait.
The French public hospital’s 26 ICU beds are almost all occupied by unvaccinated patients, people ”who refuse care, who refuse the medicine or who demand medicines that have no effectiveness,” Helms said.
She denied 12 requests for admission Tuesday, and 10 on Wednesday night.
“When you have three patients for a single bed, we try to take the one who has the best odds of benefiting from it,” Helms said.
In Britain, like France, omicron is causing cracks in the health system even though the variant appears to cause milder illness than its predecessors. The British government this month assigned military personnel, including medics, to fill in at London hospitals, adding to the ranks of service members already helping administer vaccines and operate ambulances.
At the Royal Free Hospital in London, Dr. Leye Ajayi described a patient who faced delays in his initial cancer diagnosis.
“Unfortunately, when we eventually got round to seeing the patient, his cancer had already spread,” Ajayi told Sky News. “So we’re now dealing with a young patient in his mid-50s who, perhaps if we’d seen him a year ago, could have offered curative surgery. We’re now dealing with palliative care.”
Nearly 13,000 patients in England were forced to wait on stretchers more than 12 hours before a hospital bed opened, according to figures released last week from the National Health Service.
Britain has a backlog of around 5.9 million people awaiting cancer screenings, scheduled surgeries and other planned care. Some experts estimate that figure could double in the next three years.
“We need to focus on why performance has continued to fall and struggle for years and build the solutions to drive improvement in both the short and long term,” said Dr. Tim Cooksley, president of the Society for Acute Medicine.
Having the capacity to accommodate a surge is crucial, and it’s just this surge capacity that many in Europe were surprised to learn their countries lacked. The people in a position to turn that around were the same ones dealing with the crisis daily.
In the midst of the first wave, in April 2020, WHO’s Europe office put out a how-to guide for health systems to build slack into their systems for new outbreaks, including identifying a temporary health workforce.
“Despite the fact that countries thought they were prepared for a pandemic that might come along, they were not. So it’s building the ship as it sails,” said Dr. David Heymann, who previously led the World Health Organization’s infectious diseases department.
But France had been cutting back hospital beds — and doctors and nurses — for years before the pandemic. Building it back up in a matter of months proved too much when the current wave infected hospital staff by the hundreds each day. Even allowing symptomatic COVID-19-positive health workers to report for work hasn’t been enough.
Britain’s NHS Confederation, a membership organization for sponsors and providers, says the public health service went into the pandemic with a shortage of 100,000 health workers that has only worsened.
The first wave of the pandemic pushed Spain’s health system to its limit. Hospitals improvised ways to treat more patients by setting up ICUs in operating rooms, gymnasiums and libraries. The public witnessed, appalled, retirees dying in nursing homes without ever being taken to state hospitals that were already well over capacity.
After that, the Spanish government vowed not to let such a collapse happen again. Working with regional health departments, it designed what officials call “elasticity plans” to deal with sudden variations in service demands, especially in ICUs.
The idea is that hospitals have the equipment and, in theory, the personnel, to increase capacity depending on the need. But critics of government health policy say they’ve warned for years of inadequate hospital staffing, a key driver of the difficulty delivering care in the current wave.
“The key thing is flexibility, having flexible buildings that can expand, having staff that are flexible in terms of accepting task shifting, having flexibility in terms of sharing loads more of a regional structure,” said Dr. Martin McKee, a public health professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
Ultimately, though, McLee said: “A bed is an item of furniture. What counts is the staff around it,” McKee said.
Helms, the Strasbourg intensive care doctor, knows that all too well. Her unit has space for 30 beds. But it has only enough staff to care for the patients in the 26 beds currently occupied, a situation unlikely to change quickly after omicron burns through the region.
In the same hospital’s infectious diseases unit, frantic schedulers are borrowing staff from elsewhere in the facility, even if it means non-COVID-19 patients get less care.
“We’re still in the middle of a complex epidemic that is changing every day. It’s hard to imagine what we need to build for the future for other epidemics, but we’re going to have to reflect on the system of how we organize care,” said Dr. Nicolas Lefebvre, who runs the infectious diseases unit at the Strasbourg hospital.
He said Europe is prepared to handle isolated outbreaks as it has in the past, but the pandemic has exposed weakened foundations across entire health systems, even those considered among the world’s best.
Frédéric Valletoux, the head of the French Hospital Federation, said policymakers at the national level are acutely aware of the problem now. For 2022, the federation has requested more resources from nursing staff on up.
“The difficulty in our system is to shake things up, especially when we’re in the heart of the crisis,” Valletoux said.
Omicron exposes inflexibility of Europe’s public hospitals
https://arab.news/w3tbm
Omicron exposes inflexibility of Europe’s public hospitals

- That includes doctors, nurses and technicians at public hospitals
Putin says Slovakia offered to host Ukraine peace talks

MOSCOW: Russian President Vladimir Putin said Thursday that Slovakia had offered to be a “platform” for possible peace talks between Russia and Ukraine, nearly three years since the launch of Moscow’s offensive.
Putin told a televised press conference Slovakia’s Prime Minister Robert Fico “said that if there are any negotiations, they would be happy to provide their country as a platform.”
He added that Russia was “not against it,” praising Slovakia’s “neutral position.”
Fico, one of the few European leaders to maintain ties with the Kremlin, met with the Russian president in Moscow on December 22.
His visit came despite Western efforts to isolate Putin and present a united front in support for Kyiv.
Slovakia, an EU and NATO member, has already halted military aid to Ukraine since autumn 2023 under Fico’s government, and called for peace talks.
Fico has accused Kyiv of jeopardizing his country’s supply of Russian natural gas, on which it is heavily dependent.
Ukraine has said it will not renew a contract expiring at the end of this year to allow Russia gas to transit its country toward Europe, and no feasible alternative has yet been found.
Ukrainians “are already punishing Europe by ending the contract to supply our gas,” Putin said, adding that no new contract could be reached “in three or four days.”
But he suggested he was ready to supply gas to the EU, possibly via the Yamal-Europe pipeline that transits Poland.
The prospect of peace talks to end the conflict in Ukraine that began in February 2022 has grown since the re-election of Donald Trump to the White House.
Trump has vowed to push for a quick deal to halt the fighting when he takes office in January.
That has sparked fears in Kyiv and Europe that Ukraine could be pushed to make concessions to Moscow.
Putin reiterated his vow that his country would achieve “all the objectives in Ukraine.”
“This is our number one task,” he said, warning that Moscow was ready to again use its latest-generation Oreshnik missile, first fired in a strike last month.
Putin has repeatedly threatened to strike “decision-making centers” in Kyiv in retaliation for its use of Western-supplied long-range missiles to hit targets in Russia.
He also claimed Thursday that in 2021, US President Joe Biden offered to “push back” Ukraine’s entry into NATO — a move urgently sought by Kyiv but that Putin considers an unacceptable threat.
“In 2021, the current President Biden offered exactly that: push back Ukraine’s NATO membership by 10 to 15 years, because it was not yet ready.”
“I answered reasonably that ‘Yes, today it is not ready. But you will prepare it for it and you will accept it.’“
But for Russia, “What is the difference — today, tomorrow or in 10 years?“
US says kills two Al-Shabab fighters in airstrike

WASHINGTON: The US military said Thursday it had killed two members of the jihadist Al-Shabab group in southern Somalia in an airstrike.
The strike took place on Tuesday about 10 kilometers (six miles) southwest of the town of Quyno Barrow, south of Mogadishu, the United States Africa Command (US AFRICOM) said in a statement.
The strike was conducted “in coordination” with Somalia’s federal government, it said.
“The command will continue to assess the results of the operation and provide additional information as appropriate,” the statement said, providing no further details.
The Somalian government issued a statement lauding a “meticulously planned operation” that was conducted alongside “international partners” in the same district.
That statement said the operation “has successfully eliminated the terrorist ring leader Mohamed Mire Jama, also known as Abu Abdirahman, in the Kunyo-Barow district of Lower Shabelle province.”
Somalia is one of the poorest countries on the planet, enduring decades of civil war, a bloody insurgency by the Al-Qaeda-linked Al-Shabab, and frequent climate disasters.
Washington has invested massively for several decades in the fight against the insurgency.
During his first term, US President-elect Donald Trump announced the withdrawal of US troops from Somalia, a decision reversed by his successor Joe Biden.
Earlier this week, Egypt said it was joining a new African Union peacekeeping force in Somalia.
The mandate of the current African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) ends on December 31, and it will make way for a new force against the Al-Shabab insurgents, the African Union Support and Stabilization Mission in Somalia (AUSSOM).
India’s former PM Manmohan Singh dies aged 92

- Singh became a vocal critic of Modi’s economic policies, and more recently warned about the risks that rising communal tensions posed to India’s democracy
NEW DELHI: Manmohan Singh, the former Indian prime minister whose economic reforms made his country a global powerhouse, has died at the age of 92, current leader Narendra Modi said Thursday.
India “mourns the loss of one of its most distinguished leaders,” Modi posted on social media platform X shortly after news broke of Singh’s passing.
“As our Prime Minister, he made extensive efforts to improve people’s lives.”
Singh was taken to a hospital in New Delhi after he lost consciousness at his home on Thursday, but could not be resuscitated and was pronounced dead at 9:51 p.m. local time, according to a statement by the All India Institute of Medical Sciences.
Singh, who held office from 2004 to 2014, is credited with having overseen an economic boom in Asia’s fourth-largest economy in his first term, although slowing growth in later years marred his second stint.
“I have lost a mentor and guide,” opposition Congress leader Rahul Gandhi said in a statement, adding that Singh had “led India with immense wisdom and integrity.”
“Millions of us who admired him will remember him with the utmost pride,” said Gandhi, a scion of India’s powerful Nehru-Gandhi dynasty and the most prominent challenger to Modi.
Mallikarjun Kharge, leader of the opposition in parliament’s upper house, said “India has lost a visionary statesman, a leader of unimpeachable integrity, and an economist of unparalleled stature.”
President Droupadi Murmu wrote on X that Singh will “always be remembered for his service to the nation, his unblemished political life and his utmost humility.”
Born in 1932 in the mud-house village of Gah in what is now Pakistan, Singh studied economics to find a way to eradicate poverty in India and never held elected office before taking the vast nation’s top job.
He won scholarships to attend both Cambridge, where he obtained a first in economics, and Oxford, where he completed his PhD.
Singh worked in a string of senior civil posts, served as a central bank governor and also held various jobs with global agencies including the United Nations.
He was tapped in 1991 by then Congress prime minister P.V. Narasimha Rao to reel India back from the worst financial crisis in its modern history.
In his first term Singh steered the economy through a period of nine-percent growth, lending India the international clout it had long sought.
He also sealed a landmark nuclear deal with the United States that he said would help India meet its growing energy needs.
Known as “Mr Clean,” Singh nonetheless saw his image tarnished during his decade-long tenure when a series of corruption cases became public.
Several months before the 2014 elections, Singh said he would retire after the polls, with Sonia Gandhi’s son Rahul earmarked to take his place if Congress won.
But Congress crashed to its worst-ever result at that time as the Hindu-nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party, led by Modi, won in a landslide.
Singh — who said historians would be kinder to him than contemporary detractors — became a vocal critic of Modi’s economic policies, and more recently warned about the risks that rising communal tensions posed to India’s democracy.
Russia missile suspected in Azerbaijani plane crash, Moscow warns against ‘hypotheses’

- Pro-government Azerbaijani website Caliber cited officials as saying they believed a Russian missile fired from a Pantsir-S air defense system downed the plane
ASTANA: Azerbaijani and US officials believe a Russian surface-to-air missile caused the deadly crash of an Azerbaijani passenger jet, media reports and a US official said Thursday, as the Kremlin cautioned against “hypotheses” over the disaster.
The Azerbaijan Airlines jet crashed near the Kazakh city of Aktau, an oil and gas hub, on Wednesday after going off course for undetermined reasons.
Thirty-eight of the 67 people on board died.
The Embraer 190 aircraft was supposed to fly northwest from the Azerbaijani capital Baku to the city of Grozny in Chechnya, southern Russia, but instead diverted far off course across the Caspian Sea.
An investigation is underway, with pro-government Azerbaijani website Caliber citing unnamed officials as saying they believed a Russian missile fired from a Pantsir-S air defense system downed the plane.
The claim was also reported by The New York Times, broadcaster Euronews and the Turkish news agency Anadolu.
Some aviation and military experts said the plane might have been accidentally shot by Russian air defense systems because it was flying in an area where Ukrainian drone activity had been reported.
A former expert at France’s BEA air accident investigation agency said there appeared to be “a lot of shrapnel” damage on the wreckage.
Speaking on condition of anonymity, he said the damage was “reminiscent” of Malaysia Airlines flight MH17, which was downed with a surface-to-air missile by Russia-backed rebels over eastern Ukraine in 2014.
Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told reporters: “It would be wrong to make any hypotheses before the investigation’s conclusions.”
Euronews cited Azerbaijani government sources as saying that “shrapnel hit the passengers and cabin crew as it exploded next to the aircraft mid-flight.”
A US official, speaking on condition of anonymity, also said early indications suggested a Russian anti-aircraft system struck the plane.
Kazakhstan news agency Kazinform cited a regional prosecutor as saying that two black-box flight recorders had been recovered.
Azerbaijan Airlines initially said the plane flew through a flock of birds, before withdrawing the statement.
Kazakh officials said 38 people had been killed and there were 29 survivors, including three children.
Jalil Aliyev, the father of flight attendant Hokume Aliyeva, told AFP that this was supposed to have been her last flight before starting a job as a lawyer for the airline.
“Why did her young life have to end so tragically?” the man said in a trembling voice before hanging up the phone.
Eleven of the injured are in intensive care, the Kazakh health ministry said.
Azerbaijani President Ilham Aliyev declared Thursday a day of mourning and canceled a planned visit to Russia for an informal summit of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), a grouping of former Soviet nations.
“I extend my condolences to the families of those who lost their lives in the crash... and wish a speedy recovery to the injured,” Aliyev said in a social media post Wednesday.
The Flight Radar website showed the plane deviating from its normal route, crossing the Caspian Sea and then circling over the area where it eventually crashed near Aktau, on the eastern shore of the sea.
Kazakhstan said the plane was carrying 37 Azerbaijani passengers, six Kazakhs, three Kyrgyz and 16 Russians.
A Kazakh woman told the local branch of Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL) she was near where the plane crashed and rushed to the site to help survivors.
“They were covered in blood. They were crying. They were calling for help,” said the woman, who gave her name as Elmira.
She said they saved some teenagers.
“I’ll never forget their look, full of pain and despair,” said Elmira. “A girl pleaded: ‘Save my mother, my mother is back there’.”
Russian President Vladimir Putin held a phone conversation with Aliyev and “expressed his condolences in connection with the crash,” Peskov told a news conference.
Manmohan Singh, India’s reluctant prime minister, dies aged 92

- The first Sikh in office, 92-year-old Singh was being treated for age-related medical conditions
- He is credited with steering India to unprecedented economic growth, lifting millions out of poverty
NEW DELHI: Described as a “reluctant king” in his first stint as prime minister, the quietly spoken Manmohan Singh was arguably one of India’s most successful leaders.
The first Sikh in office, Singh, 92, was being treated for age-related medical conditions and died after he was brought to hospital after a sudden loss of consciousness on Thursday.
He is credited with steering India to unprecedented economic growth and lifting hundreds of millions out of dire poverty. He went on to serve a rare second term.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi said: “India mourns the loss of one of its most distinguished leaders, Dr. Manmohan Singh Ji.”
He applauded the economist-turned-politician’s body of work.
Born into a poor family in a part of British-ruled India now in Pakistan, Singh studied by candlelight to win a place at Cambridge University before heading to Oxford, earning a doctorate with a thesis on the role of exports and free trade in India’s economy.
He became a respected economist, then India’s central bank governor and a government adviser but had no apparent plans for a political career when he was suddenly tapped to become finance minister in 1991.
During that tenure to 1996, Singh was the architect of reforms that saved India’s economy from a severe balance of payments crisis, promoted deregulation and other measures that opened an insular country to the world.
Famously quoting Victor Hugo in his maiden budget speech, he said: “No power on earth can stop an idea whose time has come,” before adding: “The emergence of India as a major economic power in the world happens to be one such idea.”
Singh’s ascension to prime minister in 2004 was even more unexpected.
He was asked to take on the job by Sonia Gandhi, who led the center-left Congress party to a surprise victory. Italian by birth, she feared her ancestry would be used by Hindu-nationalist opponents to attack the government if she were to lead the country.
Riding an unprecedented period of economic growth, Singh’s government shared the spoils of the country’s new found wealth, introducing welfare schemes such as a jobs program for the rural poor.
In 2008, his government also clinched a landmark deal that permitted peaceful trade in nuclear energy with the United States for the first time in three decades, paving the way for strong relations between New Delhi and Washington.
But his efforts to further open up the Indian economy were frequently frustrated by political wrangling within his own party and demands made by coalition partners.
“HISTORY WILL BE KINDER TO ME”
And while he was widely respected by other world leaders, at home Singh always had to fend off the perception that Sonia Gandhi was the real power in the government.
The widow of former prime minister Rajiv Gandhi, whose family has dominated Indian politics since independence from Britain in 1947, she remained Congress party leader and often made key decisions.
Known for his simple lifestyle and with a reputation for honesty, Singh was not personally seen as corrupt. But he came under attack for failing to crack down on members of his government as a series of scandals erupted in his second term, triggering mass protests.
The latter years of his premiership saw India’s growth story, which he had helped engineer, wobble as global economic turbulence and slow government decision-making battered investment sentiment.
In 2012, his government was tipped into a minority after the Congress party’s biggest ally quit their coalition in protest at the entry of foreign supermarkets.
Two years later Congress was decisively swept aside by the Bharatiya Janata Party under Narendra Modi, a strongman who promised to end the economic standstill, clean up graft and bring inclusive growth to the hinterlands.
But at a press conference just months before he left office, Singh insisted he had done the best he could.
“I honestly believe that history will be kinder to me than the contemporary media or, for that matter, the opposition parties in parliament,” he said.
Singh is survived by his wife and three daughters.