DUBAI: Since the Taliban seized control of Afghanistan in August last year amid a chaotic US military withdrawal, the war-battered country has slid deeper into disaster, sparking fresh waves of displacement and raising the specter of mass hunger.
Deprived of billions of dollars in aid, loans and assets by an international community reluctant to recognize the new, ultraconservative government in Kabul, Afghanistan is fast becoming the world’s worst and most complex humanitarian emergency.
Afghans who are unable, or unwilling, to join the tide of refugees are left to scrape by amid the bleakest winter in recent memory, enduring chronic shortages of food, fuel and medicine.
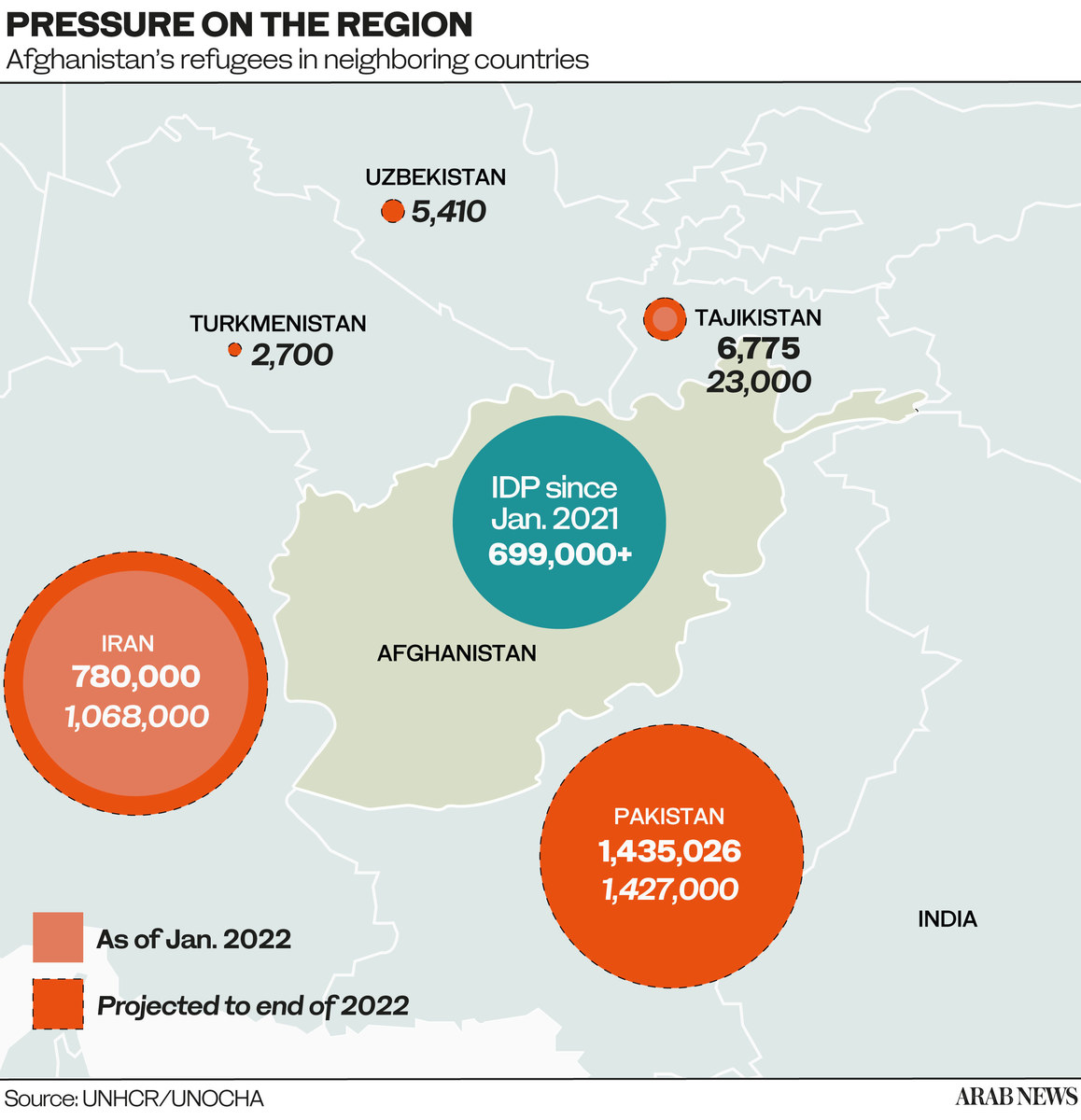
But even the 5.7 million Afghans who have fled to five neighboring countries (Iran, Pakistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan) still need vital relief.
The gloom deepened when at least 22 people died and hundreds of buildings were damaged after twin earthquakes struck the isolated western province of Badghis on Jan. 17.
In response to the deteriorating situation from every perspective, the UN launched a $5 billion aid appeal on Jan. 11 — the largest ever for a country experiencing a humanitarian crisis — to help shore up basic services during the bitterly cold winter.
In an urgent plea on Jan. 13, UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres warned of “a nightmare unfolding” in Afghanistan unless further funding is released. “Virtually every man, woman and child could face acute poverty,” he said.
Many in the international community have been reluctant to send aid to Afghanistan, fearing it might empower the Taliban, a group whose extreme interpretation of Islam denies girls an education, bars women from the workplace, and limits freedom of expression.
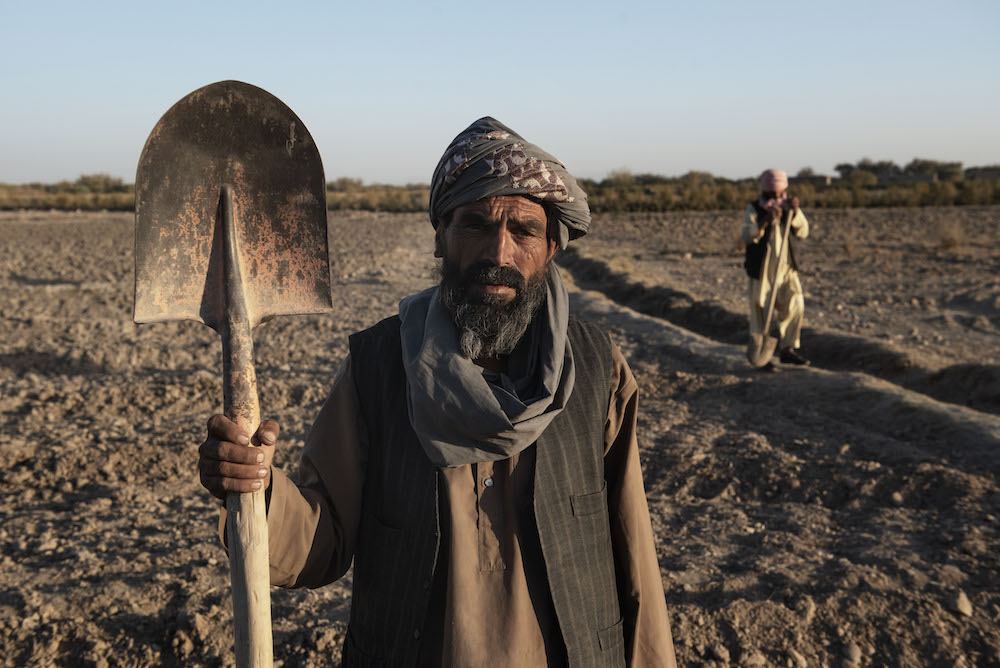

Beneficiaries work their land around Ghra village in Daman district south of Kandahar. (©FAO/Alessio Romenzi)
When the Taliban toppled the UN-backed government of Ashraf Ghani last summer, it lost access to billions of dollars in financing from the World Bank and the IMF, saw its assets frozen, and development aid abruptly suspended.
Additionally, the administration of President Joe Biden froze $7 billion in Afghan foreign reserves held in New York.
Despite 20 years of Western intervention, successive Afghan governments had failed to diversify the economy beyond rudimentary agriculture. In fact, almost 80 percent of the previous government’s budget came from the US and other foreign donors. Denied this assistance, the nation’s economy now teeters on the brink of collapse.
Policymakers around the world have been left wondering how to address the unfolding emergency without giving the Taliban the oxygen of legitimacy. As such, Washington has sought to bypass the group by directly channeling funds though UN agencies.
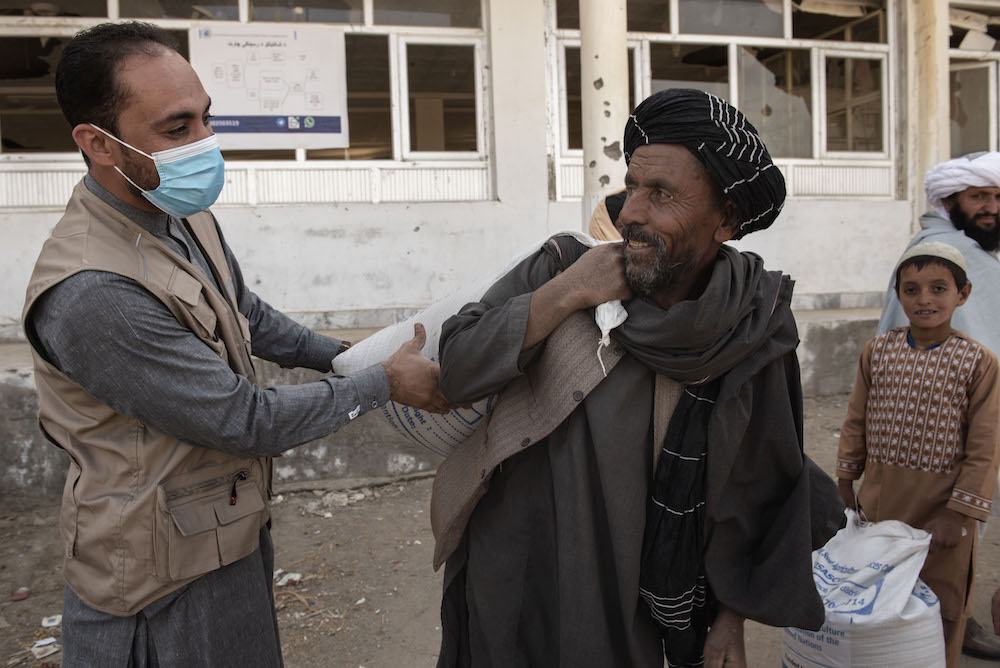
FAO staff members Baryal Mumtaz and Feroz Aryan help a beneficiary put his sack of improved wheat seeds on his shoulders. (©FAO/Alessio Romenzi)
On Jan. 11, the United States Agency for International Development announced more than $308 million in additional assistance, bringing total US humanitarian spending on Afghanistan and Afghan refugees in the region to nearly $782 million since Oct. 2020.
Campaigners caution that increasing aid contributions is not a sustainable solution, and that Afghans will only achieve lasting security and financial independence when they regain access to their bank accounts and hard currency.
Masuda Sultan is an Afghan women’s rights activist and a co-founder of Unfreeze Afghanistan, an advocacy group established in Sept. 2021 to lobby policymakers on behalf of ordinary Afghans deprived of their savings by the chaos in the banking system attributable to the sanctions regime.
She acknowledges that there has been some progress. “The UN announced its largest humanitarian funding appeal in its history, and last week the US announced $308 million in additional humanitarian aid on top of the $474 already committed,” Sultan told Arab News.
“But without addressing the underlying economic freeze related to the banking sector, which is a result of sanctions, the needs of the Afghan people can never be met. In fact, the number of people needing emergency humanitarian assistance will just grow.”
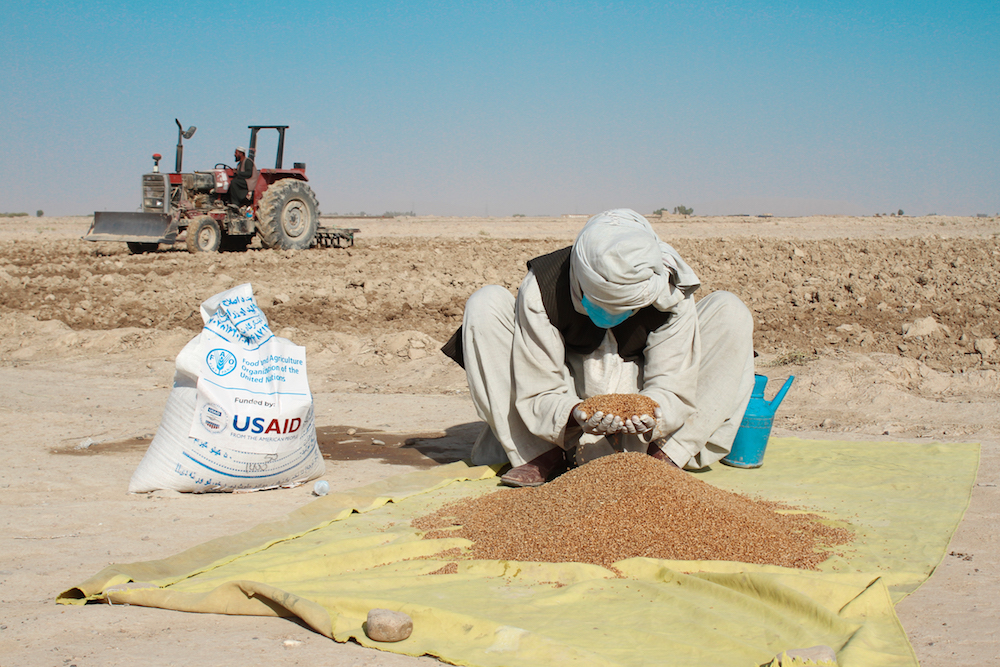

Noor Mohammad applies fungicide to the certified wheat seeds provided by FAO before sowing in Sahibzada Kalacha village, Daman district, of Kandahar, Afghanistan on 8 November 2021. (©FAO/Hashim Azizi)
Aware of the growing pressure on Washington to release Afghanistan’s frozen assets, Zabihullah Mujahid, the spokesperson for the Taliban government, recently posted a message on Twitter that said: “The United States must respond positively to the international voice and release Afghan capital.”
Cheryl Benard, another of Unfreeze Afghanistan’s co-founders and the president of ARCH International, an organization in Washington dedicated to the preservation of cultural heritage in conflict zones, said giving Afghans access to their savings would prevent a currency collapse and allow them to develop their communities independently.
“The bottom line is this is a post-conflict country,” Benard told Arab News. “In Germany (after the Second World War), we had the Marshall Plan and it helped them become a normal country again and rebuild their livelihoods.
“In the case of Afghanistan, they have the money themselves, $9 billion, and we are holding it back and are instead raising new donor funds. But this was exactly what ruined the Afghan experiment for the past 20 years: We kept them dependent on foreign experts and foreign funding. What they need now is to get on their own feet — and they want to.”
FASTFACTS
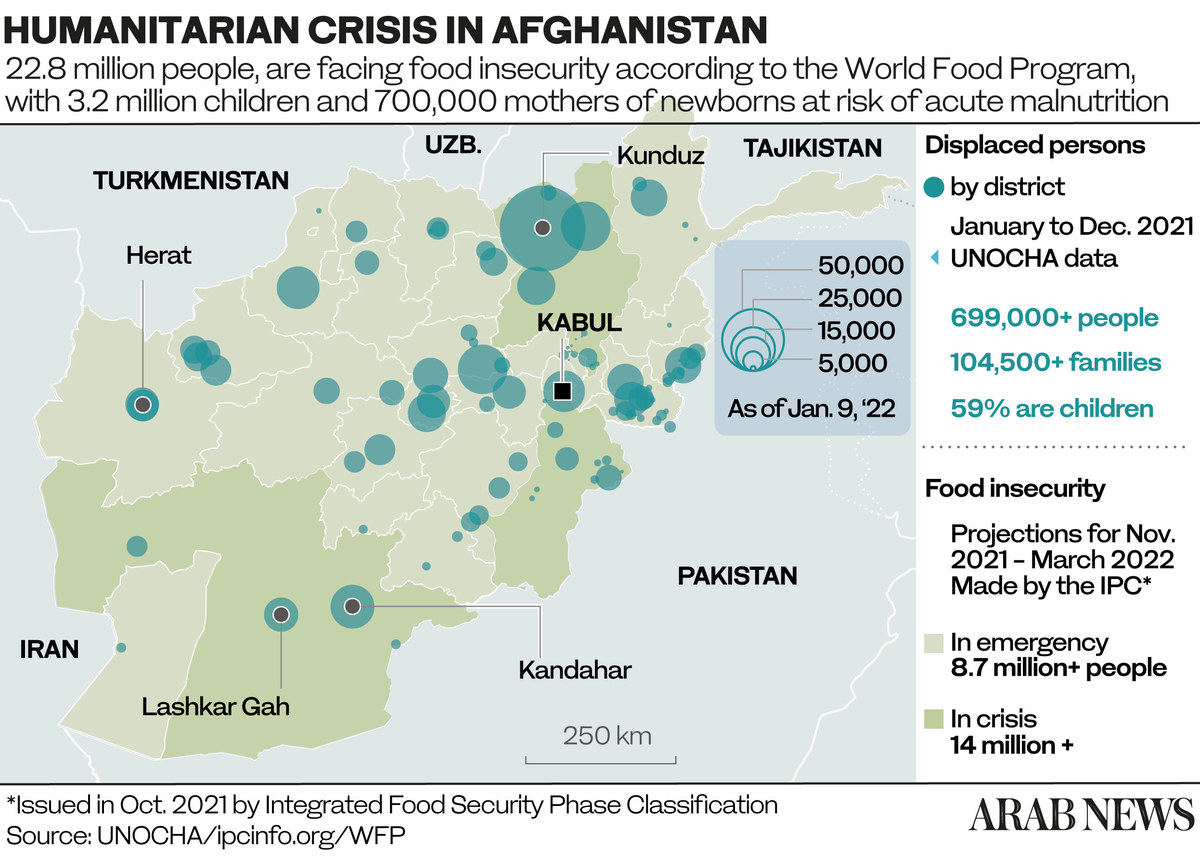
* UN agencies say 22.8 million Afghans are experiencing acute hunger and food insecurity.
* US, World Bank and IMF urged to unfreeze Afghan assets, loans and aid packages.
Under the sanctions regime imposed on Afghanistan, individuals, nongovernmental organizations and owners of small businesses cannot access savings held in foreign banks because Western powers are worried the Taliban might try to appropriate the money.
Benard said this could be prevented by releasing the money “in small monthly amounts and if they try to take it, you can always freeze it again. You don’t give them $9 billion all at once.”
The money could go directly to the Afghan central bank, where it would be regulated by law, before it is distributed to Afghan savers through currency exchanges across the country.
“This is totally normal,” said Benard. “What is not normal is for the US to say, ‘We don’t like the outcome of the war, so we are freezing your money.’”
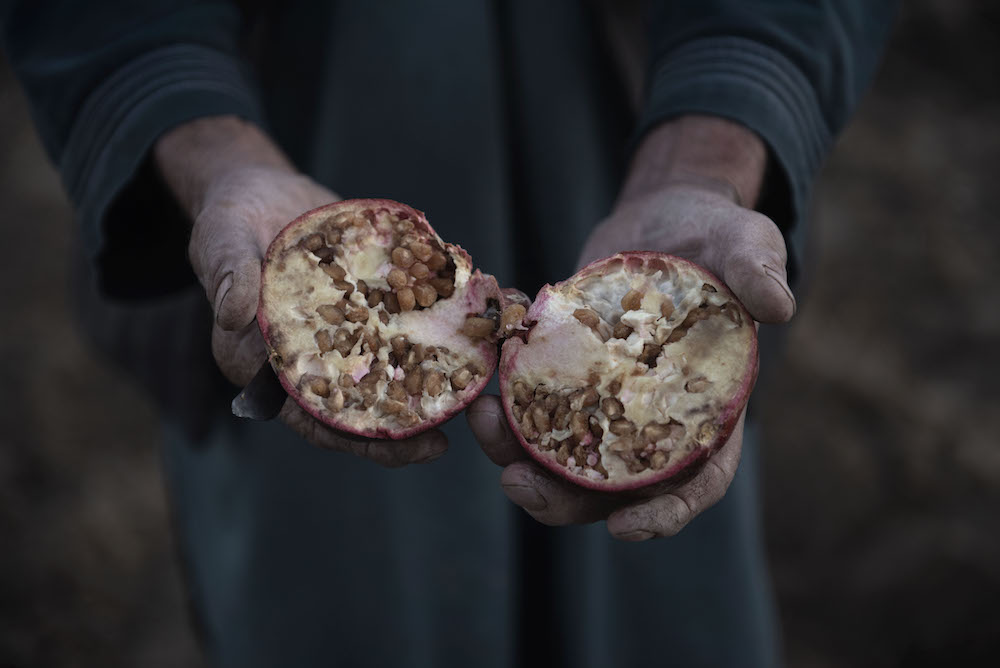

Beneficiary Niaz Mohammad shows how the pomegranates he has harvested don't ripen in his orchard around Ghra village in Daman district south of Kandahar. After realising that the lack of irrigation didn't let his pomegranate trees grow, Niaz decided to fell his orchard and plant instead wheat that needs of less water. (©FAO/Alessio Romenzi)
Shakib Noori, US-based director of sustainable development at AMS, told Arab News the best solution for Afghanistan is to ensure aid remains “apolitical and not a carrot-or-stick tool of the Western world to coerce the Taliban.”
However, he said it is also important “to ensure that the current regime in Kabul does not benefit from the flow of the humanitarian assistance designated specifically for the ordinary residents of Afghanistan.”
Aid agencies said banking is not the only sector in need of support to stave off economic collapse. According to the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization, a crucial way to support the Afghan people is to shore up agriculture, which forms the backbone of the nation’s economy and its food security.
“Afghanistan is now one of the world’s largest and most severe hunger crises,” Rein Paulsen, director of the FAO’s Office of Emergencies and Resilience, told Arab News.
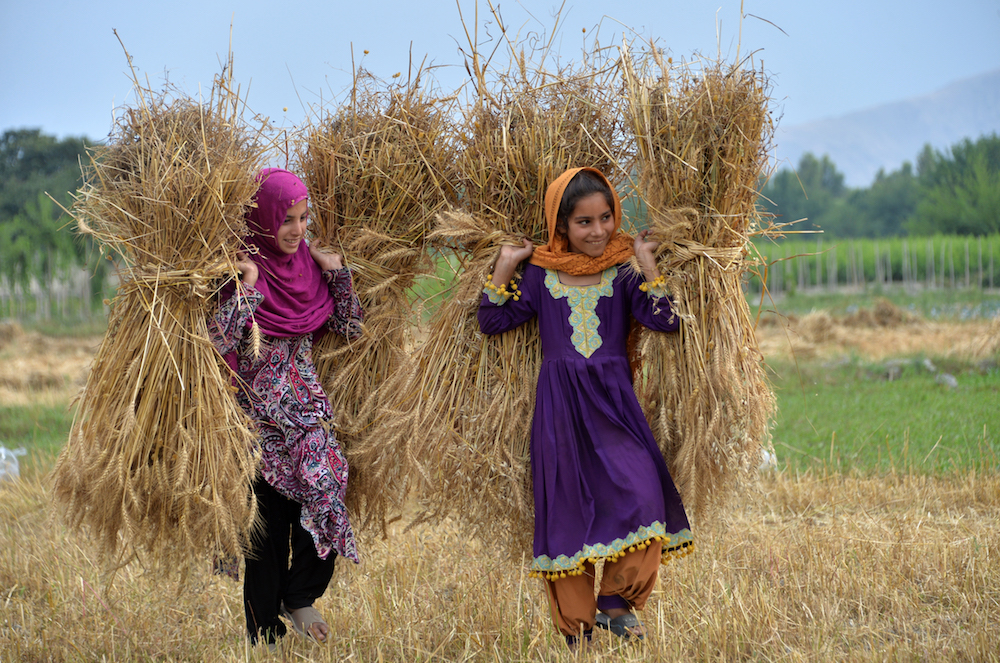

Khialy Gul’s neighbor girls carry wheat bunches at a field in Nawju village, Kuz Kunar district of Nangarhar, Afghanistan on 10 May 2021. (©FAO/Farshad Usyan)
“Half the population — 22.8 million people — are confronting acute hunger and food insecurity at the moment. Not only do they not know where their next meal may be coming from, but a majority of them are also agriculture-reliant, rural families who are being forced to make horrific choices about whether to stay in their homes or to walk away from their livelihoods in search of aid elsewhere.
“Unless we tackle the causes that underlie this crisis, we can expect things to continue to get worse. This crisis is the result of a combination of factors but one key factor involves the underlying vulnerabilities that affect what is the bedrock of Afghanistan’s economy and food security: agriculture.”
Agriculture accounts for 25 percent of Afghanistan’s gross domestic product, 70 percent of Afghans directly rely on domestic agricultural production for their food or income, and 80 percent receive some sort of economic benefit from the sector.
“The criticality of agriculture in the country simply cannot be overstated,” said Paulsen. “Paradoxically, the people most affected right now by Afghanistan’s hunger crisis are its food producers.
“Out of the 22.8 million Afghans (faced with hunger and food insecurity), the largest share — 17.8 million people — reside in rural areas and depend primarily on agriculture.”
Sultan of Unfreeze Afghanistan summed up the situation bluntly: Afghanistan is falling off a cliff, with the economic shock of losing 45 percent of GDP overnight. If the banking sector collapses, a further 30 percent of GDP could be lost.
The US and other countries are going to have to “work with current Afghan authorities, despite the fraught history and long war,” if they hope to avert further suffering, she added.


























