WASHINGTON D.C.: Israeli airstrikes on Iranian and Hezbollah targets in Syria have been growing in scale and frequency in recent months as Tehran seeks to cement its hold over Syrian seaports, airports and overland smuggling routes.
From the Israeli standpoint, Iran’s ability to deliver precision-guided missile technology to Syrian territory via these routes poses a serious strategic threat, allowing Iran and its Hezbollah proxies to attack from short range at short notice in the event of a regional war.
Israel does not always claim responsibility for its strikes on sensitive Syrian facilities controlled by Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, giving it a measure of plausible deniability to avoid open conflict or Syrian retaliation.
The country is nevertheless thought to be behind scores of recent strikes across Syrian regime territories, from the capital Damascus and the coastal province of Latakia in the northwest to Deir el-Zour in the east.
Latakia was struck twice in December amid suspicions the IRGC was using the port to move precision-guided weapons. The resulting fireball following one such strike revealed just how much dangerous material Iran was attempting to transfer to its regional terror network.
Benny Gantz, Israel’s defense minister, issued a stark warning to Iran following the Latakia strikes, vowing that “game-changing” weapons were a red line and Israel would not allow their proliferation.
However, the strikes do not appear to have deterred Iran.
“Preventing Iranian entrenchment in Syria is probably impossible. The question is the rate and quantity of Iranian entrenchment and the quality of this entrenchment,” Tal Beeri, head of the research department at the Alma Research and Education Center in Israel, told Arab News.
“Israel does this without plunging the region into war by attacking only armaments and almost completely refraining from attacking commanders. The attacks are carried out in a targeted manner based on accurate intelligence and only against targets that clearly will not have collateral damage or, alternatively, only minor collateral damage.”
According to Beeri, Israel primarily targets deliveries of components destined for air-defense systems, cruise missiles, long-range missiles, drones and electronic combat systems.
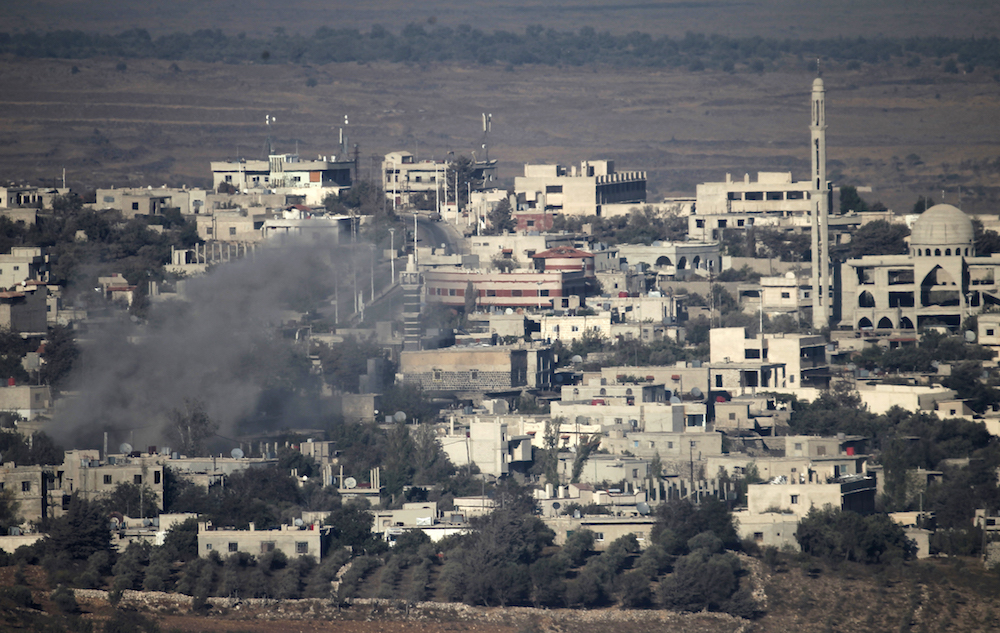

A picture taken on September 9, 2016 from the Isaeli-annexed Golan Heights shows smoke rising from the Syrian village of Jubata Al-Khashab after fire reportedly struck the Israeli-held zone. (AFP/File Photo)
“It is estimated that about 70 percent of the time, the air, sea and land arms-smuggling routes are closed due to Israeli activity,” he said.
“However, although arms smuggling has decreased compared with 2020, we do not know what has managed to evade Israeli intelligence and reached Syria and Lebanon.”
Constant pressure on the IRGC and its smuggling routes is seen by Israeli officials as the best means of preventing, or at least slowing, an Iranian military build-up on its doorstep.
“In light of this, we have been witnessing an increasing volume of airstrikes on Syrian soil that has been taking place for a long time now. This is the only way the ‘mowing the grass’ strategy can succeed,” said Beeri.
“It is not just in Israel’s interest. It is in the interest of all relevant players in the Middle East that are threatened by Iran and the international community’s interests, especially the US, Russia and Europe.”
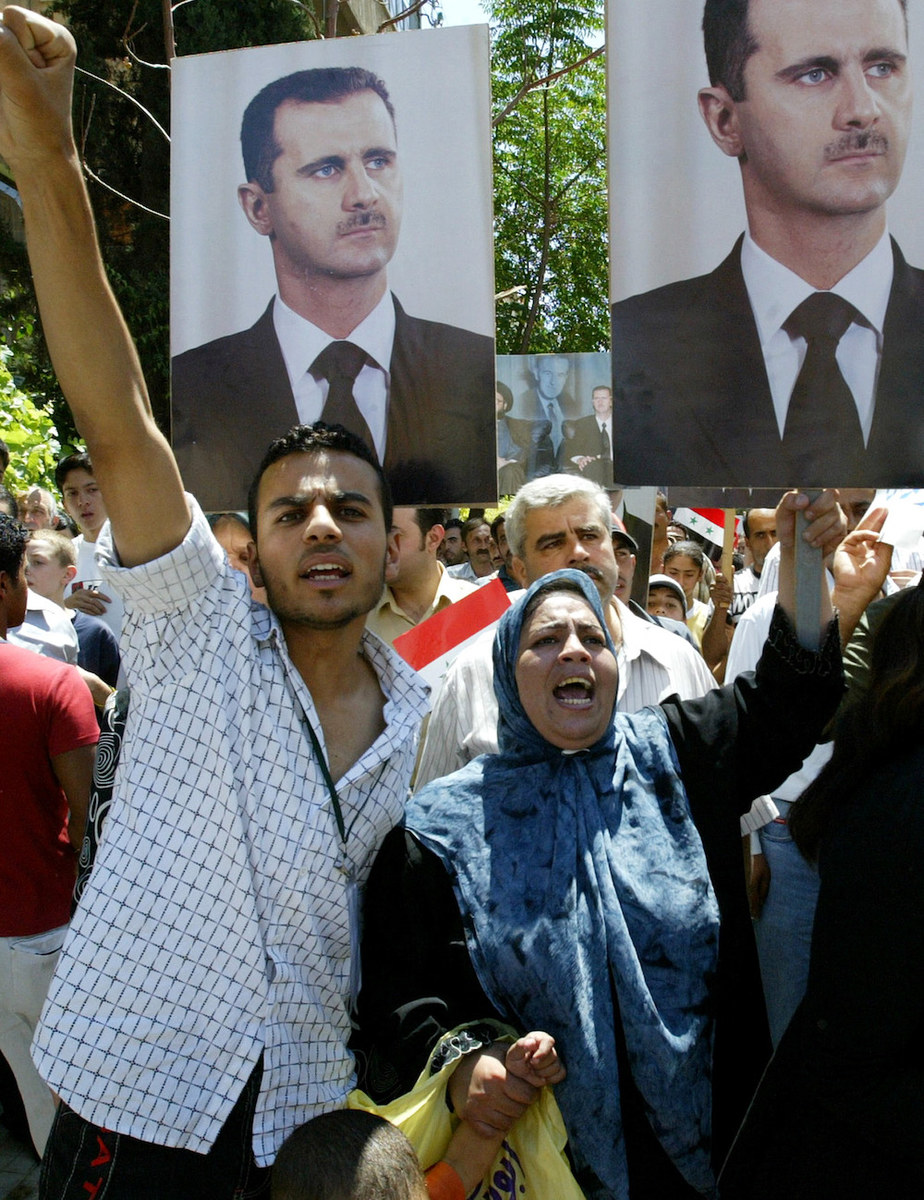

Syrians hold pictures of Syrian President Bashar Assad during a demonstration in front of the UN office in Damascus, 30 July 2006, condemning an Israeli air strike on the southern Lebanese village of Qana. (AFP/File Photo)
Beeri warned that ballistic missiles on Syrian and Lebanese soil could be easily directed toward Europe.
“Nowadays, the Saudis understand this well in light of the fighting in Yemen and the physical threat posed to them from a direct geographic front under Iranian auspices,” he said.
Indeed, in his most recent speech, Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah spoke at length of his group’s intentions to target Saudi Arabia and broader Arab interests not aligned with Iran’s regional hegemonic aims.
Jason Brodsky, policy director at United Against Nuclear Iran, said that Israeli strikes on targets in Syria are already having an impact.
“Israel has achieved impressive results in its campaign in Syria to prevent advanced weaponry from reaching Iran’s proxies and partners,” Brodsky told Arab News.
“According to recent Israeli estimates, Iran has been unable to make such transfers through the region — via, air, land and sea — around 70 percent of the time. Israel aims to increase the cost for Bashar Assad in allowing such illicit Iranian activity to take place on Syrian soil.”
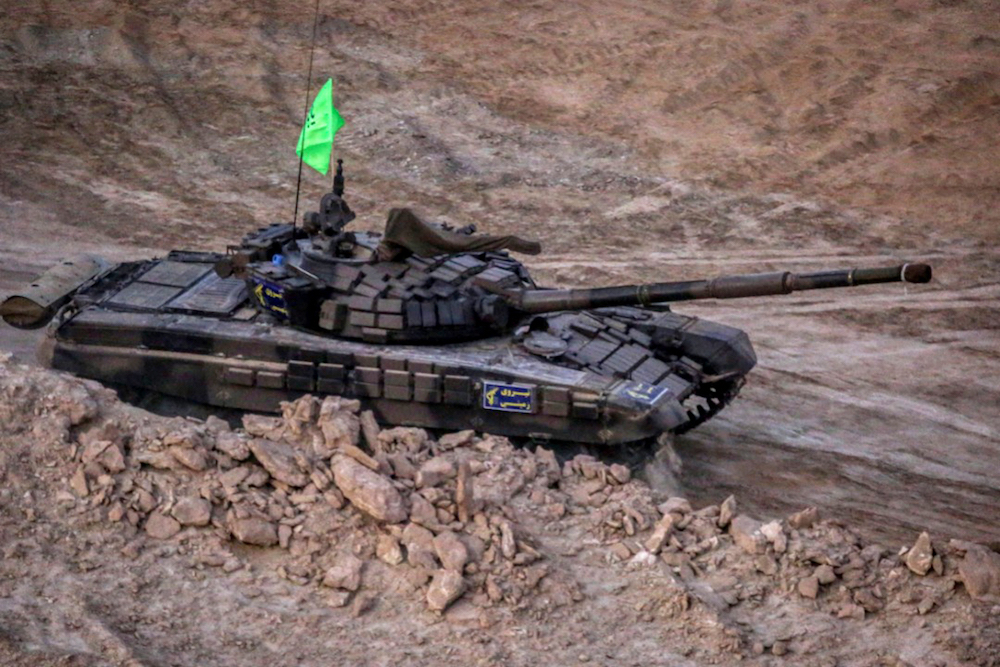

Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) riding a tank as part of five-days military exercises in three provinces. (AFP)
However, Brodsky suspects it is only a matter of time before Iran finds alternative routes and methods to move its weaponry.
“As it relates to Iran’s calculus, I don’t see Tehran letting up on its designs to use Lebanon and Syria as a launchpad for attacks against Israel in the future. But such Israeli strikes will cause the Iranians to improvise their smuggling routes,” he said.
“According to public reports citing Syrian sources, Iran has ramped up arms transfers by sea in an attempt to avoid Israeli strikes in eastern Syria. That explains the uptick in Israeli strikes targeting Latakia port, with two alone in December.”
Israel’s fast-paced approach to containing Iranian activity coincides with international negotiations in the Austrian capital Vienna aimed at reviving the 2015 Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, or Iran nuclear deal.
Donald Trump, the former US president, withdrew from the accord in 2018, arguing that the agreement reached by the administration of Barack Obama did not go far enough in reducing Iran’s ballistic missile program or its policy of arming and funding militia proxies throughout the Middle East.
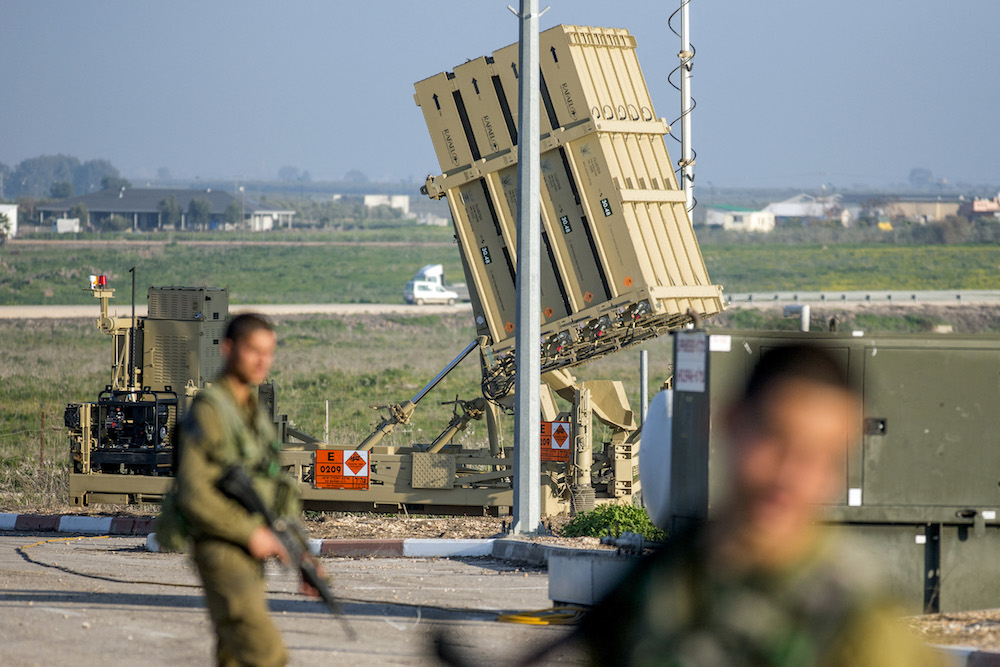

Israeli soliders patrol near an Iron Dome defence system, designed to intercept and destroy incoming short-range rockets and artillery shells, in the Israeli-annexed Golan Heights, on January 20, 2015, two days after an Israeli air strike killed six Hezbollah members in the Syrian-controlled side of the area. (AFP/File Photo)
Israeli defense officials worry that history might repeat itself if US President Joe Biden’s team signs a new nuclear deal that fails to address the issues cited by Trump. These widening strategic differences between the US and Israel could lead to more unilateral Israeli action.
Brodsky believes Israeli strikes against IRGC targets in Syria may also be intended to show Iran that Israel means business, no matter what the US decides in Vienna.
“While the timing of these strikes is driven by the operational needs of the moment, they have a secondary upside for Israel as it seeks to demonstrate to Tehran that it is prepared to hold it accountable militarily, all while the nuclear talks are happening in Vienna,” he said.
Farhad Rezaei, a senior research fellow at the Philos Project, also believes Israel is sending an unambiguous message to Tehran, showing that it is prepared for any scenario, especially if it concludes that Iran’s nuclear program can be halted only by military means.

A damaged hotel near Syria’s Latakia port after an Israeli air strike targeted the port early on December 28, 2021. (AFP)
“My understanding is that Israel is trying to minimize a Hezbollah missile attack in case it has to bomb the Iranian nuclear facilities, so Israel is bombing the convoys that bring precision-guided missiles to Lebanon via Syria, as well as the workshops in Syria and storage facilities where precision-guided missiles and rockets are built and stored,” Rezaei told Arab News.
“Israeli papers are talking about a multi-domain operation to prepare for a strike, such as training pilots, obtaining aerial-refueling craft, and trying to limit the potential damage from a Hezbollah barrage once the operation is launched.”
For the time being, according to most experts, neither Israel nor Iran appears interested in starting an open conflict. But with ever more advanced Iranian missile technology finding its way into Hezbollah hands and an isolated Syrian regime growing increasingly reliant on Iran, the stakes are getting higher.
If a fresh nuclear deal is signed in Vienna without additional restrictions on IRGC activity and Iranian missile proliferation, then the chances of a military escalation will rise dramatically.

































